Abstract
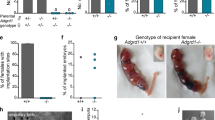
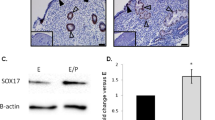
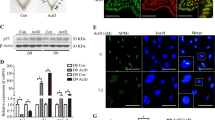
Embryo implantation remains a poorly understood process. We demonstrate here that activation of the epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) in mouse endometrial epithelial cells by an embryo-released serine protease, trypsin, triggers Ca2+ influx that leads to prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) release, phosphorylation of the transcription factor CREB and upregulation of cyclooxygenase 2, the enzyme required for prostaglandin production and implantation1,2,3. We detected maximum ENaC activation, as indicated by ENaC cleavage4, at the time of implantation in mice. Blocking or knocking down uterine ENaC in mice resulted in implantation failure. Furthermore, we found that uterine ENaC expression before in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatment is markedly lower in women with implantation failure as compared to those with successful pregnancy. These results indicate a previously undefined role of ENaC in regulating the PGE2 production and release required for embryo implantation, defects that may be a cause of miscarriage and low success rates in IVF.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruan, Y.C., Zhou, W. & Chan, H.C. Regulation of smooth muscle contraction by the epithelium: role of prostaglandins. Physiology (Bethesda) 26, 156–170 (2011).
Bonventre, J.V. et al. Reduced fertility and postischaemic brain injury in mice deficient in cytosolic phospholipase A2. Nature 390, 622–625 (1997).
Lim, H. et al. Multiple female reproductive failures in cyclooxygenase 2-deficient mice. Cell 91, 197–208 (1997).
Kleyman, T.R., Carattino, M.D. & Hughey, R.P. ENaC at the cutting edge: regulation of epithelial sodium channels by proteases. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 20447–20451 (2009).
Ansell, J.D., Barlow, P.W. & McLaren, A. Binucleate and polyploid cells in the decidua of the mouse. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 31, 223–227 (1974).
Enders, A.C. & Schlafke, S. Comparative aspects of blastocyst-endometrial interactions at implantation. Ciba Found. Symp. 64, 3–32 (1978).
Parkening, T.A. Apposition of uterine luminal epithelium during implantation in senescent golden hamsters. J. Gerontol. 34, 335–344 (1979).
Hedlund, K., Nilsson, O., Reinius, S. & Aman, G. Attachment reaction of the uterine luminal epithelium at implantation: light and electron microscopy of the hamster, guinea-pig, rabbit and mink. J. Reprod. Fertil. 29, 131–132 (1972).
Martin, L., Finn, C.A. & Carter, J. Effects of progesterone and oestradiol-17 β on the luminal epithelium of the mouse uterus. J. Reprod. Fertil. 21, 461–469 (1970).
Finn, C.A. Endocrine control of endometrial sensitivity during the induction of the decidual cell reaction in the mouse. J. Endocrinol. 36, 239–248 (1966).
Lejeune, B., Lecocq, R., Lamy, F. & Leroy, F. Changes in the pattern of endometrial protein synthesis during decidualization in the rat. J. Reprod. Fertil. 66, 519–523 (1982).
Lejeune, B., Van Hoeck, J. & Leroy, F. Transmitter role of the luminal uterine epithelium in the induction of decidualization in rats. J. Reprod. Fertil. 61, 235–240 (1981).
Almog, B., Shalom-Paz, E., Dufort, D. & Tulandi, T. Promoting implantation by local injury to the endometrium. Fertil. Steril. 94, 2026–2029 (2010).
Salamonsen, L.A. & Nie, G. Proteases at the endometrial-trophoblast interface: their role in implantation. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 3, 133–143 (2002).
Salamonsen, L.A., Hannan, N.J. & Dimitriadis, E. Cytokines and chemokines during human embryo implantation: roles in implantation and early placentation. Semin. Reprod. Med. 25, 437–444 (2007).
Sawada, H., Yamazaki, K. & Hoshi, M. Trypsin-like hatching protease from mouse embryos: evidence for the presence in culture medium and its enzymatic properties. J. Exp. Zool. 254, 83–87 (1990).
Kellenberger, S. & Schild, L. Epithelial sodium channel/degenerin family of ion channels: a variety of functions for a shared structure. Physiol. Rev. 82, 735–767 (2002).
Yang, J.Z. et al. Differential expression and localization of CFTR and ENaC in mouse endometrium during pre-implantation. Cell Biol. Int. 28, 433–439 (2004).
Vallet, V., Chraibi, A., Gaeggeler, H.P., Horisberger, J.D. & Rossier, B.C. An epithelial serine protease activates the amiloride-sensitive sodium channel. Nature 389, 607–610 (1997).
Fronius, M. & Clauss, W.G. Mechano-sensitivity of ENaC: may the (shear) force be with you. Pflugers Arch. 455, 775–785 (2008).
Kawabe, A. et al. Production of prostaglandinE2 via bile acid is enhanced by trypsin and acid in normal human esophageal epithelial cells. Life Sci. 75, 21–34 (2004).
Rastogi, P., Young, D.M. & McHowat, J. Tryptase activates calcium-independent phospholipase A2 and releases PGE2 in airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 295, L925–L932 (2008).
Orehek, J., Douglas, J.S. & Bouhuys, A. Contractile responses of the guinea-pig trachea in vitro: modification by prostaglandin synthesis–inhibiting drugs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 194, 554–564 (1975).
Donaldson, S.H. et al. Regulation of the epithelial sodium channel by serine proteases in human airways. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 8338–8345 (2002).
Nesterov, V., Dahlmann, A., Bertog, M. & Korbmacher, C. Trypsin can activate the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) in microdissected mouse distal nephron. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 295, F1052–F1062 (2008).
Sakoff, J.A. & Murdoch, R.N. The role of calcium in the artificially induced decidual cell reaction in pseudopregnant mice. Biochem. Mol. Med. 57, 81–90 (1996).
Ruan, Y.C. et al. Regulation of smooth muscle contractility by the epithelium in rat vas deferens: role of ATP-induced release of PGE2. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 586, 4843–4857 (2008).
Kennedy, T.G., Gillio-Meina, C. & Phang, S.H. Prostaglandins and the initiation of blastocyst implantation and decidualization. Reproduction 134, 635–643 (2007).
Tsatsanis, C., Androulidaki, A., Venihaki, M. & Margioris, A.N. Signalling networks regulating cyclooxygenase-2. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 38, 1654–1661 (2006).
Fouladi Nashta, A.A., Andreu, C.V., Nijjar, N., Heath, J.K. & Kimber, S.J. Role of leukemia inhibitor factor (LIF) in decidualisation of murine uterine stromal cells in vitro. J. Endocrinol. 181, 477–492 (2004).
Pakrasi, P.L. & Jain, A.K. Cyclooxygenase-2 derived PGE2 and PGI2 play an important role via EP2 and PPARδ receptors in early steps of oil induced decidualization in mice. Placenta 29, 523–530 (2008).
Yee, G.M. & Kennedy, T.G. Prostaglandin E2, cAMP and cAMP-dependent protein kinase isozymes during decidualization of rat endometrial stromal cells in vitro. Prostaglandins 46, 117–138 (1993).
Dolphin, A.C. A short history of voltage-gated calcium channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 147 (suppl. 1), S56–S62 (2006).
Toth, B. et al. Disorders of implantation—are there diagnostic and therapeutic options? J. Reprod. Immunol. 90, 117–123 (2011).
Carattino, M.D., Hughey, R.P. & Kleyman, T.R. Proteolytic processing of the epithelial sodium channel gamma subunit has a dominant role in channel activation. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 25290–25295 (2008).
Chan, L.N. et al. Distribution and regulation of ENaC subunit and CFTR mRNA expression in murine female reproductive tract. J. Membr. Biol. 185, 165–176 (2002).
Salker, M.S. et al. Deregulation of the serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase SGK1 in the endometrium causes reproductive failure. Nat. Med. 17, 1509–1513 (2011).
Sugimoto, Y. & Narumiya, S. Prostaglandin E receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 11613–11617 (2007).
Chan, L.N., Wang, X.F., Tsang, L.L. & Chan, H.C. Pyrimidinoceptors-mediated activation of Ca2+-dependent Cl− conductance in mouse endometrial epithelial cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1497, 261–270 (2000).
Nie, H.G. et al. Regulation of epithelial sodium channels by cGMP/PKGII. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 587, 2663–2676 (2009).
Strauss, O. & Wienrich, M. Ca2+−conductances in cultured rat retinal pigment epithelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 160, 89–96 (1994).
Braüner, T., Hulser, D.F. & Strasser, R.J. Comparative measurements of membrane potentials with microelectrodes and voltage-sensitive dyes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 771, 208–216 (1984).
Krötz, F. et al. Membrane-potential-dependent inhibition of platelet adhesion to endothelial cells by epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 24, 595–600 (2004).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by National 973 projects of China (2012CB944900, 2009CB522102, 2010CB945403), Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30770817; No. 81161120006; No. 31071019), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Ji Nan University), the Focused Investment Scheme and Li Ka Shing Institute of Health Sciences of The Chinese University of Hong Kong, and the Morningside Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.C.C. and Y.C.R.: conception and design; Y.C.R., J.H.G., X.L., R.Z., L.L.T., J.D.D., H.C., M.K.Y., X.J., X.H.Z., K.L.F. and Y.W.C.: experiments and/or data analysis; H.H.: clinical materials and consultancy; W.L.Z.: intellectual input and supervision; Y.C.R. and H.C.C.: article writing with contributions from other authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–3 and Supplementary Tables 1 and 2 (PDF 1934 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruan, Y., Guo, J., Liu, X. et al. Activation of the epithelial Na+ channel triggers prostaglandin E2 release and production required for embryo implantation. Nat Med 18, 1112–1117 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2771
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2771
This article is cited by
-
Role of Immunological Testing in Infertility
Current Obstetrics and Gynecology Reports (2024)
-
Protease secretions by the invading blastocyst induce calcium oscillations in endometrial epithelial cells via the protease-activated receptor 2
Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology (2023)
-
Activation of SGK1/ENaC Signaling Pathway Improves the Level of Decidualization in Unexplained Recurrent Spontaneous Abortion
Reproductive Sciences (2023)
-
Secretory phospholipase A2-X (Pla2g10) is a novel progesterone receptor target gene exclusively induced in uterine luminal epithelium for uterine receptivity in mice
Cell & Bioscience (2020)
-
Spatial organization of endometrial gene expression at the onset of embryo attachment in pigs
BMC Genomics (2019)