Abstract
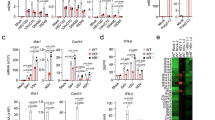
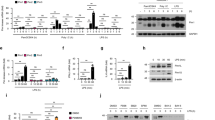
A key function of interferons is priming multiple cell types for enhanced activation by cytokines and inflammatory factors, including tumor necrosis factor, bacterial lipopolysaccharide and interferons themselves. Here we show that interferon-α (IFN-α)–induced activation of the transcriptional activator STAT1 and inflammatory STAT1 target genes was enhanced in IFN-γ-primed macrophages. Enhanced IFN-α signaling and proinflammatory function were dependent on the tyrosine kinase Syk and on adaptor proteins that activate Syk through immunoreceptor tyrosine activation motifs. Increased STAT1 expression contributed to enhanced IFN-α-induced STAT1 activation in primed macrophages. These results identify a mechanism by which crosstalk between cytokine and immune cell–specific immunoreceptor tyrosine activation motif–dependent signaling pathways regulates macrophage responses to IFN-α.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Stark, G.R., Kerr, I.M., Williams, B.R., Silverman, R.H. & Schreiber, R.D. How cells respond to interferons. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67, 227–264 (1998).
Biron, C.A. Interferons α and β as immune regulators—a new look. Immunity 14, 661–664 (2001).
Levy, D.E. & Darnell, J.E., Jr. Stats: transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 3, 651–662 (2002).
Durbin, J.E., Hackenmiller, R., Simon, M.C. & Levy, D.E. Targeted disruption of the mouse Stat1 gene results in compromised innate immunity to viral disease. Cell 84, 443–450 (1996).
Meraz, M.A. et al. Targeted disruption of the Stat1 gene in mice reveals unexpected physiologic specificity in the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Cell 84, 431–442 (1996).
Prejean, C. & Colamonici, O.R. Role of the cytoplasmic domains of the type I interferon receptor subunits in signaling. Semin. Cancer Biol. 10, 83–92 (2000).
Kotenko, S.V. et al. IFN-λs mediate antiviral protection through a distinct class II cytokine receptor complex. Nat. Immunol. 4, 69–77 (2003).
Sheppard, P. et al. IL-28, IL-29 and their class II cytokine receptor IL-28R. Nat. Immunol. 4, 63–68 (2003).
Fasler-Kan, E., Pansky, A., Wiederkehr, M., Battegay, M. & Heim, M.H. Interferon-α activates signal transducers and activators of transcription 5 and 6 in Daudi cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 254, 514–519 (1998).
Jaster, R., Tschirch, E., Bittorf, T. & Brock, J. Role of STAT5 in interferon-α signal transduction in Ba/F3 cells. Cell Signal. 11, 331–335 (1999).
Farrar, J.D., Smith, J.D., Murphy, T.L. & Murphy, K.M. Recruitment of Stat4 to the human interferon-α/β receptor requires activated Stat2. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 2693–2697 (2000).
Taniguchi, T. & Takaoka, A. A weak signal for strong responses: interferon-α/β revisited. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2, 378–386 (2001).
Marie, I., Durbin, J.E. & Levy, D.E. Differential viral induction of distinct interferon-α genes by positive feedback through interferon regulatory factor-7. EMBO J. 16, 6660–6669 (1998).
Sato, M. et al. Distinct and essential roles of transcription factors IRF-3 and IRF-7 in response to viruses for IFN-α/β gene induction. Immunity 13, 539–548 (2000).
Takaoka, A. et al. Cross talk between interferon-γ and -α/β signaling components in caveolar membrane domains. Science 288, 2357–2360 (2000).
Mitani, Y. et al. Cross talk of the interferon-α/β signalling complex with gp130 for effective interleukin-6 signalling. Genes Cells 6, 631–640 (2001).
Adams, D.O. & Hamilton, T.A. The cell biology of macrophage activation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2, 283–318 (1984).
Schroder, K., Hertzog, P.J., Ravasi, T. & Hume, D.A. Interferon-γ: an overview of signals, mechanisms and functions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 75, 163–189 (2004).
Hu, X. et al. Sensitization of IFN-γ Jak-STAT signaling during macrophage activation. Nat. Immunol. 3, 859–866 (2002).
Turner, M., Schweighoffer, E., Colucci, F., Di Santo, J.P. & Tybulewicz, V.L. Tyrosine kinase SYK: essential functions for immunoreceptor signalling. Immunol. Today 21, 148–154 (2000).
Ravetch, J.V. & Bolland, S. IgG Fc receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19, 275–290 (2001).
Mocsai, A. et al. The immunomodulatory adapter proteins DAP12 and Fc receptor γ-chain (FcRγ) regulate development of functional osteoclasts through the Syk tyrosine kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 6158–6163 (2004).
Koga, T. et al. Costimulatory signals mediated by the ITAM motif cooperate with RANKL for bone homeostasis. Nature 428, 758–763 (2004).
Vines, C.M. et al. Inhibition of β2 integrin receptor and Syk kinase signaling in monocytes by the Src family kinase Fgr. Immunity 15, 507–519 (2001).
Mocsai, A., Zhou, M., Meng, F., Tybulewicz, V.L. & Lowell, C.A. Syk is required for integrin signaling in neutrophils. Immunity 16, 547–558 (2002).
Deckert, M., Tartare-Deckert, S., Couture, C., Mustelin, T. & Altman, A. Functional and physical interactions of Syk family kinases with the Vav proto-oncogene product. Immunity 5, 591–604 (1996).
Bulanova, E. et al. The IL-15R α chain signals through association with Syk in human B cells. J. Immunol. 167, 6292–6302 (2001).
Zhou, Y.J. et al. Hierarchy of protein tyrosine kinases in interleukin-2 (IL-2) signaling: activation of Syk depends on Jak3; however, neither Syk nor Lck is required for IL-2-mediated STAT activation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 4371–4380 (2000).
Minami, Y. et al. Protein tyrosine kinase Syk is associated with and activated by the IL-2 receptor: possible link with the c-myc induction pathway. Immunity 2, 89–100 (1995).
Levy, D.E., Kessler, D.S., Pine, R. & Darnell, J.E., Jr. Cytoplasmic activation of ISGF3, the positive regulator of interferon-α-stimulated transcription, reconstituted in vitro. Genes Dev. 3, 1362–1371 (1989).
Li, X., Leung, S., Burns, C. & Stark, G.R. Cooperative binding of Stat1-2 heterodimers and ISGF3 to tandem DNA elements. Biochimie. 80, 703–710 (1998).
Gil, M.P. et al. Biologic consequences of Stat1-independent IFN signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 6680–6685 (2001).
Ramana, C.V. et al. Stat1-independent regulation of gene expression in response to IFN-γ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 6674–6679 (2001).
Ivashkiv, L.B. Type I interferon modulation of cellular responses to cytokines and infectious pathogens: potential role in SLE pathogenesis. Autoimmunity 36, 473–479 (2003).
Shimoda, K. et al. Tyk2 plays a restricted role in IFN α signaling, although it is required for IL-12-mediated T cell function. Immunity 13, 561–571 (2000).
Karaghiosoff, M. et al. Partial impairment of cytokine responses in Tyk2-deficient mice. Immunity 13, 549–560 (2000).
Karaghiosoff, M. et al. Central role for type I interferons and Tyk2 in lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxin shock. Nat. Immunol. 4, 471–477 (2003).
Li, X., Leung, S., Kerr, I.M. & Stark, G.R. Functional subdomains of STAT2 required for preassociation with the α interferon receptor and for signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17, 2048–2056 (1997).
Leung, S., Qureshi, S.A., Kerr, I.M., Darnell, J.E., Jr. & Stark, G.R. Role of STAT2 in the α interferon signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 1312–1317 (1995).
Farrar, J.D. et al. Selective loss of type I interferon-induced STAT4 activation caused by a minisatellite insertion in mouse Stat2. Nat. Immunol. 1, 65–69 (2000).
Park, C., Li, S., Cha, E. & Schindler, C. Immune response in Stat2 knockout mice. Immunity 13, 795–804 (2000).
David, M., Chen, H.E., Goelz, S., Larner, A.C. & Neel, B.G. Differential regulation of the α/β interferon-stimulated Jak/Stat pathway by the SH2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase SHPTP1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 7050–7058 (1995).
Petricoin, E.F., 3rd et al. Antiproliferative action of interferon-α requires components of T-cell-receptor signalling. Nature 390, 629–632 (1997).
Turner, M. et al. Perinatal lethality and blocked B-cell development in mice lacking the tyrosine kinase Syk. Nature 378, 298–302 (1995).
Nguyen, K.B. et al. Critical role for STAT4 activation by type 1 interferons in the interferon-γ response to viral infection. Science 297, 2063–2066 (2002).
Doyle, S.E. et al. Toll-like receptors induce a phagocytic gene program through p38. J. Exp. Med. 199, 81–90 (2004).
Herrero, C. et al. Reprogramming of IL-10 activity and signaling by IFN-γ. J. Immunol. 171, 5034–5041 (2003).
Sharif, N.M., Tassiulas, I., Hu, Y., Mecklenbraucker, I., Tarakhovsky, A. & Ivashkiv, L.B. IFN-α priming results in a gain of proinflammatory function by IL-10: implications for systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis. J. Immunol. 172, 6476–6481 (2004).
Kasperkovitz, P.V. et al. Activation of the STAT1 pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 63, 233–239 (2004).
van der Pouw Kraan, T.C. et al. Rheumatoid arthritis is a heterogeneous disease: evidence for differences in the activation of the STAT-1 pathway between rheumatoid tissues. Arthritis Rheum. 48, 2132–2145 (2003).
Baechler, E.C. et al. Interferon-inducible gene expression signature in peripheral blood cells of patients with severe lupus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 2610–2615 (2003).
Bennett, L. et al. Interferon and granulopoiesis signatures in systemic lupus erythematosus blood. J. Exp. Med. 197, 711–723 (2003).
Kuroiwa, T., Schlimgen, R., Illei, G.G. & Boumpas, D.T. Monocyte response to Th1 stimulation and effector function toward human mesangial cells are not impaired in patients with lupus nephritis. Clin. Immunol. 106, 65–72 (2003).
Yasukawa, H., Sasaki, A. & Yoshimura, A. Negative regulation of cytokine signaling pathways. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18, 143–164 (2000).
Malakhova, O.A. et al. Protein ISGylation modulates the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Genes Dev. 17, 455–460 (2003).
Lee, I.H., Li, W.P., Hisert, K.B. & Ivashkiv, L.B. Inhibition of interleukin 2 signaling and signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)5 activation during T cell receptor-mediated feedback inhibition of T cell expansion. J. Exp. Med. 190, 1263–1274 (1999).
Strobl, B. et al. A completely foreign receptor can mediate an interferon-γ-like response. EMBO J. 20, 5431–5442 (2001).
Rubinson, D.A. et al. A lentivirus-based system to functionally silence genes in primary mammalian cells, stem cells and transgenic mice by RNA interference. Nat. Genet. 33, 401–406 (2003).
Acknowledgements
We thank V. Tybulewicz, M. Muller, G. Yap, C. Schindler and L. van Parijs for providing mice, bone marrow cells and plasmids; X. Ma and K. Park-Min for critically reviewing the manuscript; and M. Humphrey and M. Nakamura for discussions. Supported by the National Institutes of Health (L.B.I.), Abbott Scholar Program (I.T.) and Cancer Research Institute (X.H.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tassiulas, I., Hu, X., Ho, H. et al. Amplification of IFN-α-induced STAT1 activation and inflammatory function by Syk and ITAM-containing adaptors. Nat Immunol 5, 1181–1189 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1126
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1126
This article is cited by
-
The immune receptor CD300e negatively regulates T cell activation by impairing the STAT1-dependent antigen presentation
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Matrix metalloproteinases in the CNS: interferons get nervous
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2019)
-
In vitro blood cell responsiveness to IFN-α predicts clinical response independently of IL28B in hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infected patients
Journal of Translational Medicine (2014)
-
Regulation of type I interferon responses
Nature Reviews Immunology (2014)
-
Association of common single-nucleotide polymorphisms in innate immune genes with differences in TLR-induced cytokine production in neonates
Genes & Immunity (2013)