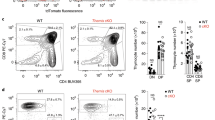
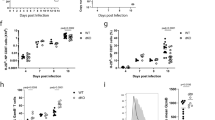
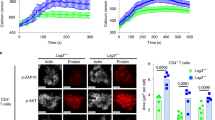
Abstract
A region of the interleukin-2 (IL-2) promoter known as the RE/AP element is activated in concert by signals that originate from the T cell antigen receptor and the CD28 coreceptor. We show here that the serine-threonine kinase Akt can provide a costimulatory signal for RE/AP activation that is indistinguishable from the signal provided by CD28. This includes the ability of Akt, like antibodies to CD28, to synergize with protein kinase C θ (PKC-θ) in the induction of RE/AP. Retrovirus-mediated expression of activated Akt in primary T cells from CD28-deficient mice is capable of selectively restoring production of IL-2 and interferon γ, but not IL-4 or IL-5. Our results provide evidence that CD28 costimulation of different cytokines is mediated by discrete signaling pathways, one of which includes Akt.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lenschow, D. J., Walunas, T. L. & Bluestone, J. A. CD28/B7 system of T cell costimulation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14, 233–258 (1996).
Noel, P. J., Boise, L. H. & Thompson, C. B. Regulation of T cell activation by CD28 and CTLA4. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 406, 209–217 (1996).
Howland, K. C., Ausubel, L. J., London, C. A. & Abbas, A. K. The roles of CD28 and CD40 ligand in T cell activation and tolerance. J. Immunol. 164, 4465–4470 (2000).
King, C. L., Xianli, J., June, C. H., Abe, R. & Lee, K. P. CD28-deficient mice generate an impaired Th2 response to Schistosoma mansoni infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 26, 2448–2455 (1996).
Villegas, E. N., Elloso, M. M., Reichmann, G., Peach, R. & Hunter, C. A. Role of CD28 in the generation of effector and memory responses required for resistance to Toxoplasma gondii. J. Immunol. 163, 3344–3353 (1999).
Dahl, A. M. et al. Expression of Bcl-XL restores cell survival, but not proliferation and effector differentiation, in CD28-deficient T lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 191, 2031–2038 (2000).
Lucas, P. J., Negishi, I., Nakayama, K., Fields, L. E. & Loh, D. Y. Naive CD28-deficient T cells can initiate but not sustain an in vitro antigen-specific immune response. J. Immunol. 154, 5757–5768 (1995).
Shahinian, A. et al. Differential T cell costimulatory requirements in CD28-deficient mice. Science 261, 609–612 (1993).
Wülfing, C. & Davis, M. M. A receptor/cytoskeletal movement triggered by costimulation during T cell activation. Science 282, 2266–2269 (1998).
Ward, S. G. CD28: a signaling perspective. Biochem J. 318, 361–377 (1996).
Viola, A., Schroeder, S., Sakakibara, Y. & Lanzavecchia, A. T lymphocyte costimulation mediated by reorganization of membrane microdomains. Science 283, 680–682 (1999).
Shapiro, V. S., Truitt, K. E., Imboden, J. B. & Weiss, A. CD28 mediates transcriptional upregulation of the interleukin-2 (IL-2) promoter through a composite element containing the CD28RE and NF-IL-2B AP-1 sites. Mol. Cell Biol. 17, 4051–4058 (1997).
Hutchcroft, J. E. & Bierer, B. E. Signaling through CD28/CTLA-4 family receptors. J. Immunol. 156, 4071–4074 (1996).
June, C. H., Bluestone, J. A., Nadler, L. M. & Thompson, C. B. The B7 and CD28 receptor families. Immunol. Today 15, 321–331 (1994).
Crabtree, G. R. & Clipstone, N. A. Signal transduction between the plasma membrane and nuclues of T lymphocytes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 63, 1045–1083 (1994).
Jain, J., Loh, C. & Rao, A. Transcriptional regulation of the IL-2 gene. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 7, 333–342 (1995).
Civil, A., Geerts, M., Aarden, L. A. & Verweij, C. L. Evidence for a role of CD28RE as a response element for distinct mitogenic T cell activation signals. Eur. J. Immunol. 22, 3041–3043 (1992).
Fraser, J. D., Irving, B. A., Crabtree, G. R. & Weiss, A. Regulation of Interleukin-2 gene enhancer activity by the T cell accessory molecule CD28. Science 251, 313–316 (1991).
McGuire, K. L. & Iacobelli, M. Involvement of Rel, Fos, and Jun proteins in binding activity to the IL-2 promoter CD28 element/AP-1 sequence in human T cells. J. Immunol. 159, 1319–1327 (1997).
Verweij, C. L., Geerts, M. & Aarden, L. A. Activation of interleukin-2 gene transcription via the T-cell surface molecule CD28 is mediated through an NF-κB-like response element. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 14179–14182 (1991).
Butscher, W. G., Powers, C., Olive, M., Vinson, C. & Gardner, K. Coordinate transactivation of the interleukin-2 CD28 response element by c-Rel and ATF-1/CREB2. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 552–560 (1998).
Curtiss, V. E., Smilde, R. & McGuire, K. L. Requirements for interleukin 2 promoter transactivation by the Tax protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. Mol. Cell Biol. 16, 3567–3575 (1996).
Fraser, J. D. & Weiss, A. Regulation of T-cell lymphokine gene transcription by the accessory molecule CD28. Mol. Cell Biol. 12, 4357–4363 (1992).
Cerdan, C. et al. Prolonged IL-2 receptor α/CD25 expression after T cell activation via the adhesion molecules CD2 and CD28. J. Immunol. 149, 2255–2261 (1992).
Thompson, C. B. et al. CD28 activation pathway regulates the production of multiple T-cell- derived lymphokines/cytokines. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 86, 1333–1337 (1989).
Wechsler, A. S., Gordon, M. C., Dendorfer, U. & LeClair, K. P. Induction of IL-8 expression in T cells uses the CD28 costimulatory pathway. J. Immunol. 153, 2515–2523 (1994).
Ghosh, P., Tan, T.-H., Rice, N. R., Sica, A. & Young, H. A. The interleukin 2 CD28-responsive complex contains at least three members of the NF-κB family: c-Rel, p50, and p65. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 1696–1700 (1993).
Maggirwar, S. B., Harhaj, E. W. & Sun, S.-C. Regulation of the interleukin-2 CD28-responsive element by NF-ATp and various NF-κB/Rel transcription factors. Mol. Cell Biol. 17, 2605–2614 (1997).
Bryan, R. G. et al. Effect of CD28 signal transduction on c-Rel in human peripheral blood T cells. Mol. Cell Biol. 14, 7933–7942 (1994).
Lai, J.-H. & Tan, T.-H. CD28 signaling causes a sustained down-regulation of IκBα which can be prevented by the immunosuppressant rapamycin. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 30077–30080 (1994).
Kontgen, F. et al. Mice lacking the c-rel proto-oncogene exhibit defects in lymphocyte proliferation, humoral immunity, and interleukin-2 expression. Genes Dev. 9, 1965–1977 (1995).
Parry, R. V. et al. Ligation of the T cell co-stimulatory receptor CD28 activates the serine-threonine protein kinase protein kinase B. Eur J. Immunol. 27, 2495–2501 (1997).
Fruman, D. A. et al. Impaired B cell development and proliferation in absence of phosphoinositide 3-kinase p85α. Science 283, 393–397 (1999).
Ueda, Y. et al. Both CD28 ligands CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2) activate phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and wortmannin reveals heterogeneity in the regulation of T cell IL-2 secretion. Int. Immunol. 7, 957–966 (1995).
Kane, L. P., Shapiro, V. S. S., Stokoe, D. & Weiss, A. Induction of NF-κB by the Akt/PKB kinase. Curr. Biol. 9, 601–604 (1999).
Jones, R. G. et al. Protein Kinase B Regulates T Lymphocyte Survival, Nuclear Factor κB Activation, and Bcl-X(L) Levels In vivo. J. Exp. Med. 191, 1721–1734 (2000).
Eder, A. M., Dominguez, L., Franke, T. F. & Ashwell, J. D. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulation of T cell receptor-mediated interleukin-2 gene expression in normal T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 28025–28031 (1998).
Vanhaesebroeck, B. & Alessi, D. R. The PI3K-PDK1 connection: more than just a road to PKB. Biochem. J. 346, 561–576 (2000).
Manger, B., Weiss, A., Imboden, J., Laing, T. & Stobo, J. D. The role of protein kinase C in transmembrane signaling by the T cell antigen receptor complex. Effects of stimulation with soluble or immobilized CD3 antibodies. J. Immunol. 139, 2755–2760 (1987).
Weiss, A., Manger, B. & Imboden, J. Synergy between the T3/antigen receptor complex and Tp44 in the activation of human T cells. J. Immunol. 137, 819–825 (1986).
Shapiro, V. S., Mollenauer, M. N. & Weiss, A. Nuclear factor of activated T cells and AP-1 are insufficient for IL-2 promoter activation: requirement for CD28 up-regulation of RE/AP. J. Immunol. 161, 6455–6458 (1998).
Fraser, J. D., Newton, M. E. & Weiss, A. CD28 and T cell antigen receptor signal transduction coordinately regulate interleukin 2 gene expression in response to superantigen stimulation. J. Exp. Med. 175, 1131–1134 (1992).
Alessi, D. R. et al. Mechanism of activation of protein kinase B by insulin and IGF-1. EMBO J. 15, 6541–6551 (1996).
Lin, X., O'Mahony, A., Mu, Y., Geleziunas, R. & Greene, W. C. Protein kinase C-θ participates in NF-κB activation induced by CD3-CD28 costimulation through selective activation of IκB kinase β. Mol. Cell Biol. 20, 2933–2940 (2000).
Coudronniere, N., Villalba, M., Englund, N. & Altman, A. NF-κ B activation induced by T cell receptor/CD28 costimulation is mediated by protein kinase C-θ. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 3394–3399 (2000).
Monks, C. R., Kupfer, H., Tamir, I., Barlow, A. & Kupfer, A. Selective modulation of protein kinase C-θ during T-cell activation. Nature 385, 83–86 (1997).
Wilkinson, S. E., Parker, P. J. & Nixon, J. S. Isoenzyme specificity of bisindolylmaleimides, selective inhibitors of protein kinase C. Biochem. J. 294, 335–337 (1993).
Van Parijs, L. et al. Uncoupling IL-2 signals that regulate T cell proliferation, survival, and Fas-mediated activation-induced cell death. Immunity 11, 281–288 (1999).
Stokoe, D. et al. Dual role of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate in the activation of protein kinase B. Science 277, 567–570 (1997).
Khattri, R., Auger, J. A., Griffin, M. D., Sharpe, A. H. & Bluestone, J. A. Lymphoproliferative disorder in CTLA-4 knockout mice is characterized by CD28-regulated activation of Th2 responses. J. Immunol. 162, 5784–5791 (1999).
Kubo, M. et al. CD28 costimulation accelerates IL-4 receptor sensitivity and IL-4- mediated Th2 differentiation. J. Immunol. 163, 2432–2442 (1999).
Rulifson, I. C., Sperling, A. I., Fields, P. E., Fitch, F. W. & Bluestone, J. A. CD28 costimulation promotes the production of Th2 cytokines. J. Immunol. 158, 658–665 (1997).
Ronchese, F., Hausmann, B., Hubele, S. & Lane, P. Mice transgenic for a soluble form of murine CTLA-4 show enhanced expansion of antigen-specific CD4+ T cells and defective antibody production in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 179, 809–817 (1994).
Lenschow, D. J. et al. CD28/B7 regulation of Th1 and Th2 subsets in the development of autoimmune diabetes. Immunity 5, 285–293 (1996).
Peterson, R. T. & Schreiber, S. L. Kinase phosphorylation: Keeping it all in the family. Curr. Biol. 9, R521–524 (1999).
Li-Weber, M., Giasi, M. & Krammer, P. H. Involvement of Jun and Rel proteins in up-regulation of interleukin-4 gene activity by the T cell accessory molecule CD28. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 32460–32466 (1998).
Stack, R. M., Thompson, C. B. & Fitch, F. W. IL-4 enhances long-term survival of CD28-deficient T cells. J. Immunol. 160, 2255–2262 (1998).
Chan, T. O., Rittenhouse, S. E. & Tsichlis, P. N. Akt/PKB and other D3 phosphoinositide-regulated kinases: kinase activation by phosphoinositide-dependent phosphorylation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68, 965–1014 (1999).
Parekh, D. B., Ziegler, W. & Parker, P. J. Multiple pathways control protein kinase C phosphorylation. EMBO J. 19, 496–503 (2000).
Ott, M. et al. Immune hyperactivation of HIV-1-infected T cells mediated by Tat and the CD28 pathway. Science 275, 1481–1485 (1997).
Borgatti, P. et al. Extracellular HIV-1 Tat protein activates phosphatidylinositol 3- and Akt/PKB kinases in CD4+ T lymphoblastoid Jurkat cells. Eur J. Immunol. 27, 2805–2811 (1997).
Reif, K., Lucas, S. & Cantrell, D. A negative role for phosphoinositide 3-kinase in T-cell antigen receptor function. Curr. Biol. 7, 285–293 (1997).
Crooks, M. E. et al. CD28-mediated costimulation in the absence of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase association and activation. Mol. Cell Biol. 15, 6820–6828 (1995).
Ward, S. G., Wilson, A., Turner, L., Westwick, J. & Sansom, D. M. Inhibition of CD28-mediated T cell costimulation by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor wortmannin. Eur. J. Immunol. 25, 526–532 (1995).
Ward, S. G., June, C. H. & Olive, D. PI 3-kinase: a pivotal pathway in T-cell activation? Immunol. Today 17, 187–197 (1996).
Shan, X. et al. Deficiency of PTEN in jurkat T cells causes constitutive localization of itk to the plasma membrane and hyperresponsiveness to CD3 stimulation. Mol. Cell Biol. 20, 6945–6957 (2000).
Hehner, S. P. et al. Mixed-lineage kinase 3 delivers CD3/CD28-derived signals into the IκB kinase complex. Mol. Cell Biol. 20, 2556–2568 (2000).
Lin, X., Cunningham, E. T., Mu, Y., Geleziunas, R. & Greene, W. C. The proto-oncogene Cot kinase participates in CD3/CD28 induction of NF-κB acting through the NF-κB-inducing kinase and IκB kinases. Immunity 10, 271–280 (1999).
Tsatsanis, C., Patriotis, C. & Tsichlis, P. N. Tpl-2 induces IL-2 expression in T-cell lines by triggering multiple signaling pathways that activate NFAT and NF-κB. Oncogene 17, 2609–2618 (1998).
Tuosto, L. et al. Mitogen-activated kinase kinase kinase 1 regulates T cell receptor-and CD28-mediated signaling events which lead to NF-κB activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 30, 2445–2454 (2000).
Tsatsanis, C., Patriotis, C., Bear, S. E. & Tsichlis, P. N. The Tpl-2 protooncoprotein activates the nuclear factor of activated T cells and induces interleukin 2 expression in T cell lines. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 3827–3832 (1998).
Ballester, A., Tobena, R., Lisbona, C., Calvo, V. & Alemany, S. Cot kinase regulation of IL-2 production in Jurkat T cells. J. Immunol. 159, 1613–1618 (1997).
Durand, D. B., Bush, M. R., Morgan, J. G., Weiss, A. & Crabtree, G. R. A 275 basepair fragment at the 5′ end of the interleukin 2 gene enhances expression from a heterologous promoter in response to signals from the T cell antigen receptor. J. Exp. Med. 165, 395–407 (1987).
Refaeli, Y., Van Parijs, L., London, C. A., Tschopp, J. & Abbas, A. K. Biochemical mechanisms of IL-2-regulated Fas-mediated T cell apoptosis. Immunity 8, 615–623 (1998).
Naviaux, R. K., Costanzi, E., Haas, M. & Verma, I. M. The pCL vector system: rapid production of helper-free, high-titer, recombinant retroviruses. J. Virol. 70, 5701–5705 (1996).
Acknowledgements
We thank R. Locksley and C. McArthur for use of the MoFlo sorter and expert flow cytometry, respectively. Supported by the Cancer Research Institute (L. P. K.), the Glaxo Wellcome Institute for Digestive Health (P. G. A.) and National Institutes of Health grants AI25022 and AI35297 (A. K. A.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kane, L., Andres, P., Howland, K. et al. Akt provides the CD28 costimulatory signal for up-regulation of IL-2 and IFN-γ but not TH2 cytokines. Nat Immunol 2, 37–44 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/83144
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/83144
This article is cited by
-
Reverse immune suppressive microenvironment in tumor draining lymph nodes to enhance anti-PD1 immunotherapy via nanovaccine complexed microneedle
Nano Research (2020)
-
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor ACY241 enhances anti-tumor activities of antigen-specific central memory cytotoxic T lymphocytes against multiple myeloma and solid tumors
Leukemia (2018)
-
SNX27 links DGKζ to the control of transcriptional and metabolic programs in T lymphocytes
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
PTEN at the interface of immune tolerance and tumor suppression
Frontiers in Biology (2017)
-
Dose-Dependent Suppression of Cytokine production from T cells by a Novel Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Delta Inhibitor
Scientific Reports (2016)