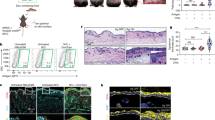
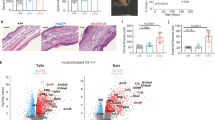
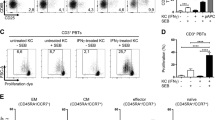
Abstract
Psoriasis is a complex disorder involving alterations of many cell types. Although evidence suggests a T-cell pathogenesis for psoriasis, a primary role of T cells has not been directly demonstrated. Here, we show that reconstitution of scid/scid mice with minor histocompatibility mismatched naive CD4+ T lymphocytes resulted in skin alterations that strikingly resembled human psoriasis clinically, histopathologically and in cytokine expression. This skin disorder was diminished when memory T cells were coinjected. Thus, a subset of dysregulated CD4+ T cells can cause tissue alterations seen in psoriasis without the presence of CD8+ cells or a primary epithelial abnormality.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christophers, E. & Sterry, W. in Dermatology in General Medicine (eds. Fitzpatrick, T. B., Eisen, A. Z., Wolff, K., Freedberg, I.M. & Austen, K.F.) 489–514 (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1993).
Barker, J.N.W.N. The immunopathology of psoriasis. Bailliere's Clin. Rheumatol. 8, 429–437 (1994).
Christophers, E. The immunopathology of psoriasis. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 110, 199–206 (1996).
Gottlieb, S.L. et al. Response of psoriasis to a lymphocyte-selective toxin (DAB389IL-2) suggests a primary immune, but not keratinocyte, pathogenic basis. Nature Med. 1, 442–447 (1995).
Carroll, J.M., Romero, M.R. & Watt, F.M. Suprabasal integrin expression in the epidermis of transgenic mice results in developmental defects and a phenotype resembling psoriasis. Cell 83, 957–968 (1995).
Groves, R.W., Mizutani, H., Kieffer, J.D. & Kupper, T.S. Inflammatory skin disease in transgenic mice that express high levels of interleukin 1α in basal epidermis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 11874–11878 (1995).
Wilson, J.B., Weinberg, W., Johnson, R., Yuspa, S. & Levine, A.J. Expression of the BNLF-1 oncogene of Epstein-Barr virus in the skin of transgenic mice induces hyperplasia and aberrant expression of keratin 6. Cell 61, 1315–1327 (1990).
Hammer, R.E., Maika, S.D., Richardson, J.A., Tang, J.P. & Taurog, J.D. Spontaneous inflammatory disease in transgenic rats expressing HLA-B27 and human (β2m: An animal model of HLA-B27-associated human disorders. Cell 63, 1099–1112 (1990).
Bullard, D.C. et al. A polygenic mouse model of psoriasiform skin disease in CD18-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 2116–2121 (1996).
Sundberg, J.C., Beamer, W.G., Shultz, L.D. & Dunstan, R.W. Inherited mouse mutations as models of human adnexal, cornification, and papulosquamous dermatoses. J. Invest. Dermatol. 95, 62s–63s (1990).
Grammer, S.F. & Streilein, J.W. The immune system in cutaneous disease: The search for a mouse model of the immunopathology of psoriasis. in Handbook of Mouse Mutations with Skin and Hair Abnormalities. (ed. Sundberg, J.P.) 143–153 (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1994).
Powrie, F., Leach, M.W., Mauze, S., Caddie, L.B. & Coffman, R.L. Phenotypically distinct subsets of CD4+ T Cells induce or protect from chronic intestinal inflammation in C.B-17 scid mice. Int. Immunol. 5, 1461–471 (1993).
Morrissey, P.J., Charrier, K., Braddy, S., Liggitt, D. & Watson, J.D. CD4+ T Cells that express high levels of CD45RB induce wasting disease when transferred into congenie severe combined immunodeficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 178, 237–244 (1993).
McGuire, J., Osber, M. & Lightfoot, L. Two keratins MW 50,000 and 56,000 are synthesized by psoriaticepidermis. Br. J. Dermatol. 111, 27–37 (1984).
Bernard, B.A., Reano, A., Darmon, Y.M. & J. Precocious appearance of involucrin and epidermal transglutaminase during differentiation of psoriatic skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 114, 279–283 (1986).
DeLisser, H.M., Newman, P.J. & Albelda, S.M. Molecular and functional aspects of PECAM-1/CD31. Immunol. Today 15, 490–495 (1994).
Detmar, M. et al. Overexpression of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in psoriasis. J. Exp. Med. 180, 1141–1146 (1994).
Keck, P.J. et al. Vascular permeability factor, an endothelial Cell mitogen related to PDCF. Science 246, 1309 (1989).
Finnerty, H. et al. Molecular cloning of murine FLT and FLT4. Oncogene 8, 2293–2298 (1993).
Matthews, W. et al. A receptor tyrosine kinase cDNA isolated from a population of enriched primitive hematopoietic Cells and exhibiting close genetic linkage to c-kit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 9026–9030 (1991).
Birkeland, M.L., Johnson, P., Trowbridge, I.S. & Purz, E. Changes in CD45 isoform expression accompany antigen-induced murine T-Cell activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 6734–6738 (1989).
Nickoloff, B.J., Griffiths, C.E. & Barker, J.N. The role of adhesion molecules, chemotactic factors, and cytokines in inflammatory and neoplastic skin disease—1990 update. J. Invest. Dermatol. 94, 151S–157S (1990).
Sundberg, J.P., Boggess, D., Shultz, L.D. & Beamer, W.G. The flaky skin (fsn) mutation, chromosome?. in Handbook of Mouse Mutations with Skin and Hair Abnormalities, (ed. Sundberg, J.D.) 253–268 (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1994).
Nanney, L.B., Sundberg, J.P. & King, L.E. Increased epidermal growth factor receptor in fsn/fsn mice. J. Invest. Dermatol. 106, 1169–1174 (1996).
Kupper, T.S. Immune and inflammatory processes in cutaneous tissues: Mechanisms and speculations. J. Clin. Invest. 86, 1783–1786 (1990).
Frank, S. et al. Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in cultured keratinocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 12607–12613 (1995).
Grossman, R.M. et al. Interleukin 6 is expressed in high levels in psoriatic skin and stimulates proliferation of cultured human keratinocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 6367–6371 (1989).
Gottlieb, A.B., Luster, A.D., Posnett, D.N. & Carter, D.M. Detection of a gamma interferon-induced protein IP-10 in psoriatic plaques. J. Exp. Med. 168, 941–948 (1988).
Frater-Schrpder, M., Risau, W., Hallmann, R., Gautschi, P. & Bohlen, P. Tumor necrosis factor type α, a potent inhibitor of endothelial growth in vitro, is angiogenic in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 5277–5281 (1987).
Subramanian, N. & Bray, M.A. Interleukin 1 releases histamine from human basophils and mast Cells in vitro. J. Immunol. 138, 271–275 (1987).
Arnaout, M.A., Wang, E.A., Clark, S.C. & Sieff, C.A. Human recombinant granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor increases Cell-to-Cell adhesion and surface expression of adhesion-promoting surface glycoproteins on mature granulocytes. J. Clin. Invest. 78, 597–601 (1986).
Powrie, F., Leach, M.W., Mauze, S., Caddie, L.B. & Coffman, R.L. Phenotypically distinct subsets of CD4+ T Cells induce or protect from chronic intestinal inflammation in C.B-17 scid mice. Int. Immunol. 5, 1461–1471 (1993).
Forman, J., Riblet, R., Brooks, K., Vitetta, S. & Henderson, L.A. H-40, an antigen controlled by an IgH linked gene and recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. I. Genetic analysis of H-40 and distribution of its product on B Cell tumors. J. Exp. Med. 159, 1724–1740 (1984).
Nickoloff, B.J., Kunkel, S.L., Burdick, M. & Stricter, R.M. Severe combined immunodeficiency mouse and human psoriatic skin chimeras: Validation of a new animal model. Am. J. Pathol. 146, 580–588 (1995).
Mueller, W. & Herrmann, B. Cyclosporin A for psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 301, 555 (1979).
Ellis, C.N. et al. Cyclosporine improves psoriasis in a double-blind study. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 256, 3110–3116 (1986).
Tomfohrde, J. et al. Gene for familial psoriasis susceptibility mapped to the distal end of human chromosome 17q. Science 264, 1141–1145 (1994).
Eedy, D.J., Burrows, D., Bridges, J.M. & Jones, F.G.C. Clearance of severe psoriasis after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Br. Med. J. 300, 908 (1990).
Nicolas, J.F. et al. CD4 antibody treatment of severe psoriasis. Lancet 338, 321 (1991).
Prinz, J. et al. Chimaeric CD4 monoclonal antibody in treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis. Lancet 338, 320–321 (1991).
Onuma, S. Immunohistochemical studies of infiltrating Cells in early and chronic lesions of psoriasis. J. Dermatol. 21, 223–232 (1994).
Chang, J.C.C. et al. CD8+ T Cells in psoriatic lesions preferentially use T-Cell receptor Vβ3 and/or Vβ13.1 genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 9282–9286 (1994).
Gilliam, A.C. & Murphy, G.F. Cutaneous graft-versus-host disease. in Graft-vs.-Host Disease, (eds. Ferrara, J.L.M., Deeg, H.J. & Burakoff, S.J.) 291–313 (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1996).
Schlegel, P.G., Vaysburd, M., Chen, Y., Butcher, E.C. & Chao, N.J. Inhibition of T Cell costimulation by VCAM-1 prevents murine graft-versus-host disease across minor histocompatibility barriers. J. Immunol. 155, 3856–3865 (1995).
Murphy, G.F., Sueki, H., Teuscher, C., Whitaker, D., & Korngold, R. Role of mast Cells in early epithelial target Cell injury in experimental acute graft-versus-host disease. J. Invest. Dermatol. 102, 451–461 (1994).
Gilliam, A.C., Whitaker-Menezes, D., Korngold, R. & Murphy, G.F. Apoptosis is the predominant form of epithelial target Cell injury in acute experimental graft-versus-host disease. J. Invest. Dermatol. 107, 377–383 (1996).
Korngold, R. & Sprent, J. Variable capacity of L3T4+ T Cells to cause lethal graft-versus-host disease across minor histocompatibility barriers in mice. J. Exp. Med. 165, 1552–1557 (1987).
Townsend, R.M., Briggs, C., Marini, J.C., Murphy, G.F. & Korngold, R. Inhibitory effect of a CD4-CDR3 peptide analog on graft-versus-host disease across a major histocompatibility complex-haploidentical barrier. Blood 88, 3038–3047 (1996).
Powrie, F., Carlino Leach, M.W., Mauze, S. & Coffman, R.L. A critical role for transforming growth factor b but not interleukin 4 in the suppression of T helper type 1-mediated colitis by CD45RBIow CD4+ T Cells. J. Exp. Med. 183, 2669–2674 (1996).
Menssen, A. et al. Evidence for an antigen-specific Cellular immune response in skin lesions of patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J. Immunol. 155, 4078–4083 (1995).
Yam, L.T., Li, C.Y., St Crosby, W.H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 55, 283–290 (1971).
Brown, L.F. et al. Increased expression of vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) in bullous pemphigoid, dermatitis herpetiformis, and erythema multiforme. J. Invest. Dermatol. 104, 744–749 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SchÖn, M., Detmar, M. & Parker, C. Murine psoriasis-like disorder induced by naive CD4+ T cells. Nat Med 3, 183–188 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0297-183
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0297-183
This article is cited by
-
Bitter taste receptor T2R38 is expressed on skin-infiltrating lymphocytes and regulates lymphocyte migration
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Single cell transcriptional zonation of human psoriasis skin identifies an alternative immunoregulatory axis conducted by skin resident cells
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
Early Recognition and Treatment Heralds Optimal Outcomes: the Benefits of Combined Rheumatology–Dermatology Clinics and Integrative Care of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Patients
Current Rheumatology Reports (2018)
-
Pathogenese der Psoriasis vulgaris
Der Hautarzt (2016)
-
Inositoylated Platelet-Activating Factor (Ino-C2-PAF) Modulates Dynamic Lymphocyte–Endothelial Cell Interactions and Alleviates Psoriasis-Like Skin Inflammation in Two Complementary Mouse Models
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2014)