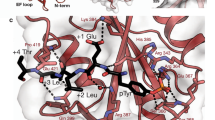
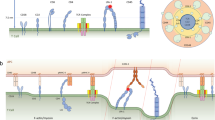
Abstract
Adaptors are molecular scaffolds that recruit effectors, which are critical for immune cell activation. Recent work has underscored the requirement for adaptors in propagating stimulatory signals as well as their ability to inhibit immune cell function. The mechanisms by which adaptors function rely not only on the intermolecular interactions they mediate, but also on where they are localized within the cell. The use of sophisticated genetic, biochemical, cellular and imaging approaches has provided important new insights into the biology of adaptor protein function. Here we focus on T lymphocytes as a model to illustrate the critical roles adaptors play as regulators of cellular activation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weiss, A. & Littman, D.R. Signal transduction by lymphocyte antigen receptors. Cell 76, 263–274 (1994).
Finco, T.S., Kadlecek, T., Zhang, W., Samelson, L.E. & Weiss, A. LAT is required for TCR-mediated activation of PLCγ1 and the Ras pathway. Immunity 9, 617–626 (1998).
Zhang, W., Irvin, B.J., Trible, R.P., Abraham, R.T. & Samelson, L.E. Functional analysis of LAT in TCR-mediated signaling pathways using a LAT-deficient Jurkat cell line. Int. Immunol 11, 943–950 (1999).
Yablonski, D., Kuhne, M.R., Kadlecek, T. & Weiss, A. Uncoupling of nonreceptor tyrosine kinases from PLC-γ1 in an SLP-76-deficient T cell. Science 281, 413–416 (1998).
Zhang, W., Trible, R.P. & Samelson, L.E. LAT palmitoylation: its essential role in membrane microdomain targeting and tyrosine phosphorylation during T cell activation. Immunity 9, 239–246 (1998).
Zhang, W., Sloan-Lancaster, J., Kitchen, J., Trible, R.P. & Samelson, L.E. LAT: the ZAP-70 tyrosine kinase substrate that links T cell receptor to cellular activation. Cell 92, 83–92 (1998).
Asada, H. et al. Grf40, A novel Grb2 family member, is involved in T cell signaling through interaction with SLP-76 and LAT. J. Exp. Med. 189, 1383–1390 (1999).
Liu, S.K., Fang, N., Koretzky, G.A. & McGlade, C.J. The hematopoietic-specific adaptor protein gads functions in T-cell signaling via interactions with the SLP-76 and LAT adaptors. Curr. Biol 9, 67–75 (1999).
Wardenburg, J.B. et al. Phosphorylation of SLP-76 by the ZAP-70 protein-tyrosine kinase is required for T-cell receptor function. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 19641–19644 (1996).
Fang, N. & Koretzky, G.A. SLP-76 and Vav function in separate, but overlapping pathways to augment interleukin-2 promoter activity. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 16206–16212 (1999).
Wu, J., Motto, D.G., Koretzky, G.A. & Weiss, A. Vav and SLP-76 interact and functionally cooperate in IL-2 gene activation. Immunity 4, 593–602 (1996).
Wunderlich, L., Farago, A., Downward, J. & Buday, L. Association of Nck with tyrosine-phosphorylated SLP-76 in activated T lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 29, 1068–1075 (1999).
Bunnell, S.C. et al. Biochemical interactions integrating Itk with the T cell receptor-initiated signaling cascade. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 2219–2230 (2000).
Su, Y.W. et al. Interaction of SLP adaptors with the SH2 domain of Tec family kinases. Eur. J. Immunol. 29, 3702–3711 (1999).
da Silva, A.J. et al. Cloning of a novel T-cell protein FYB that binds FYN and SH2-domain- containing leukocyte protein 76 and modulates interleukin 2 production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 7493–7498 (1997).
Musci, M.A. et al. Molecular cloning of SLAP-130, an SLP-76-associated substrate of the T cell antigen receptor-stimulated protein tyrosine kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 11674–11677 (1997).
Sauer, K. et al. Hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 associates physically and functionally with the adaptor proteins B cell linker protein and SLP-76 in lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 45207–45216 (2001).
Zhang, W. et al. Association of Grb2, Gads, and phospholipase C-γ 1 with phosphorylated LAT tyrosine residues. Effect of LAT tyrosine mutations on T cell antigen receptor-mediated signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 23355–23361 (2000).
Yablonski, D., Kadlecek, T. & Weiss, A. Identification of a phospholipase C-γ1 (PLC-γ1) SH3 domain-binding site in SLP-76 required for T-cell receptor-mediated activation of PLC-γ1 and NFAT. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 4208–4218 (2001).
Veri, M.C. et al. Membrane raft-dependent regulation of phospholipase Cγ-1 activation in T lymphocytes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 6939–6950 (2001).
Buday, L., Egan, S.E., Rodriguez Viciana, P., Cantrell, D.A. & Downward, J.A complex of Grb2 adaptor protein, Sos exchange factor, and a 36-kDa membrane-bound tyrosine phosphoprotein is implicated in ras activation in T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 9019–9023 (1994).
Lin, J. & Weiss, A. Identification of the minimal tyrosine residues required for linker for activation of T cell function. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 29588–29595 (2001).
Paz, P.E. et al. Mapping the Zap-70 phosphorylation sites on LAT (linker for activation of T cells) required for recruitment and activation of signalling proteins in T cells. Biochem. J. 356, 461–471 (2001).
Dower, N.A. et al. RasGRP is essential for mouse thymocyte differentiation and TCR signaling. Nat. Immunol. 1, 317–321 (2000).
Clements, J.L. et al. Requirement for the leukocyte-specific adapter protein SLP-76 for normal T cell development. Science 281, 416–419 (1998).
Pivniouk, V. et al. Impaired viability and profound block in thymocyte development in mice lacking the adaptor protein SLP-76. Cell 94, 229–238 (1998).
Zhang, W. et al. Essential role of LAT in T cell development. Immunity 10, 323–332. (1999).
Aguado, E. et al. Induction of T helper type 2 immunity by a point mutation in the LAT adaptor. Science 296, 2036–2040 (2002).
Kumar, L., Pivniouk, V., de la Fuente, M.A., Laouini, D. & Geha, R.S. Differential role of SLP-76 domains in T cell development and function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 884–889 (2002).
Myung, P.S. et al. Differential requirement for SLP-76 domains in T cell development and function. Immunity 15, 1011–1026 (2001).
Sommers, C.L. et al. A LAT mutation that inhibits T cell development yet induces lymphoproliferation. Science 296, 2040–2043 (2002).
Turner, M. et al. A requirement for the Rho-family GTP exchange factor Vav in positive and negative selection of thymocytes. Immunity 7, 451–460 (1997).
Yoder, J. et al. Requirement for the SLP-76 adaptor GADS in T cell development. Science 291, 1987–1991 (2001).
Griffiths, E.K. et al. Positive regulation of T cell activation and integrin adhesion by the adapter Fyb/Slap. Science 293, 2260–2263 (2001).
Peterson, E.J. et al. Coupling of the TCR to integrin activation by Slap-130/Fyb. Science 293, 2263–2265 (2001).
Leo, A. & Schraven, B. Adapters in lymphocyte signalling. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 13, 307–316 (2001).
Brdicka, T. et al. Phosphoprotein associated with glycosphingolipid-enriched microdomains (PAG), a novel ubiquitously expressed transmembrane adaptor protein, binds the protein tyrosine kinase csk and is involved in regulation of T cell activation. J. Exp. Med. 191, 1591–1604 (2000).
Kawabuchi, M. et al. Transmembrane phosphoprotein Cbp regulates the activities of Src-family tyrosine kinases. Nature 404, 999–1003 (2000).
Nada, S., Okada, M., MacAuley, A., Cooper, J.A. & Nakagawa, H. Cloning of a complementary DNA for a protein-tyrosine kinase that specifically phosphorylates a negative regulatory site of p60c-src. Nature 351, 69–72 (1991).
Jones, N. & Dumont, D.J. Recruitment of Dok-R to the EGF receptor through its PTB domain is required for attenuation of Erk MAP kinase activation. Curr. Biol. 9, 1057–1060 (1999).
Suzu, S. et al. p56(dok-2) as a cytokine-inducible inhibitor of cell proliferation and signal transduction. EMBO J. 19, 5114–5122 (2000).
Veillette, A., Latour, S. & Davidson, D. Negative regulation of immunoreceptor signaling. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20, 669–707 (2002).
Yamanashi, Y. et al. Role of the rasGAP-associated docking protein p62(dok) in negative regulation of B cell receptor-mediated signaling. Genes Dev. 14, 11–16 (2000).
Carpino, N. et al. p62(dok): a constitutively tyrosine-phosphorylated, GAP-associated protein in chronic myelogenous leukemia progenitor cells. Cell 88, 197–204 (1997).
Jones, N. & Dumont, D.J. The Tek/Tie2 receptor signals through a novel Dok-related docking protein, Dok-R. Oncogene 17, 1097–1108 (1998).
Lemay, S., Davidson, D., Latour, S. & Veillette, A. Dok-3, a novel adapter molecule involved in the negative regulation of immunoreceptor signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 2743–2754 (2000).
Rafnar, T. et al. Stimulation of the high-affinity IgE receptor results in the tyrosine phosphorylation of a 60 kD protein which is associated with the protein-tyrosine kinase, Csk. Mol. Immunol. 35, 249–257 (1998).
Tamir, I. et al. The RasGAP-binding protein p62dok is a mediator of inhibitory FcγRIIB signals in B cells. Immunity 12, 347–358 (2000).
Coffey, A.J. et al. Host response to EBV infection in X-linked lymphoproliferative disease results from mutations in an SH2-domain encoding gene. Nat. Genet. 20, 129–135 (1998).
Nichols, K.E. et al. Inactivating mutations in an SH2 domain-encoding gene in X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 13765–13770 (1998).
Sayos, J. et al. The X-linked lymphoproliferative-disease gene product SAP regulates signals induced through the co-receptor SLAM. Nature 395, 462–469 (1998).
Czar, M.J. et al. Altered lymphocyte responses and cytokine production in mice deficient in the X-linked lymphoproliferative disease gene SH2D1A/DSHP/SAP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 7449–7454 (2001).
Wu, C. et al. SAP controls T cell responses to virus and terminal differentiation of TH2 cells. Nat. Immunol. 2, 410–414 (2001).
Morra, M. et al. X-linked lymphoproliferative disease: a progressive immunodeficiency. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19, 657–682 (2001).
Latour, S. et al. Regulation of SLAM-mediated signal transduction by SAP, the X-linked lymphoproliferative gene product. Nat. Immunol. 2, 681–690 (2001).
Tangye, S.G., Phillips, J.H., Lanier, L.L. & Nichols, K.E. Functional requirement for SAP in 2B4-mediated activation of human natural killer cells as revealed by the X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. J. Immunol. 165, 2932–2936 (2000).
Fu, C., Turck, C.W., Kurosaki, T. & Chan, A.C. BLNK: a central linker protein in B cell activation. Immunity 9, 93–103 (1998).
Wienands, J. et al. SLP-65: a new signaling component in B lymphocytes which requires expression of the antigen receptor for phosphorylation. J. Exp. Med. 188, 791–795 (1998).
Ishiai, M. et al. BLNK required for coupling Syk to PLCγ2 and Rac1-JNK in B cells. Immunity 10, 117–125 (1999).
Chiu, C.W., Dalton, M., Ishiai, M., Kurosaki, T. & Chan, A.C. BLNK: molecular scaffolding through 'cis'-mediated organization of signaling proteins. EMBO J. 21, 6461–6472 (2002).
Hayashi, K. et al. The B cell-restricted adaptor BASH is required for normal development and antigen receptor-mediated activation of B cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 2755–2760 (2000).
Jumaa, H. et al. Abnormal development and function of B lymphocytes in mice deficient for the signaling adaptor protein SLP-65. Immunity 11, 547–554 (1999).
Pappu, R. et al. Requirement for B cell linker protein (BLNK) in B cell development. Science 286, 1949–1954 (1999).
Xu, S. et al. B cell development and activation defects resulting in xid-like immunodeficiency in BLNK/SLP-65-deficient mice. Int. Immunol. 12, 397–404 (2000).
Xu, S., Wong, S.C. & Lam, K.P. Cutting edge: B cell linker protein is dispensable for the allelic exclusion of immunoglobulin heavy chain locus but required for the persistence of CD5+ B cells. J. Immunol. 165, 4153–4157 (2000).
Minegishi, Y. et al. An essential role for BLNK in human B cell development. Science 286, 1954–1957 (1999).
Flemming, A., Brummer, T., Reth, M. & Jumaa, H. The adaptor protein SLP-65 acts as a tumor suppressor that limits pre-B cell expansion. Nat. Immunol. 4, 38–43 (2003).
Engels, N., Wollscheid, B. & Wienands, J. Association of SLP-65/BLNK with the B cell antigen receptor through a non-ITAM tyrosine of Ig-α. Eur. J. Immunol. 31, 2126–2134 (2001).
Kabak, S. et al. The direct recruitment of BLNK to immunoglobulin α couples the B-cell antigen receptor to distal signaling pathways. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 2524–2535 (2002).
Cassard, S., Choquet, D., Fridman, W.H. & Bonnerot, C. Regulation of ITAM signaling by specific sequences in Ig-β B cell antigen receptor subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 23786–23791 (1996).
Judd, B.A. et al. Differential requirement for LAT and SLP-76 in GPVI versus T cell receptor signaling. J. Exp. Med. 195, 705–717 (2002).
Clements, J.L. et al. Fetal hemorrhage and platelet dysfunction in SLP-76-deficient mice. J. Clin. Invest. 103, 19–25 (1999).
Judd, B.A. et al. Hematopoietic reconstitution of SLP-76 corrects hemostasis and platelet signaling through α IIb β 3 and collagen receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 12056–12061 (2000).
Pasquet, J.M. et al. LAT is required for tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase cγ2 and platelet activation by the collagen receptor GPVI. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 8326–8334 (1999).
Burack, W.R., Cheng, A.M. & Shaw, A.S. Scaffolds, adaptors and linkers of TCR signaling: theory and practice. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 14, 312–316 (2002).
Geng, L. & Rudd, C.E. Signalling scaffolds and adaptors in T-cell immunity. Br. J. Haematol. 116, 19–27 (2002).
Werlen, G. & Palmer, E. The T-cell receptor signalosome: a dynamic structure with expanding complexity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 14, 299–305 (2002).
Dustin, M.L. & Shaw, A.S. Costimulation: building an immunological synapse. Science 283, 649–650 (1999).
Grakoui, A. et al. The immunological synapse: a molecular machine controlling T cell activation. Science 285, 221–227 (1999).
Monks, C.R., Freiberg, B.A., Kupfer, H., Sciaky, N. & Kupfer, A. Three-dimensional segregation of supramolecular activation clusters in T cells. Nature 395, 82–86 (1998).
Lee, K.H. et al. T cell receptor signaling precedes immunological synapse formation. Science 295, 1539–1542 (2002).
Freiberg, B.A. et al. Staging and resetting T cell activation in SMACs. Nat. Immunol. 3, 911–917 (2002).
Bunnell, S.C. et al. T cell receptor ligation induces the formation of dynamically regulated signaling assemblies. J. Cell. Biol. 158, 1263–1275 (2002).
Zhu, M., Janssen, E., Leung, K. & Zhang, W. Molecular cloning of a novel gene encoding a membrane-associated adaptor protein (LAX) in lymphocyte signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 46151–46158 (2002).
Brdicka, T. et al. NTAL (non-T cell activation linker): a transmembrane adaptor protein involved in immunoreceptor signaling. J. Exp. Med. 196, 1617–1626 (2002).
Janssen, E., Zhu, M., Zhang, W., Koonpaew, S. & Zhang, W. LAB: A new membrane-associated adaptor molecule in B cell activation. Nat. Immunol. 4, 117–123 (2003).
Abtahian, F. et al. Regulation of blood and lymphatic vascular separation by the signaling proteins SLP-76 and Syk. Science 299, 247–251 (2003).
Takaki, S. et al. Control of B cell production by the adaptor protein lnk. Definition of a conserved family of signal-modulating proteins. Immunity 13, 599–609 (2000).
Takaki, S., Morita, H., Tezuka, Y. & Takatsu, K. Enhanced hematopoiesis by hematopoietic progenitor cells lacking intracellular adaptor protein, Lnk. J. Exp. Med. 195, 151–160 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank J.N. Wu, K.E. Nichols and J.S. Maltzman for critical reading of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jordan, M., Singer, A. & Koretzky, G. Adaptors as central mediators of signal transduction in immune cells. Nat Immunol 4, 110–116 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni0203-110
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni0203-110
This article is cited by
-
Signal-transducing adaptor protein 1 (STAP1) in microglia promotes the malignant progression of glioma
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2023)
-
Serum cytokine dependent hematopoietic cell linker (CLNK) as a predictor for the duration of illness in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders (2020)
-
Immune adaptor SKAP1 acts a scaffold for Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) for the optimal cell cycling of T-cells
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Association between the BANK1 rs3733197 polymorphism and polymyositis/dermatomyositis in a Chinese Han population
Clinical Rheumatology (2019)
-
Immune adaptor protein SKAP1 (SKAP-55) forms homodimers as mediated by the N-terminal region
BMC Research Notes (2018)