Abstract
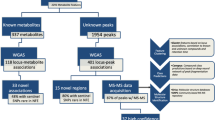
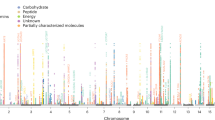
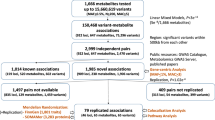
Characterizing the relationships between genomic and phenotypic variation is essential to understanding disease etiology. Information-dense data sets derived from pathophysiological1, proteomic2,3 and transcriptomic4 profiling have been applied to map quantitative trait loci (QTLs). Metabolic traits, already used in QTL studies in plants5, are essential phenotypes in mammalian genetics to define disease biomarkers. Using a complex mammalian system, here we show chromosomal mapping of untargeted plasma metabolic fingerprints derived from NMR spectroscopic analysis6 in a cross between diabetic and control rats. We propose candidate metabolites for the most significant QTLs. Metabolite profiling in congenic strains provided evidence of QTL replication. Linkage to a gut microbial metabolite (benzoate) can be explained by deletion of a uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase. Mapping metabotypic QTLs provides a practical approach to understanding genome-phenotype relationships in mammals and may uncover deeper biological complexity, as extended genome7 (microbiome) perturbations that affect disease processes through transgenomic effects8 may influence QTL detection.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Valdar, W. et al. Genome-wide genetic association of complex traits in heterogeneous stock mice. Nat. Genet. 38, 879–887 (2006).
Damerval, C., Maurice, A., Josse, J.M. & de Vienne, D. Quantitative trait loci underlying gene product variation: a novel perspective for analyzing regulation of genome expression. Genetics 137, 289–301 (1994).
Klose, J. et al. Genetic analysis of the mouse brain proteome. Nat. Genet. 30, 385–393 (2002).
Rockman, M.V. & Kruglyak, L. Genetics of global gene expression. Nat. Rev. Genet. 7, 862–872 (2006).
Keurentjes, J.J. et al. The genetics of plant metabolism. Nat. Genet. 38, 842–849 (2006).
Nicholson, J.K., Connelly, J., Lindon, J.C. & Holmes, E. Metabonomics: a platform for studying drug toxicity and gene function. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 1, 153–161 (2002).
Lederberg, J. Infectious history. Science 288, 287–293 (2000).
Turnbaugh, P.J. et al. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 444, 1027–1031 (2006).
Flint, J., Valdar, W., Shifman, S. & Mott, R. Strategies for mapping and cloning quantitative trait genes in rodents. Nat. Rev. Genet. 6, 271–286 (2005).
Nicholson, J.K., Lindon, J.C. & Holmes, E. 'Metabonomics': understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica 29, 1181–1189 (1999).
Nicholson, J.K., Holmes, E., Lindon, J.C. & Wilson, I.D. The challenges of modeling mammalian biocomplexity. Nat. Biotechnol. 22, 1268–1274 (2004).
Clayton, T.A. et al. Pharmaco-metabonomic phenotyping and personalized drug treatment. Nature 440, 1073–1077 (2006).
Schauer, N. et al. Comprehensive metabolic profiling and phenotyping of interspecific introgression lines for tomato improvement. Nat. Biotechnol. 24, 447–454 (2006).
Morreel, K. et al. Genetical metabolomics of flavonoid biosynthesis in Populus: a case study. Plant J. 47, 224–237 (2006).
Jansen, R.C. & Nap, J.P. Genetical genomics: the added value from segregation. Trends Genet. 17, 388–391 (2001).
Bihoreau, M.T. et al. A linkage map of the rat genome derived from three F2 crosses. Genome Res. 7, 434–440 (1997).
Gauguier, D. et al. Chromosomal mapping of genetic loci associated with non-insulin dependent diabetes in the GK rat. Nat. Genet. 12, 38–43 (1996).
Broman, K.W., Wu, H., Sen, S. & Churchill, G.A. R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics 19, 889–890 (2003).
Hubner, N. et al. Integrated transcriptional profiling and linkage analysis for identification of genes underlying disease. Nat. Genet. 37, 243–253 (2005).
Lindon, J.C., Nicholson, J.K., Holmes, E. & Everett, J.R. Metabonomics: Metabolic processes studied by NMR spectroscopy of biofluids. Concepts Magn. Reson. 12, 289–320 (2000).
Argoud, K. et al. Genetic control of plasma lipid levels in a cross derived from normoglycaemic Brown Norway and spontaneously diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Diabetologia 49, 2679–2688 (2006).
Gauguier, D. The rat as a model physiological system. in Encyclopedia of Genetics Vol. 3 (eds. Jorde, L.B., Little, P., Dunn, M. & Subramaniam, S.) 1154–1171 (Wiley, London, U.K., 2006).
Nicholson, J.K. & Wilson, I.D. Opinion: understanding 'global' systems biology: metabonomics and the continuum of metabolism. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2, 668–676 (2003).
Bridges, J.W., French, M.R., Smith, R.L. & Williams, R.T. The fate of benzoic acid in various species. Biochem. J. 118, 47–51 (1970).
Tukey, R.H. & Strassburg, C.P. Human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases: metabolism, expression, and disease. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 40, 581–616 (2000).
Watanabe, T.K. et al. Mutated G-protein-coupled receptor GPR10 is responsible for the hyperphagia/dyslipidaemia/obesity locus of Dmo1 in the OLETF rat. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 32, 355–366 (2005).
Collins, S.C. et al. Mapping diabetes QTL in an intercross derived from a congenic strain of the Brown Norway and Goto-Kakizaki rats. Mamm. Genome 17, 538–547 (2006).
Dumas, M.E. et al. Metabolic profiling reveals a contribution of gut microbiota to fatty liver phenotype in insulin-resistant mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 12511–12516 (2006).
Wilder, S.P. et al. Integration of the rat recombination and EST maps in the rat genomic sequence and comparative mapping analysis with the mouse genome. Genome Res. 14, 758–765 (2004).
Dudbridge, F. & Koeleman, B.P. Efficient computation of significance levels for multiple associations in large studies of correlated data, including genomewide association studies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 75, 424–435 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We thank O. Cloarec for discussions and for the use of OPLS routine. This work is supported by the Wellcome Functional Genomics Initiatives BAIR (Biological Atlas of Insulin Resistance; 066786) and CFG (Cardiovascular Functional Genomics; 066780) and by the grant FGENTCARD (Functional genomic diagnostic tools for coronary artery disease; LSHG-CT-2006-037683) from the European Commission. S.P.W. is a recipient of a Wellcome Prize studentship. D.G. holds a Wellcome senior fellowship in basic biomedical science (057733).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study was designed by M.-E.D., J.S., J.K.N. and D.G. Genotyping and congenic studies were performed by M.-T.B., J.F.F., K.A. and R.H.W. NMR metabonomic data processing, analysis and interpretation was performed by M.-E.D., R.H.B., H.C.K., D.B., U.G.S. and J.K.N. Liver gene transcription profiling was performed by M.-T.B., K.A. and C.B. Statistical analysis of microarray data and QTL mapping were performed by S.P.W. Bioinformatic studies, Ugt2b sequence analysis and DNA blots were performed by M.-T.B. and L.D. Metabotypic QTL data interpretation was performed by M.-E.D, S.P.W., M.-T.B., R.H.B., J.S., J.N.K. and D.G. The manuscript was written by M.-E.D., S.P.W., J.S., J.K.N. and D.G.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Plasma metabolic profiling by 1H-NMR in BN, GK and WKY rat strains. (PDF 65 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Data analysis from ANOVA and PLS. (PDF 42 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
Impact of sex and cross on PCA score plots of plasma 1H-NMR data in F2 rats. (PDF 23 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 4
Detailed linkage analyses using R/qtl and QTL Reaper. (PDF 40 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 5
A lod score map of PCA data and genetic interactions in the cross. (PDF 158 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 6
NMR characterization of spiked Ugt2b−/− rat plasma. (PDF 94 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 7
DNA blot analysis of Ugt2b in inbred rat strains. (PDF 34 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
Candidate metabolites for metabotypic QTLs mapped in the GK×BN cross. (PDF 112 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dumas, ME., Wilder, S., Bihoreau, MT. et al. Direct quantitative trait locus mapping of mammalian metabolic phenotypes in diabetic and normoglycemic rat models. Nat Genet 39, 666–672 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng2026
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng2026
This article is cited by
-
The role of the gut microbiota in health and cardiovascular diseases
Molecular Biomedicine (2022)
-
Identification of optimal prediction models using multi-omic data for selecting hybrid rice
Heredity (2019)
-
Systems Genetics of Hepatic Metabolome Reveals Octopamine as a Target for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Treatment
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Metabolic Profiling and Phenotyping of Central Nervous System Diseases: Metabolites Bring Insights into Brain Dysfunctions
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology (2015)
-
Associations between thyroid hormones and serum metabolite profiles in an euthyroid population
Metabolomics (2014)