Abstract
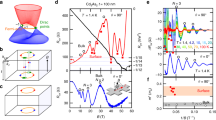
SmB6 is a strongly correlated mixed-valence Kondo insulator1,2 with a newly discovered surface state3,4, proposed to be of non-trivial topological origin5,6. However, the surface state dominates electrical conduction only below T∗ ≈ 4 K (ref. 3), limiting its scientific investigation and device application. Here, we report the enhancement of T∗ in SmB6 under the application of tensile strain. With 0.7% tensile strain we report surface-dominated conduction at up to a temperature of 240 K, persisting even after the strain has been removed. This can be explained in the framework of strain-tuned temporal and spatial fluctuations of f-electron configurations, which might be generally applied to other mixed-valence materials. We note that this amount of strain can be induced in epitaxial SmB6 films via substrate in potential device applications.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fisk, Z. et al. Kondo insulators. Physica B 223, 409–412 (1996).
Riseborough, P. S. Heavy fermion semiconductors. Adv. Phys. 49, 257–320 (2000).
Kim, D. J. et al. Surface Hall effect and nonlocal transport in SmB6: evidence for surface conduction. Sci. Rep. 3, 3150 (2013).
Wolgast, S. et al. Low-temperature surface conduction in the Kondo insulator SmB6 . Phys. Rev. B 88, 180405 (2013).
Dzero, M., Sun, K., Coleman, P. & Galitski, V. Theory of topological Kondo insulators. Phys. Rev. B 85, 045130 (2012).
Alexandrov, V., Dzero, M. & Coleman, P. Cubic topological Kondo insulators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 226403 (2013).
Li, G. et al. Two-dimensional Fermi surfaces in Kondo insulator SmB6 . Science 346, 1208–1212 (2014).
Dzero, M., Sun, K., Galitski, V. & Coleman, P. Topological Kondo insulators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 106408 (2010).
Stern, A., Efimkin, D. K., Galitski, V., Fisk, Z. & Xia, J. Radio frequency tunable oscillator device based on a SmB6 microcrystal. Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 166603 (2016).
Choi, K. et al. Enhancement of ferroelectricity in strained BaTiO3 thin films. Science 306, 1005–1009 (2004).
Cooley, J. C., Aronson, M. C., Fisk, Z. & Canfield, P. C. SmB6: Kondo insulator or exotic metal? Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 1629–1632 (1995).
Derr, J. et al. From unconventional insulating behavior towards conventional magnetism in the intermediate-valence compound SmB6 . Phys. Rev. B 77, 193107 (2008).
Hicks, C. W., Barber, M. E., Edkins, S. D., Brodsky, D. O. & Mackenzie, A. P. Piezoelectric-based apparatus for strain tuning. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85, 065003 (2014).
Hicks, C. W. et al. Strong increase of Tc of Sr2RuO4 under both tensile and compressive strain. Science 344, 283–285 (2014).
Goldstein, R. V., Gorodtsov, V. A. & Lisovenko, D. S. Relation of Poisson’s ratio on average with Young’s modulus. Auxetics on average. Dokl. Phys. 57, 174–178 (2012).
Tamaki, T. et al. Elastic properties of SmB6 and Sm3Se4 . J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 47, 469–471 (1985).
Beille, J., Maple, M. B., Wittig, J., Fisk, Z. & DeLong, L. E. Suppression of the energy gap in SmB6 under pressure. Phys. Rev. B 28, 7397–7400 (1983).
Moshchalkov, V. V. et al. SmB6 at high pressures: the transition from insulating to the metallic Kondo lattice. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 47, 289–291 (1985).
Ren, Z., Taskin, A. A., Sasaki, S., Segawa, K. & Ando, Y. Large bulk resistivity and surface quantum oscillations in the topological insulator Bi2Te2Se. Phys. Rev. B 82, 241306 (2010).
He, L. et al. Surface-dominated conduction in a 6 nm thick Bi2Se3 thin film. Nano Lett. 12, 1486–1490 (2012).
Mizumaki, M., Tsutsui, S. & Iga, F. Temperature dependence of Sm valence in SmB6 studied by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 176, 012034 (2009).
Butch, N. P. et al. Pressure-resistant intermediate valence in the Kondo insulator SmB6 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 156401 (2016).
Varma, C. M. Mixed-valence compounds. Rev. Mod. Phys. 48, 219–238 (1976).
Lawrence, J. M., Riseborough, P. S. & Parks, R. D. Valence fluctuation phenomena. Rep. Prog. Phys. 44, 1–84 (1981).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NSF grant DMR-1350122. V.M.G. acknowledges the support from DOEBES (DESC0001911) and Simons Foundation. M.D. acknowledges the support from NSF (DMR-1506547). We thank S. Thomas, B. Casas and D. Trinh for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.S. performed the measurements. M.D. and V.M.G. developed the theory. Z.F. fabricated the samples. J.X. designed the project. All authors discussed the result, and contributed to the writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 569 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stern, A., Dzero, M., Galitski, V. et al. Surface-dominated conduction up to 240 K in the Kondo insulator SmB6 under strain. Nature Mater 16, 708–711 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4888
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4888
This article is cited by
-
Tunable valence tautomerism in lanthanide–organic alloys
Nature Chemistry (2024)
-
Enabling magnetoelastic coupling in Ni/VO2 heterostructure by structural phase transition
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics (2018)
-
Negative pressure tuning
Nature Materials (2017)