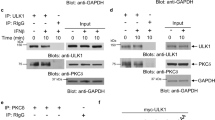
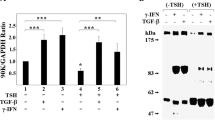
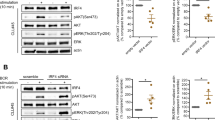
Abstract
We have identified an interferon-like cytokine, limitin, on the basis of its ability to arrest the growth of or kill lympho–hematopoietic cells. Limitin strongly inhibited B lymphopoiesis in vitro and in vivo but had little influence on either myelopoiesis or erythropoiesis. Because limitin uses the interferon α/β receptors and induces interferon regulatory factor-1, it may represent a previously unknown type I interferon prototype. However, preferential B-lineage growth inhibition and activation of Janus kinase 2 in a myelomonocytic leukemia line have not been described for previously known interferons.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kincade, P.W. et al. Cell interaction molecules utilized in bone marrow. Cell Adhes. Commun. 6, 211–215 (1998).
Oritani, K. & Kincade, P.W. Lymphopoiesis and matrix glycoprotein SC1/ECM2. Leuk. Lymphoma 32, 1–7 (1998).
Morrison, S.J., Shah, N.M. & Anderson, D.J. Regulatory mechanisms in stem cell biology. Cell 88, 287–298 (1997).
Burrows, P.D. & Cooper, M.D. B cell development and differentiation. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 9, 239–344 (1997).
Lyman, S.D. & Jacobsen, S.E.W. c-kit ligand and flt3 ligand: Stem/progenitor cell factors with overlapping yet distinct activities. Blood 91, 1101–1134 (1998).
Whetton, A.D. & Spooncer, E. Role of cytokines and extracellular matrix in the regulation of haemopoietic stem cells. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 10, 721–726 (1998).
Wang, J., Lin, Q., Langston, H. & Cooper, M.D. Resident bone marrow macrophages produce type I interferons that can selectively inhibit interleukin-7-driven growth of B lineage cells. Immunity 3, 475–484 (1995).
VerFaillie, C.M. Chemokines as inhibitors of hematopoietic progenitors. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 127, 148–150 (1996).
Graham, G.J. & Wright, E.G. Haemopoietic stem cells: their heterogeneity and regulation. Int. J. Exp. Path. 78, 197–218 (1997).
Cohen, P.L. & Eisenberg, R.A. Lpr and gld: single gene models of systemic autoimmunity and lymphoproliferative disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 9, 243–269 (1991).
Pietrangeli, C.E., Hayashi, S-I. & Kincade, P.W. Stromal cell lines which support lymphocyte growth: Characterization, sensitivity to radiation and responsiveness to growth factors. Eur. J. Immunol. 18, 863–872 (1988).
Gimble, J.M. et al. Response of bone marrow stromal cells to adipogenic antagonists. Mol. Cell. Biol. 9, 4587–4595 (1989).
Kelly, K.A., Tanaka, S., Baron, R. & Gimble, J.M. Murine bone marrow stromally derived BMS2 adipocytes support differentiation and function of osteoclast-like cells in vitro. Endocrinology 139, 2092–2101 (1998).
Kincade, P.W., Medina, K., Pietrangeli, C.E., Hayashi, S-I. & Naemen, A.E. Stromal cell lines which support lymphocyte growth II. Characteristics of a suppressive subclone. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 292, 227–234 (1991).
Oritani, K. et al. Both Stat3-activation and Stat3-independent BCL2 down-regulation are important for IL-6-induced apoptosis of 1A9-M cells. Blood 93, 1346–1354 (1999).
Shaw, G.D. et al. Structure and expression of cloned murine IFN-αgenes. Nucleic Acids Res. 11, 555–573 (1983).
Higashi, Y. et al. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for mouse interferon-β. J. Biol. Chem. 258, 9522–9529 (1983).
Hauptmann, R. & Swetly, P. A novel class of human type I interferons. Nucleic Acids Res. 13, 4739–4749 (1985).
Leaman, D.W. & Roberts, R.M. Genes for the trophoblast interferons in sheep, goat, and musk ox and distribution of related genes among mammals. J. Interferon Res. 12, 1–11 (1992).
Whitlock, C.A., Robertson, D. & Witte, O.N. Murine B cell lymphopoiesis in long term culture. J. Immunol. Methods 6, 7353–7569 (1984).
Muller, U. et al. Functional role of type I and type II interferons in antiviral defence. Science 264, 1918–1921 (1994).
Ihle, J.N. STATs: Signal transducers and activators of transcription. Cell 84, 331–334 (1996).
Domanski, P. & Colamonici, O.R. The type-I interferon receptor. The long and short of it. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 7, 143–151. (1996).
Zav'Yalov, V.P. & Zav'Yalov, G.A. Interferons alpha/beta and their receptors: place in the hierarchy of cytokines. APMIS 105, 161–186 (1997).
Haque, S.J. & Williams, B.G. Signal transduction in the interferon system. Semin. Oncol. 25, 14–22 (1998).
Velazquez, L., Felous, M., Stark, G.R. & Pellegrini, S. A protein tyrosine kinase in the interferonα/β signaling pathway. Cell 70, 313–322 (1992).
Muller, M. et al. The protein tyrosine kinase JAK1 complements defects in interferon-α/β and -γ signal transduction. Nature 366, 129–135 (1993).
Colamonici, O. et al. Direct binding to and tyrosine phosphorylation of the α subunit of the type I interferon receptor by p135tyk2 tyrosine kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14, 8133–8142 (1994).
Novick, D., Cohen, B. & Rubinstein, M. The human interferon alpha/beta receptor: Characterization and molecular cloning. Cell 77, 391–400 (1994).
Rani, S.M.R. et al. Characterization of β-R1, a gene that is selectively induced by interferon-beta (IFN-β) compared with IFN-α. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 22878–22884 (1996).
Platanias, L.C., Uddin, S., Domanski, P. & Colamonici, O.R. Differences in interferon α and β signaling. Interferon β selectively induces the interaction of the α and βL subunits of the type I interferon receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 23630–23633 (1996).
Abramovich, C. et al. Differential tyrosine phosphorylation of the IFNAR chain of the type I interferon receptor and an associated surface protein in response to IFN alpha and IFN beta. EMBO J. 13, 5871–5877 (1994).
Borghesi, L.A., Smithson, G. & Kincade, P.W. Stromal cell modulation of negative regulatory signals that influence apoptosis and proliferation of B lineage lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 159, 4171–4179 (1997).
Mazur, E.M., Richtsmeier, W.J. & South, K. Alpha-interferon: differential suppression of colony growth from human erythroid, myeloid, and megakaryocytic hematopoietic progenitor cells. J. Interferon Res. 6, 199–206 (1986).
Grawunder, U., Melchers, F. & Rolink, A. Interferon- arrests proliferation and causes apoptosis in stromal cell/interleukin-7-dependent normal murine pre-B cell lines and clones in vitro, but does not induce differentiation to surface immunoglobulin-positive B cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 23, 544–551 (1993).
Gimble, J.M., Medina, K., Hudson, J., Robinson, M. & Kincade, P.W. Modulation of lymphohematopoiesis in long-term cultures by gamma interferon: direct and indirect action on lymphoid and stromal cells. Exp. Hematol. 21, 224–230 (1993).
Broxmeyer, H.E. Suppressor cytokines and regulation of myelopoiesis. Biology and possible clinical uses. Am. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 14, 22–30 (1992).
Lee, G., Ellingsworth, L.R., Gillis, S., Wall, R. & Kincade, P.W. β transforming growth factors are potential regulators of B lymphopoiesis. J. Exp. Med. 166, 1290–1299 (1987).
Dorskind, K. IL-1 inhibits B cell differentiation in long term bone marrow cultures. J. Immunol. 141, 531–538 (1988).
Hirayama, F., Clark, S.C. & Ogawa, M. Negative regulation of early B lymphopoiesis by interleukin 3 and interleukin 1α. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 469–473 (1994).
Medina, K. & Kincade, P.W. Pregnancy related steroids are potential negative regulators of B lymphopoiesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 5382–5386 (1994).
Medina, K.L., Smithson, G. & Kincade, P.W. Suppression of B lymphopoiesis during normal pregnancy. J. Exp. Med. 178, 1507–1515 (1995).
Smithson, G., Medina, K., Ponting, I. & Kincade, P.W. Estrogen suppresses stromal celldependent lymphopoiesis in culture. J. Immunol. 155, 3409–3417 (1995).
Shimozato, T. & Kincade P.W. Indirect suppression of IL-7-responsive B cell precursors by vasoactive intestinal peptide. J. Immunol. 158, 5178–5184 (1997).
Lengyel, P. Tumor-suppressor genes: new about the interferon connection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 5893–5895 (1993).
Taniguchi, T., Harada, H. & Lamphier, M. Regulation of the interferon system and cell growth by the IRF transcription factors. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 121, 516–520 (1995).
Nguyen, H., Hiscott, J. & Pitha, P.M. The growing family of interferon regulatory factors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 8, 293–312 (1997).
Tamura, T. et al. An IRF-1-dependent pathway of DNA damage-induced apoptosis in mitogen-activated T lymphocytes. Nature 376, 596–599 (1995).
Kirchoff, S. et al. IRF-1 induced cell growth inhibition and interferon induction requires the activity of the protein kinase PKR. Oncogene 11, 439–445 (1995).
Kimura, T. et al. Involvement of the IRF-1 transcription factor in antiviral responses to interferons. Science 264, 1921–1924 (1994).
Itri, L.M. The interferon. Cancer 70, 940–945 (1992).
Weiss, K. Safety profile of interferon-αtherapy. Semin. Oncolo. 25, 9–13 (1998).
Oritani, K. & Kincade, P.W. Identification of stromal cell products that interact with pre-B cells. J. Cell Biol. 134, 771–782 (1996).
Yokota, T. et al. Growth-supporting activities of fibronectin on hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells in vitro and in vivo: structural requirement for fibronectin activities of CS1 and cell-binding domains. Blood 91, 3263–3272 (1998).
Dexter, T.M. & Testa, N.G. Differentiation and proliferation of hemopoietic cells in culture. Methods Cell Biol. 14, 387–405 (1976).
Tomiyama, Y. et al. The Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) recognition site of platelet glycoprotein Iib-IIIa on nonactivated platelets is accessible to high-affinity macromolecules. Blood 79, 2303–2312 (1992).
Matsumura, I. et al. Thrombopoietin-induced differentiation of a human megakaryoblastic leukemia cell line, CMK, involves transcriptional activation of p21WAF1/Cip1 by STAT5. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17, 2933–2943 (1997).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from the Yamanouchi Foundation for Research on Metabolic Disorders, the Kowa Life Science Foundation, the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science as well as grants AI-33085 and AI-20069 from the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oritani, K., Medina, K., Tomiyama, Y. et al. Limitin: An interferon-like cytokine that preferentially influences B-lymphocyte precursors. Nat Med 6, 659–666 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/76233
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/76233
This article is cited by
-
Functional signatures of evolutionarily young CTCF binding sites
BMC Biology (2020)
-
Acquired immunodeficiency associated with thymoma: a case report
BMC Cancer (2019)
-
Good’s Syndrome, CVID, and Selective Antibody Deficiency in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Current Allergy and Asthma Reports (2014)
-
Distinct evolution process among type I interferon in mammals
Protein & Cell (2013)
-
Macrophages and cytokines in the early defence against herpes simplex virus
Virology Journal (2005)