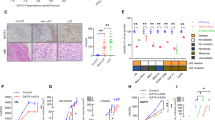
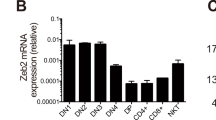
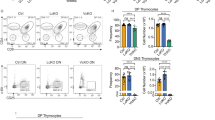
Abstract
T lymphocyte activation is associated with activation of diverse AGC serine kinases (named after family members protein kinase A, protein kinase G and protein kinase C). It has been difficult to assess the function of these molecules in T cell development with simple gene-deletion strategies because different isoforms of AGC kinases are coexpressed in the thymus and have overlapping, redundant functions. To circumvent these problems, we explored the consequences of genetic manipulation of phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 (PDK1), a rate-limiting 'upstream' activator of AGC kinases. Here we analyzed the effect of PDK1 deletion on T lineage development. We also assessed the consequences of reducing PDK1 levels to 10% of normal. Complete PDK1 loss blocked T cell differentiation in the thymus, whereas reduced PDK1 expression allowed T cell differentiation but blocked proliferative expansion. These studies show that AGC family kinases are essential for T cell development.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borowski, C. et al. On the brink of becoming a T cell. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 14, 200–206 (2002).
Michie, A.M., Soh, J.W., Hawley, R.G., Weinstein, I.B. & Zuniga-Pflucker, J.C. Allelic exclusion and differentiation by protein kinase C-mediated signals in immature thymocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 609–614 (2001).
Michie, A.M. & Zuniga-Pflucker, J.C. Regulation of thymocyte differentiation: pre-TCR signals and β-selection. Semin. Immunol. 14, 311–323 (2002).
Spits, H. Development of αβ T cells in the human thymus. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 760–772 (2002).
Cantrell, D.A. Regulation and function of serine kinase networks in lymphocytes. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 15, 294–298 (2003).
Acuto, O. & Cantrell, D. T cell activation and the cytoskeleton. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18, 165–184 (2000).
Cantrell, D.A. Transgenic analysis of thymocyte signal transduction. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 20–27 (2002).
Samelson, L.E. Signal transduction mediated by the T cell antigen receptor: the role of adapter proteins. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20, 371–394 (2002).
Koretzky, G.A. et al. Regulation of hematopoietic cell development and activation by adapter proteins. Immunol. Res. 27, 357–366 (2003).
Marklund, U., Lightfoot, K. & Cantrell, D. Intracellular location and cell context-dependent function of protein kinase D. Immunity 19, 491–501 (2003).
Rodriguez-Borlado, L. et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulates the CD4/CD8 T cell differentiation ratio. J. Immunol. 170, 4475–4482 (2003).
Suzuki, A. et al. T cell-specific loss of Pten leads to defects in central and peripheral tolerance. Immunity 14, 523–534 (2001).
Shima, H. et al. Disruption of the p70s6k/p85s6k gene reveals a small mouse phenotype and a new functional S6 kinase. EMBO J. 17, 6649–6659 (1998).
Peng, X.D. et al. Dwarfism, impaired skin development, skeletal muscle atrophy, delayed bone development, and impeded adipogenesis in mice lacking Akt1 and Akt2. Genes. Dev. 17, 1352–1365 (2003).
Leitges, M. et al. Targeted disruption of the ζPKC gene results in the impairment of the NF-κB pathway. Mol. Cell. 8, 771–780 (2001).
Leitges, M. et al. Protein kinase C-δ is a negative regulator of antigen-induced mast cell degranulation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 3970–3980 (2002).
Leitges, M. et al. Immunodeficiency in protein kinase cβ-deficient mice. Science 273, 788–791 (1996).
Castrillo, A. et al. Protein kinase Cε is required for macrophage activation and defense against bacterial infection. J. Exp. Med. 194, 1231–1242 (2001).
Mecklenbrauker, I., Saijo, K., Zheng, N.Y., Leitges, M. & Tarakhovsky, A. Protein kinase Cδ controls self-antigen-induced B-cell tolerance. Nature 416, 860–865 (2002).
Su, T.T. et al. PKC-β controls IκB kinase lipid raft recruitment and activation in response to BCR signaling. Nat. Immunol. 3, 780–786 (2002).
Sun, Z. et al. PKC-θ is required for TCR-induced NF-κB activation in mature but not immature T lymphocytes. Nature 404, 402–407 (2000).
Parker, P.J. & Parkinson, S.J. AGC protein kinase phosphorylation and protein kinase C. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 29, 860–863 (2001).
Alessi, D.R. et al. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Bα. Curr. Biol. 7, 261–269 (1997).
Lawlor, M.A. et al. Essential role of PDK1 in regulating cell size and development in mice. EMBO J. 21, 3728–3738 (2002).
Mora, A. et al. Deficiency of PDK1 in cardiac muscle results in heart failure and increased sensitivity to hypoxia. EMBO J. 22, 4666–4676 (2003).
Takahama, Y. et al. Functional competence of T cells in the absence of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins caused by T cell-specific disruption of the Pig-a gene. Eur. J. Immunol. 28, 2159–2166 (1998).
Buckland, J., Pennington, D.J., Bruno, L. & Owen, M.J. Co-ordination of the expression of the protein tyrosine kinase p56lck with the pre-T cell receptor during thymocyte development. Eur. J. Immunol. 30, 8–18 (2000).
Aifantis, I., Buer, J., von Boehmer, H. & Azogui, O. Essential role of the pre-T cell receptor in allelic exclusion of the T cell receptor β locus. Immunity 7, 601–607 (1997).
Azzam, H.S. et al. CD5 expression is developmentally regulated by T cell receptor (TCR) signals and TCR avidity. J. Exp. Med. 188, 2301–2311 (1998).
Rodewald, H.R. et al. FcγRII/III and CD2 expression mark distinct subpopulations of immature CD4-CD8-murine thymocytes: in vivo developmental kinetics and T cell receptor β chain rearrangement status. J. Exp. Med. 177, 1079–1092 (1993).
Gomez, M., Kioussis, D. & Cantrell, D.A. The GTPaseRac-1 controls cell fate in the thymus by diverting thymocytes from positive to negative selection. Immunity 15, 703–713 (2001).
Trigueros, C. et al. Pre-TCR signaling regulates IL-7 receptor α expression promoting thymocyte survival at the transition from the double-negative to double-positive stage. Eur. J. Immunol. 33, 1968–1977 (2003).
Gallandrini, R., Henning, S. & Cantrell, D.A. Different functions for the GTPase Rho in prothymocytes and late pre-T cells. Immunity 7, 163–174 (1997).
Costello, P.S., Cleverley, S.C., Galandrini, R., Henning, S.W. & Cantrell, D.A. The GTPase rho controls a p53-dependent survival checkpoint during thymopoiesis. J. Exp. Med. 192, 77–85 (2000).
Vanhaesebroeck, B. & Alessi, D.R. The PI3K-PDK1 connection: more than just a road to PKB. Biochem. J. 346 Pt 3, 561–576 (2000).
Lizcano, J.M. et al. Insulin-induced Drosophila S6 kinase activation requires phosphoinositide 3-kinase and protein kinase B. Biochem. J. 374, 297–306 (2003).
Lafont, V., Astoul, E., Laurence, A., Liautard, J. & Cantrell, D. The T cell antigen receptor activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-regulated serine kinases protein kinase B and ribosomal S6 kinase 1. FEBS Lett. 486, 38–42 (2000).
Kane, L.P., Andres, P.G., Howland, K.C., Abbas, A.K. & Weiss, A. Akt provides the CD28 costimulatory signal for up-regulation of IL-2 and IFN-γ but not TH2 cytokines. Nat. Immunol. 2, 37–44 (2001).
Wolfer, A., Wilson, A., Nemir, M., MacDonald, H.R. & Radtke, F. Inactivation of Notch1 impairs VDJβ rearrangement and allows pre-TCR-independent survival of early αβ lineage thymocytes. Immunity 16, 869–879 (2002).
Thomas, G. The S6 kinase signaling pathway in the control of development and growth. Biol. Res. 35, 305–313 (2002).
Ward, S.G. & Cantrell, D.A. Phosphoinositide 3-kinases in T lymphocyte activation. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 13, 332–338 (2001).
Okkenhaug, K. et al. Impaired B and T cell antigen receptor signaling in p110δ PI 3-kinase mutant mice. Science 297, 1031–1034 (2002).
Cantrell, D.A. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling pathways. J. Cell. Sci. 114, 1439–1445 (2001).
Harris, T.K. PDK1 and PKB/Akt: ideal targets for development of new strategies to structure-based drug design. IUBMB Life 55, 117–126 (2003).
Williams, M.R. et al. The role of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 in activating AGC kinases defined in embryonic stem cells. Curr. Biol. 10, 439–448 (2000).
Acknowledgements
We thank N. Bailey, J. MacDonald, P. Hagger, G. Hutchinson, C Croucher and C. Watkins for mouse care; D. Davies, A. Eddaoudi, C. Simpson, G. Warnes and R. Clarke for help with flow cytometry; U. Marklund for discussions; P. Crocker for critical comments on the manuscript; and R. Spörri for help with the bone marrow chimera experiments and for critical comments on the manuscript. Supported by Cancer Research UK and a Wellcome Trust Principal Research Fellowship (D.A.C).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hinton, H., Alessi, D. & Cantrell, D. The serine kinase phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 (PDK1) regulates T cell development. Nat Immunol 5, 539–545 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1062
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1062
This article is cited by
-
SUMOylation of PDPK1 Is required to maintain glycolysis-dependent CD4 T-cell homeostasis
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
Recent insights of T cell receptor-mediated signaling pathways for T cell activation and development
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2020)
-
Stage-specific requirement of kinase PDK1 for NK cells development and activation
Cell Death & Differentiation (2019)
-
Depurinized milk downregulates rat thymus MyD88/Akt/p38 function, NF-κB-mediated inflammation, caspase-1 activity but not the endonuclease pathway: in vitro/in vivo study
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
PDK1 plays a vital role on hematopoietic stem cell function
Scientific Reports (2017)