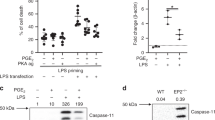
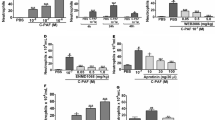
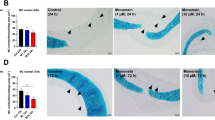
Abstract
We examined the role of a cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) in antigen-induced eosinophil infiltration of airways and in airway hyperresponsiveness to methacholine. Inhibition of cPLA2, or blockade of the platelet-activating factor (PAF) receptor, blocked antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and suppressed eosinophil infiltration. Neither cyclooxygenase nor 5-lipoxygenase inhibition had either effect. We show here that, in antigen-sensitized guinea pigs, cPLA2 inhibition prevents both eosinophilic infiltration and subsequent airway hyperresponsiveness after antigen challenge. We also show that this effect is mediated by first-step hydrolysis of membrane phospholipid into lysophospholipid rather than by prostanoid or leukotriene metabolites of arachidonate.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bousquet, J. et al. Eosinophilic inflammation in asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 323, 1033–1039 (1990).
Laitinen, L. A., Laitinen, A. & Haahtela, T. Airway mucosal inflammation even in patients with newly diagnosed asthma. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 147, 697–704 (1993).
Uozumi, N. et al. Role of cytosolic phospholipase A2 in allergic response and parturition. Nature 390, 618–622 (1997).
Nagase, T. et al. Acute lung injury by sepsis and acid aspiration: a key role for cytosolic phospholipase A2 . Nature Immunol. 1, 42–46 (2000).
Irvine, R. F. How is the level of free arachidonic acid controlled in mammalian cells? Biochem. J. 204, 3–16 (1982).
Hanahan, D. J. Platelet activating factor: a biologically active phosphoglyceride. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 55, 483–509 (1986).
Barnes, P. J. New concepts in the pathogenesis of bronchial hyperresponsiveness and asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 83, 1013–1026 (1989).
Richards, I. M. et al. Contribution of leukotriene B4 to airway inflammation and the effect of antagonists. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 629, 274–287 (1991).
Powell, W. S., Chung, D. & Gravel, S. 5-Oxo-6,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid is a potent stimulator of human eosinophil migration. J. Immunol. 154, 4123–4132 (1995).
Cuss, F. M., Dixon, C. M. & Barnes, P. J. Effects of inhaled platelet activating factor on pulmonary function and bronchial responsiveness in man. Lancet 2, 189–192 (1986).
Weiss, J. W. et al. Bronchoconstrictor effects of leukotriene C in humans. Science 216, 196–198 (1982).
Fischer, A. R. et al. Effect of chronic 5-lipoxygenase inhibition on airway hyperresponsiveness in asthmatic subjects. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 152, 1203–1207 (1995).
Fuller, R. W., Dixon, C. M., Dollery, C. T. & Barnes, P. J. Prostaglandin D2 potentiates airway responsiveness to histamine and methacholine. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 133, 252–254 (1986).
Jones, G. L., Saroea, H. G., Watson, R. M. & O'Byrne, P. M. Effect of an inhaled thromboxane mimetic (U46619) on airway function in human subjects. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 145, 1270–1274 (1992).
Zhu, X. et al. Cytosolic phospholipase A2 activation is essential for β1 and β2 integrin-dependent adhesion of human eosinophils. J. Immunol. 163, 3423–3429 (1999).
Tsunoda, H. et al. Effects of a novel PAF antagonist, E6123, on PAF-induced biological responses. Agents Actions Suppl. 31, 251–254 (1990).
Kaneko, T., Ikeda, H., Fu, L., Nishiyama, H. & Okubo, T. Platelet-activating factor mediates the ozone-induced increase in airway microvascular leakage in guinea pigs. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 292, 251–255 (1995).
Ashida, Y. et al. Pharmacological profile of AA-861, a 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor. Prostaglandins 26, 955–972 (1983).
Arima, M., Yukawa, T. & Makino, S. Effect of YM264 on the airway hyperresponsiveness and the late asthmatic response in a guinea pig model of asthma. Chest 108, 529–534 (1995).
Sun, F. F., Czuk, C. I. & Taylor, B. M. Arachidonic acid metabolism in guinea pig eosinophils: synthesis of thromboxane B2 and leukotriene B4 in response to soluble or particulate activators. J. Leukoc. Biol. 46, 152–160 (1989).
Hirata, K., Maghni, K., Borgeat, P. & Sirois, P. Guinea pig alveolar eosinophils and macrophages produce leukotriene B4 but no peptido-leukotriene. J. Immunol. 144, 1880–1885 (1990).
Sun, F. F. et al. Biochemical and functional differences between eosinophils from animal species and man. J. Leukoc. Biol. 50, 140–150 (1991).
Tohda, Y. et al. The inhibitory effect of TMK688, a novel anti-allergic drug having both 5-lipoxygenase inhibitory activity and anti-histamine activity, against bronchoconstriction, leukotriene production and inflammatory cell infiltration in sensitized guinea pigs. Clin. Exp. Allergy 27, 110–118 (1997).
Serhan, C. N. Lipoxins and novel aspirin-triggered 15-epi-lipoxins (ATL): a jungle of cell-cell interactions or a therapeutic opportunity? Prostaglandins 53, 107–137 (1997).
Quinn, M. T., Parthasarathy, S. & Steinberg, D. Lysophosphatidylcholine: a chemotactic factor for human monocytes and its potential role in atherogenesis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 85, 2805–2809 (1988).
Chilton, F. H. et al. Antigen-induced generation of lyso-phospholipids in human airways. J. Exp. Med. 183, 2235–2245 (1996).
Kagoshima, M. et al. Suppressive effects of Y-24180, a receptor antagonist to platelet activating factor (PAF), on antigen-induced asthmatic responses in guinea pigs. Inflamm. Res. 46, 147–153 (1997).
Heuer, H. O., Leon, I., Anderson, G. P. & Jennewein, H. M. Comparative effects of a glucocorticosteroid, theophylline and the peptido-leukotriene-antagonist CGP 45715A on antigen-induced early and late phase airway response and inflammatory cell influx in sensitised guinea pigs. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 369, 225–231 (1999).
Tsunoda, H. et al. Activity of a novel thienodiazepine derivative as a platelet-activating factor antagonist in guinea pig lungs. Effects on platelet-activating factor and allergen induced eosinophil accumulation. Arzneimittelforschung 41, 224–227 (1991).
Fitzgerald, M. F., Moncada, S. & Parente, L. The anaphylactic release of platelet-activating factor from perfused guinea-pig lungs. Br. J. Pharmacol. 88, 149–153 (1986).
Uchida, Y. et al. Involvement of endothelins in immediate and late asthmatic responses of guinea pigs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 277, 1622–1629 (1996).
Henderson, W. R. Jr, Lu, J., Poole, K. M., Dietsch, G. N. & Chi, E. Y. Recombinant human platelet-activating factor-acetylhydrolase inhibits airway inflammation and hyperreactivity in mouse asthma model. J. Immunol. 164, 3360–3367 (2000).
Kuitert, L. M. et al. Effect of a novel potent platelet-activating factor antagonist, modipafant, in clinical asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 151, 1331–1335 (1995).
Evans, D. J., Barnes, P. J., Cluzel, M. & O'Connor, B. J. Effects of a potent platelet-activating factor antagonist, SR27417A, on allergen-induced asthmatic responses. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 156, 11–16 (1997).
Henig, N. R., Aitken, M. L., Liu, M. C., Yu, A. S. & Henderson, W. R. Jr Effect of recombinant human platelet-activating factor-acetylhydrolase on allergen-induced asthmatic responses. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 162, 523–527 (2000).
Andersson, P. Antigen-induced bronchial anaphylaxis in actively sensitized guinea pigs. The effect of booster injection and cyclophosphamide treatment. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 64, 249–258 (1981).
Street, I. P. et al. Slow- and tight-binding inhibitors of the 85-kDa human phospholipase A2. Biochemistry 32, 5935–5940 (1993).
Yoshimoto, T. et al. 2,3,5-Trimethyl-6-(12-hydroxy-5,10-dodecadiynyl)-1,4-benzoquinone (AA861), a selective inhibitor of the 5-lipoxygenase reaction and the biosynthesis of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 713, 470–473 (1982).
Pennock, B. E., Cox, C. P., Rodgers, R. M., Cain, W. A. & Wells, J. H. A non-invasive technique for the measurement of change in specific airway resistance. J. Appl. Physiol. 46, 399–406 (1996).
Fryer, A. D. et al. Antibody to VLA-4, but not to L-selectin, protects neuronal M2 muscarinic receptors in antigen-challenged guinea pig airways. J. Clin. Invest. 99, 2036–2044 (1997).
Evans, C. M., Fryer, A. D., Jacoby, D. B., Gleich, G. J. & Costello, R. W. Pretreatment with antibody to eosinophil major basic protein prevents hyperresponsiveness by protecting neuronal M2 muscarinic receptors in antigen-challenged guinea pigs. J. Clin. Invest. 100, 2254–2262 (1997).
Konzett, H. & Roessler, R. Versuchanordnungzu Untersuchungen an der Bronchialmusukulatur. Arch. Exp. Path. Pharmak. 195, 71–74 (1940).
Jones, T. et al. Biological activity of leukotriene sulfones of respiratory tissues. Prostaglandins 24, 279–289 (1982).
Minami, S. et al. A new quantitative inhalation apparatus for small animals. Jpn. J. Chest Dis. 21, 252–258 (1982).
Kurashima, K., Fujimura, M., Tsujiura, M. & Matsuda, T. Effect of surfactant inhalation on allergic bronchoconstriction in guinea pigs. Clin. Exp. Allergy 27, 337–342 (1997).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NHLBI grant RO1-HL46368 and by NHLBI SCOR grant HL-56399. S. M. and H. S. were supported by the AstraZeneca Traveling Fellowship
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Myou, S., Sano, H., Fujimura, M. et al. Blockade of eosinophil migration and airway hyperresponsiveness by cPLA2-inhibition. Nat Immunol 2, 145–149 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/84244
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/84244
This article is cited by
-
Oral administration of cytosolic PLA2 inhibitor arachidonyl trifluoromethyl ketone ameliorates cauda equina compression injury in rats
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2015)
-
Human Macrophage ATP7A is Localized in the trans-Golgi Apparatus, Controls Intracellular Copper Levels, and Mediates Macrophage Responses to Dermal Wounds
Inflammation (2012)
-
Beta-escin has potent anti-allergic efficacy and reduces allergic airway inflammation
BMC Immunology (2010)
-
Pain following the repair of an abdominal hernia
Surgery Today (2010)