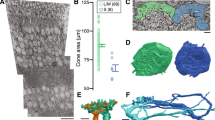
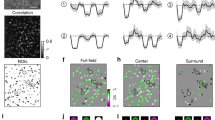
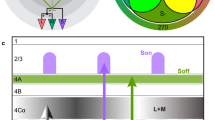
Abstract
Retinal amacrine cells are thought to lack chromatic or color-selective light responses and have only a minor role in color processing. We found that a type of mammalian (Ictidomys tridecemlineatus) amacrine cell selectively carries a blue-On signal, which is received from a blue or short wavelength–sensitive (S) cone On bipolar cell. This glycinergic inhibitory S-cone amacrine cell is ideally placed for driving blue-Off responses in downstream ganglion cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mollon, J.D. J. Exp. Biol. 146, 21–38 (1989).
Neitz, J. et al. Vision Res. 51, 633–651 (2011).
Dacey, D.M. et al. Nature 433, 749–754 (2005).
Dacey, D.M. et al. Nature 367, 731–735 (1994).
Chichilnisky, E.J. et al. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 889–893 (1999).
Calkins, D.J. et al. J. Neurosci. 18, 3373–3385 (1998).
Yin, L. et al. J. Neurosci. 29, 2706–2724 (2009).
Hemmi, J.M. et al. J. Vis. 2, 608–617 (2002).
Jacobs, G.H. et al. Vision Res. 20, 9–13 (1980).
Kouyama, N. et al. J. Neurosci. 12, 1233–1252 (1992).
Li, W. et al. Nat. Neurosci. 9, 669–675 (2006).
Mariani, A.P. Nature 308, 184–186 (1984).
Calkins, D.J. et al. Nature 381, 613–615 (1996).
Field, G.D. et al. Nat. Neurosci. 12, 1159–1164 (2009).
Dacey, D.M. in The Cognitive Neurosciences (ed. Gazzaniga, M.S.) 281–301 (MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 2004).
Li, W. et al. Nat. Neurosci. 9, 669–675 (2006).
DeVries, S.H. et al. Nature 397, 157–160 (1999).
Li, W. et al. Nat. Neurosci. 7, 751–756 (2004).
Kraft, T.W.J. Physiol. 404, 199–213 (1988).
Rushton, W.A. et al. Vision Res. 13, 2003–2015 (1973).
Kryger, Z. et al. Vis. Neurosci. 15, 685–691 (1998).
Acknowledgements
We thank D. Merriman and T. Rosenberg for editing and S. DeVries and B. Szmajda for critically reading the manuscript. This work was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Eye Institute (ZIA EY000508-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.C. and W.L. conceived the project and designed the experiments. S.C. performed the experiments. S.C. and W.L. analyzed the data. W.L. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–3 (PDF 675 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Li, W. A color-coding amacrine cell may provide a blue-Off signal in a mammalian retina. Nat Neurosci 15, 954–956 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3128
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3128
This article is cited by
-
Evolution of the circuitry for conscious color vision in primates
Eye (2017)
-
Retinal bipolar cells: elementary building blocks of vision
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2014)
-
Inverting the blues
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2012)
-
Another blue neuron in the retina
Nature Neuroscience (2012)