Abstract
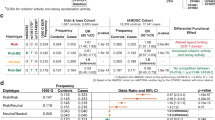
The association of variants in complement factors H and B with age-related macular degeneration has led to more intense genetic and functional analysis of the complement pathway. We identify a nonsynonymous coding change in complement factor 3 that is strongly associated with risk of age-related macular degeneration in a large case-control sample.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klein, R.J. et al. Science 308, 385–389 (2005).
Haines, J.L. et al. Science 308, 419–421 (2005).
Edwards, A.O. et al. Science 308, 421–424 (2005).
Hageman, G.S. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 7227–7232 (2005).
Gold, B. et al. Nat. Genet. 38, 458–462 (2006).
Maller, J. et al. Nat. Genet. 38, 1055–1059 (2006).
Li, M. et al. Nat. Genet. 38, 1049–1054 (2006).
Nozaki, M. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 2328–2333 (2006).
Zhou, J., Jang, Y.P., Kim, S.R. & Sparrow, J.R. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 16182–16187 (2006).
Seddon, J.M., George, S., Rosner, B. & Klein, M.L. Hum. Hered. 61, 157–165 (2006).
Botto, M., Fong, K.Y., So, A.K., Koch, C. & Walport, M.J. J. Exp. Med. 172, 1011–1017 (1990).
Wyatt, R.J., Julian, B.A., Waldo, F.E. & McLean, R.H. in Recent Developments in Mucosal Immunology (eds. Mestecky, J., McChee, J.R., Bienenstock, J. & Orga, P.L.) 1569–1575 (Plenum Press, New Sissons, 1987).
Brown, K.M. et al. N. Engl. J. Med. 354, 2014–2023 (2006).
Abrera-Abeleda, M.A. et al. J. Med. Genet. 43, 582–589 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We thank the participants, their families and numerous ophthalmologists throughout the country who participated in this study. We particularly thank D. Mirel and the National Center for Research Resources Broad Institute Center for Genotyping and Analysis for expert design and execution of the SNP genotyping reported herein. We also thank AREDS participants and investigators and the EMMES Corporation for their work on the AREDS Genetic Repository. Funding support for AREDS was provided by the National Eye Institute (N01-EY-0-2127). This research was supported by the NIH (grant EY11309); the Foundation Fighting Blindness; the Massachusetts Lions Research Fund; the Macular Degeneration Research Fund of the Ophthalmic Epidemiology and Genetics Service, the New England Eye Center, Tufts-New England Medical Center; and the Broad Institute Center for Genotyping and Analysis (through grant U54 RR020278 from the National Center for Research Resources).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.M.S. and R.C.R. collected clinical information. J.M.S. obtained the funding and samples and is an AREDS co-investigator. J.B.M. and J.A.F. analyzed the data with contributions from B.M.N., under the supervision of M.J.D. J.B.M., M.J.D. and J.M.S. wrote the paper with contributions from J.A.F. M.J.D. and J.M.S. jointly supervised this study.
Corresponding authors
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Tables 1–2, Supplementary Methods (PDF 21 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maller, J., Fagerness, J., Reynolds, R. et al. Variation in complement factor 3 is associated with risk of age-related macular degeneration. Nat Genet 39, 1200–1201 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng2131
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng2131
This article is cited by
-
The effect of systemic levels of TNF-alpha and complement pathway activity on outcomes of VEGF inhibition in neovascular AMD
Eye (2022)
-
Complement Mediators in Development to Treat Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Drugs & Aging (2022)
-
Associations of the intestinal microbiome with the complement system in neovascular age-related macular degeneration
npj Genomic Medicine (2020)
-
Hypothetical pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration and pachychoroid diseases derived from their genetic characteristics
Japanese Journal of Ophthalmology (2020)
-
Evaluation of the association of C5 with neovascular age-related macular degeneration and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy
Eye and Vision (2019)