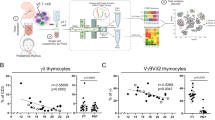
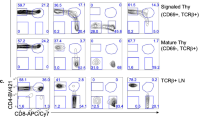
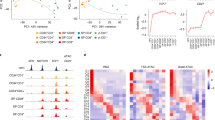
Abstract
Although T cell receptor (TCR)γδ+ and TCRαβ+ cells are commonly viewed as functionally independent, their relatedness and potential interdependence remain enigmatic. Here we have identified a gene profile that distinguishes mouse γδ cell populations from conventional αβ T cells. However, this profile was also expressed by sets of unconventional αβ T cells. Therefore, whereas TCR specificity determines the involvement of a T cell in an immune response, the cell's functional potential, as assessed by gene expression, does not segregate with the TCR. By monitoring the described gene profile, we show that γδ T cell development and function in TCRβ-deficient mice was impaired because of the absence of αβ T cell progenitors. Thus, normal γδ cell development is dependent on the development of conventional αβ T cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raulet, D.H. The structure, function, and molecular genetics of the γδ T cell receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 7, 175–207 (1989).
Haas, W., Pereira, P. & Tonegawa, S. γδ cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 11, 637–685 (1993).
Born, W. et al. Immunoregulatory functions of γδ T cells. Adv. Immunol. 71, 77–144 (1999).
Hayday, A.C. γδ cells: a right time and a right place for a conserved third way of protection. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18, 975–1026 (2000).
Chien, Y.H., Jores, R. & Crowley, M.P. Recognition by γδ T cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14, 511–532 (1996).
Mombaerts, P., Arnoldi, J., Russ, F., Tonegawa, S. & Kaufmann, S.H. Different roles of αβ and γδ T cells in immunity against an intracellular bacterial pathogen. Nature 365, 53–56 (1993).
Girardi, M. et al. Regulation of cutaneous malignancy by γδ T cells. Science 294, 605–609 (2001).
Jameson, J. et al. A role for skin γδ T cells in wound repair. Science 296, 747–749 (2002).
Mukasa, A. et al. Bacterial infection of the testis leading to autoaggressive immunity triggers apparently opposed responses of αβ and γδ T cells. J. Immunol. 155, 2047–2056 (1995).
Roberts, S.J. et al. T-cell αβ and γδ deficient mice display abnormal but distinct phenotypes toward a natural, widespread infection of the intestinal epithelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 11774–11779 (1996).
Girardi, M. et al. Resident skin-specific γδ T cells provide local, nonredundant regulation of cutaneous inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 195, 855–867 (2002).
Bucy, R.P., Chen, C.L., Cihak, J., Losch, U. & Cooper, M.D. Avian T cells expressing γδ receptors localize in the splenic sinusoids and the intestinal epithelium. J. Immunol. 141, 2200–2205 (1988).
Boismenu, R. & Havran, W.L. Modulation of epithelial cell growth by intraepithelial γδ T cells. Science 266, 1253–1255 (1994).
Fahrer, A.M. et al. Attributes of γδ intraepithelial lymphocytes as suggested by their transcriptional profile. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 10261–10266 (2001).
Shires, J., Theodoridis, E. & Hayday, A.C. Biological insights into TCRγδ+ and TCRαβ+ intraepithelial lymphocytes provided by serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE). Immunity 15, 419–434 (2001).
Hubank, M. & Schatz, D.G. Identifying differences in mRNA expression by representational difference analysis of cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 5640–5648 (1994).
Petrie, H.T., Scollay, R. & Shortman, K. Commitment to the T cell receptor-αβ or -γδ lineages can occur just prior to the onset of CD4 and CD8 expression among immature thymocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 22, 2185–2188 (1992).
Philpott, K.L. et al. Lymphoid development in mice congenitally lacking T cell receptor αβ-expressing cells. Science 256, 1448–1452 (1992).
Kehrl, J.H. & Sinnarajah, S. RGS2: a multifunctional regulator of G-protein signaling. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 34, 432–438 (2002).
He, Y.W. Orphan nuclear receptors in T lymphocyte development. J. Leukoc. Biol. 72, 440–446 (2002).
Sassone-Corsi, P. Goals for signal transduction pathways: linking up with transcriptional regulation. EMBO J. 13, 4717–4728 (1994).
Bruno, L., Fehling, H.J. & von Boehmer, H. The αβ T cell receptor can replace the γδ receptor in the development of γδ lineage cells. Immunity 5, 343–352 (1996).
Mombaerts, P. et al. Mutations in T-cell antigen receptor genes α and β block thymocyte development at different stages. Nature 360, 225–231 (1992).
Passoni, L. et al. Intrathymic δ selection events in γδ cell development. Immunity 7, 83–95 (1997).
Jarry, A., Cerf-Bensussan, N., Brousse, N., Selz, F. & Guy-Grand, D. Subsets of CD3+ (T cell receptor αβ or γδ) and CD3− lymphocytes isolated from normal human gut epithelium display phenotypical features different from their counterparts in peripheral blood. Eur. J. Immunol. 20, 1097–1103 (1990).
Lefrançois, L. Phenotypic complexity of intraepithelial lymphocytes of the small intestine. J. Immunol. 147, 1746–1751 (1991).
Hayday, A., Theodoridis, E., Ramsburg, E. & Shires, J. Intraepithelial lymphocytes: exploring the Third Way in immunology. Nat. Immunol. 2, 997–1003 (2001).
Arstila, T. et al. Identical T cell clones are located within the mouse gut epithelium and lamina propria and circulate in the thoracic duct lymph. J. Exp. Med. 191, 823–834 (2000).
Eiseman, E. & Bolen, J.B. Engagement of the high-affinity IgE receptor activates src protein-related tyrosine kinases. Nature 355, 78–80 (1992).
Heiken, H., Schulz, R.J., Ravetch, J.V., Reinherz, E.L. & Koyasu, S. T lymphocyte development in the absence of Fcε receptor Iγ subunit: analysis of thymic-dependent and independent αβ and γδ pathways. Eur. J. Immunol. 26, 1935–1943 (1996).
Laky, K., Lefrancois, L. & Puddington, L. Age-dependent intestinal lymphoproliferative disorder due to stem cell factor receptor deficiency: parameters in small and large intestine. J. Immunol. 158, 1417–1427 (1997).
Suzuki, H., Duncan, G.S., Takimoto, H. & Mak, T.W. Abnormal development of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes and peripheral natural killer cells in mice lacking the IL-2 receptor β chain. J. Exp. Med. 185, 499–505 (1997).
Diefenbach, A. et al. Selective associations with signaling proteins determine stimulatory versus costimulatory activity of NKG2D. Nat. Immunol. 3, 1142–1149 (2002).
Gilfillan, S., Ho, E.L., Cella, M., Yokoyama, W.M. & Colonna, M. NKG2D recruits two distinct adapters to trigger NK cell activation and costimulation. Nat. Immunol. 3, 1150–1155 (2002).
Kohyama, M. et al. Cytolytic and IFN-γ-producing activities of γδ T cells in the mouse intestinal epithelium are T cell receptor-β-chain dependent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 7451–7455 (1999).
Fehling, H.J., Krotkova, A., Saint-Ruf, C. & von Boehmer, H. Crucial role of the pre-T-cell receptor a gene in development of αβ but not γδ T cells. Nature 375, 795–798 (1995).
Wilson, A. & MacDonald, H.R. A limited role for β-selection during γδ T cell development. J. Immunol. 161, 5851–5854 (1998).
Blendy, J.A., Kaestner, K.H., Weinbauer, G.F., Nieschlag, E. & Schutz, G. Severe impairment of spermatogenesis in mice lacking the CREM gene. Nature 380, 162–165 (1996).
Havran, W.L. & Allison, J.P. Origin of Thy-1+ dendritic epidermal cells of adult mice from fetal thymic precursors. Nature 344, 68–70 (1990).
Cerdan, C. et al. CD28 costimulation up-regulates long-term IL-2Rβ expression in human T cells through combined transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation. J. Immunol. 154, 1007–1013 (1995).
Romero, P. et al. Expression of CD94 and NKG2 molecules on human CD4+ T cells in response to CD3-mediated stimulation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 70, 219–224 (2001).
Poussier, P., Ning, T., Banerjee, D. & Julius, M. A unique subset of self-specific intraintestinal T cells maintains gut integrity. J. Exp. Med. 195, 1491–1497 (2002).
Rabinowich, H. et al. Physical and functional association of Fcμ receptor on human natural killer cells with the ζ- and FcεRIγ-chains and with src family protein tyrosine kinases. J. Immunol. 157, 1485–1491 (1996).
Bendelac, A. Positive selection of mouse NK1+ T cells by CD1-expressing cortical thymocytes. J. Exp. Med. 182, 2091–2096 (1995).
Jenkinson, E.J., Anderson, G. & Owen, J.J. Studies on T cell maturation on defined thymic stromal cell populations in vitro. J. Exp. Med. 176, 845–853 (1992).
Shen, Y. et al. Adaptive immune response of Vγ2Vδ2+ T cells during mycobacterial infections. Science 295, 2255–2258 (2002).
Wen, L. et al. Primary γδ cell clones can be defined phenotypically and functionally as Th1/Th2 cells and illustrate the association of CD4 with Th2 differentiation. J. Immunol. 160, 1965–1974 (1998).
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Hubank, J. Dunne, G. Clark, W. Turnbull, D. Davies, A. Eddaoudi, C. Simpson, G. Barnes, C. Trigueros, J. Lewis, A. Denzel, S. Clarke, D. Oppenheim, V. Giuggio and S. Creighton for help; G. Schutz for ICER-lacZ mice; G. LeClercq for anti-Ly49E; and R. Ahmed for RNA from LCMV-specific T cells. We acknowledge a Wellcome Trust Programme Grant (A.C.H.) and the Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (Portugal) through the Gulbenkian PhD Programme (B.S.-S.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pennington, D., Silva-Santos, B., Shires, J. et al. The inter-relatedness and interdependence of mouse T cell receptor γδ+ and αβ+ cells. Nat Immunol 4, 991–998 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni979
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni979
This article is cited by
-
γδ T cells: origin and fate, subsets, diseases and immunotherapy
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
Mechanisms of activation of innate-like intraepithelial T lymphocytes
Mucosal Immunology (2020)
-
Increased TCR signal strength in DN thymocytes promotes development of gut TCRαβ(+)CD8αα(+) intraepithelial lymphocytes
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
γδ-T cells: an unpolished sword in human anti-infection immunity
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2013)
-
Extensive expansion of primary human gamma delta T cells generates cytotoxic effector memory cells that can be labeled with Feraheme for cellular MRI
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2013)