Abstract
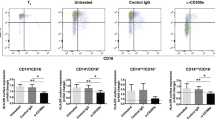
Homeostatic control of T cells involves tight regulation of effector T cells to prevent excessive activation that can cause tissue damage and autoimmunity. Little is known, however, about whether antigen-presenting cells (APCs) are also involved in maintaining immune system homeostasis once effector T cells are stimulated. Here we found that immature APCs downregulated effector T cell function by a mechanism involving the C-type lectin MGL expressed by APCs. Glycosylation-dependent interactions of MGL with CD45 on effector T cells negatively regulated T cell receptor–mediated signaling and T cell–dependent cytokine responses, which in turn decreased T cell proliferation and increased T cell death. Thus, regulation of effector T cells by MGL expressed on APCs may provide a target for regulating chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Janeway, C.A. & Medzhitov, R. Innate immune recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20, 197–216 (2002).
Steinman, R.M., Hawiger, D. & Nussenzweig, M.C. Tolerogenic dendritic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 21, 685–711 (2003).
Mosser, D.M. The many faces of macrophage activation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 73, 209–212 (2003).
Piemonti, L. et al. Glucocorticoids affect human dendritic cell differentiation and maturation. J. Immunol. 162, 6473–6481 (1999).
Schebesch, C. et al. Alternatively activated macrophages actively inhibit proliferation of peripheral blood lymphocytes and CD4+ T cells in vitro. Immunology 92, 478–486 (1997).
Figdor, C.G., van Kooyk, Y. & Adema, G.J. C-type lectin receptors on dendritic cells and Langerhans cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 77–84 (2002).
Geijtenbeek, T.B., van Vliet, S.J., Engering, A., 't Hart, B.A. & van Kooyk, Y. Self- and nonself-recognition by C-type lectins on dendritic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 22, 33–54 (2004).
Engering, A. et al. The dendritic cell-specific adhesion receptor DC-SIGN internalizes antigen for presentation to T cells. J. Immunol. 168, 2118–2126 (2002).
Bonifaz, L. et al. Efficient targeting of protein antigen to the dendritic cell receptor DEC-205 in the steady state leads to antigen presentation on major histocompatibility complex class I products and peripheral CD8+ T cell tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 196, 1627–1638 (2002).
Gantner, B.N., Simmons, R.M., Canavera, S.J., Akira, S. & Underhill, D.M. Collaborative induction of inflammatory responses by dectin-1 and Toll-like receptor 2. J. Exp. Med. 197, 1107–1117 (2003).
Raes, G. et al. Macrophage galactose-type C-type lectins as novel markers for alternatively activated macrophages elicited by parasitic infections and allergic airway inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 77, 321–327 (2005).
Higashi, N. et al. The macrophage C-type lectin specific for galactose/N-acetylgalactosamine is an endocytic receptor expressed on monocyte-derived immature dendritic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 20686–20693 (2002).
van Vliet, S.J. et al. Carbohydrate profiling reveals a distinctive role for the C-type lectin MGL in the recognition of helminth parasites and tumor antigens by dendritic cells. Int. Immunol. 17, 661–669 (2005).
Tsuiji, M. et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel mouse macrophage C-type lectin, mMGL2, which has a distinct carbohydrate specificity from mMGL1. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 28892–28901 (2002).
Hermiston, M.L., Xu, Z. & Weiss, A. CD45: a critical regulator of signaling thresholds in immune cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 21, 107–137 (2003).
Furukawa, K. et al. Structural study of the O-linked sugar chains of human leukocyte tyrosine phosphatase CD45. Eur. J. Biochem. 251, 288–294 (1998).
Zapata, J.M., Pulido, R., Acevedo, A., Sanchez-Madrid, F. & de Landazuri, M.O. Human CD45RC specificity. A novel marker for T cells at different maturation and activation stages. J. Immunol. 152, 3852–3861 (1994).
Garcia, G.G., Berger, S.B., Sadighi Akha, A.A. & Miller, R.A. Age-associated changes in glycosylation of CD43 and CD45 on mouse CD4 T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 35, 622–631 (2005).
Daniels, M.A., Hogquist, K.A. & Jameson, S.C. Sweet 'n' sour: the impact of differential glycosylation on T cell responses. Nat. Immunol. 3, 903–910 (2002).
Geijtenbeek, T.B. et al. Identification of DC-SIGN, a novel dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3 receptor that supports primary immune responses. Cell 100, 575–585 (2000).
Puig-Kroger, A. et al. Regulated expression of the pathogen receptor dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule 3 (ICAM-3)-grabbing nonintegrin in THP-1 human leukemic cells, monocytes, and macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 25680–25688 (2004).
Carlsson, S.R. & Fukuda, M. Isolation and characterization of leukosialin, a major sialoglycoprotein on human leukocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 12779–12786 (1986).
Rogers, P.R., Pilapil, S., Hayakawa, K., Romain, P.L. & Parker, D.C. CD45 alternative exon expression in murine and human CD4+ T cell subsets. J. Immunol. 148, 4054–4065 (1992).
Abraham, R.T. & Weiss, A. Jurkat T cells and development of the T-cell receptor signalling paradigm. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4, 301–308 (2004).
Xu, Z. & Weiss, A. Negative regulation of CD45 by differential homodimerization of the alternatively spliced isoforms. Nat. Immunol. 3, 764–771 (2002).
Chu, D.H. et al. The Syk protein tyrosine kinase can function independently of CD45 or Lck in T cell antigen receptor signaling. EMBO J. 15, 6251–6261 (1996).
Hintzen, R.Q. et al. Regulation of CD27 expression on subsets of mature T-lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 151, 2426–2435 (1993).
Xia, C.Q., Peng, R., Beato, F. & Clare-Salzler, M.J. Dexamethasone induces IL-10-producing monocyte-derived dendritic cells with durable immaturity. Scand. J. Immunol. 62, 45–54 (2005).
Ju, T. & Cummings, R.D. A unique molecular chaperone Cosmc required for activity of the mammalian core 1 β3-galactosyltransferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 16613–16618 (2002).
Ohta, T., Kitamura, K., Maizel, A.L. & Takeda, A. Alterations in CD45 glycosylation pattern accompanying different cell proliferation states. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 200, 1283–1289 (1994).
Stamenkovic, I., Sgroi, D., Aruffo, A., Sy, M.S. & Anderson, T. The B lymphocyte adhesion molecule CD22 interacts with leukocyte common antigen CD45RO on T cells and α2–6 sialyltransferase, CD75, on B cells. Cell 66, 1133–1144 (1991).
Walzel, H., Schulz, U., Neels, P. & Brock, J. Galectin-1, a natural ligand for the receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase CD45. Immunol. Lett. 67, 193–202 (1999).
London, C.A., Lodge, M.P. & Abbas, A.K. Functional responses and costimulator dependence of memory CD4+ T cells. J. Immunol. 164, 265–272 (2000).
Penninger, J.M., Irie-Sasaki, J., Sasaki, T. & Oliveira-dos-Santos, A.J. CD45: new jobs for an old acquaintance. Nat. Immunol. 2, 389–396 (2001).
Majeti, R., Bilwes, A.M., Noel, J.P., Hunter, T. & Weiss, A. Dimerization-induced inhibition of receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase function through an inhibitory wedge. Science 279, 88–91 (1998).
Nam, H.J., Poy, F., Saito, H. & Frederick, C.A. Structural basis for the function and regulation of the receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase CD45. J. Exp. Med. 201, 441–452 (2005).
Tchilian, E.Z. & Beverley, P.C. Altered CD45 expression and disease. Trends Immunol. 27, 146–153 (2006).
Irie-Sasaki, J. et al. CD45 is a JAK phosphatase and negatively regulates cytokine receptor signalling. Nature 409, 349–354 (2001).
Klaus, S.J., Sidorenko, S.P. & Clark, E.A. CD45 ligation induces programmed cell death in T and B lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 156, 2743–2753 (1996).
Fortin, M. et al. Apoptosis mediated through CD45 is independent of its phosphatase activity and association with leukocyte phosphatase-associated phosphoprotein. J. Immunol. 168, 6084–6089 (2002).
Lesage, S. et al. CD4+ CD8+ thymocytes are preferentially induced to die following CD45 cross-linking, through a novel apoptotic pathway. J. Immunol. 159, 4762–4771 (1997).
Liu, Z., Dawes, R., Petrova, S., Beverley, P.C. & Tchilian, E.Z. CD45 regulates apoptosis in peripheral T lymphocytes. Int. Immunol. 18, 959–966 (2006).
Latinis, K.M. et al. Regulation of CD95 (Fas) ligand expression by TCR-mediated signaling events. J. Immunol. 158, 4602–4611 (1997).
Powrie, F. et al. Inhibition of Th1 responses prevents inflammatory bowel disease in scid mice reconstituted with CD45RBhi CD4+ T cells. Immunity 1, 553–562 (1994).
Fowell, D. & Mason, D. Evidence that the T cell repertoire of normal rats contains cells with the potential to cause diabetes. Characterization of the CD4+ T cell subset that inhibits this autoimmune potential. J. Exp. Med. 177, 627–636 (1993).
Luke, P.P., O'Brien, C.A., Jevnikar, A.M. & Zhong, R. Anti-CD45RB monoclonal antibody-mediated transplantation tolerance. Curr. Mol. Med. 1, 533–543 (2001).
Gregori, S. et al. An anti-CD45RO/RB monoclonal antibody modulates T cell responses via induction of apoptosis and generation of regulatory T cells. J. Exp. Med. 201, 1293–1305 (2005).
Barrat, F.J. et al. In vitro generation of interleukin 10-producing regulatory CD4+ T cells is induced by immunosuppressive drugs and inhibited by T helper type 1 (Th1)- and Th2-inducing cytokines. J. Exp. Med. 195, 603–616 (2002).
Kumamoto, Y. et al. Identification of sialoadhesin as a dominant lymph node counter-receptor for mouse macrophage galactose-type C-type lectin 1. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 49274–49280 (2004).
van Kooyk, Y., van de Wiel-van Kemenade, P., Weder, P., Kuijpers, T.W. & Figdor, C.G. Enhancement of LFA-1-mediated cell adhesion by triggering through CD2 or CD3 on T lymphocytes. Nature 342, 811–813 (1989).
Acknowledgements
We thank R. van Lier and A. Weiss for discussions; F. Sánchez-Madrid for reagents; R. Mebius for critical review of the manuscript; E. van Liempt for assistance; and T. van der Pouw Kraan and T. Timmer for rheumatoid arthritis tissues. Supported by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development (900-02-002 to S.J.v.V. and Y.v.K.) and Dutch Asthma Foundation 3.2.03.39 (T.B.H.G. and S.I.G.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.J.v.V. designed and did all the experiments and prepared the manuscript; S.I.G. designed experiments; T.B.H.G. and Y.v.K. provided overall supervision, designed experiments and prepared the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
CD45 is a counterreceptor for MGL on lymphocytes. (PDF 178 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
MGL binding reduces TNF production by CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. (PDF 176 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
Model of MGL mediated control of effector T cell homeostasis. (PDF 251 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
MGL expression on cultured APCs. (PDF 93 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Characterization of MGLpos APCs in skin and lymph node. (PDF 88 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
MGL-Fc recognition of hematopoietic cell lines. (PDF 54 kb)
Supplementary Table 4
Expression of co-stimulatory molecules on cultured APCs. (PDF 60 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Vliet, S., Gringhuis, S., Geijtenbeek, T. et al. Regulation of effector T cells by antigen-presenting cells via interaction of the C-type lectin MGL with CD45. Nat Immunol 7, 1200–1208 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1390
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1390
This article is cited by
-
C1GalT1 expression reciprocally controls tumour cell-cell and tumour-macrophage interactions mediated by galectin-3 and MGL with double impact on cancer development and progression
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
Receptor basis of biological activity of polysaccharides
Biophysical Reviews (2023)
-
Macrophage Gal/GalNAc lectin 2 (MGL2)+ peritoneal antigen presenting cells during Fasciola hepatica infection are essential for regulatory T cell induction
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
The Pathogenic Role of Demodex Mites in Rosacea: A Potential Therapeutic Target Already in Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea?
Dermatology and Therapy (2020)
-
Macrophage galactose-type lectin (MGL) is induced on M2 microglia and participates in the resolution phase of autoimmune neuroinflammation
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2019)