Abstract
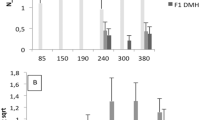
Many complex traits, including susceptibility to lung cancer, are controlled by multiple genes — quantitative trait loci (QTLs). We facilitated the mapping of QTLs by making use of recombinant congenic strains (RCS)1, a system of mouse inbred strains in which the genetic complexity is reduced, and by applying MQM-mapping2–4 (multiple-QTL models or marker-QTL-marker), a multilocus method with an increased power of detecting of individual QTLs and interacting QTLs (epistasis). The mouse strain 020 develops significantly larger N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea induced lung tumours than mice of the RC strain OcB-9 (ref. 5); the latter share approximately 87.5% of their genes with strain O20 and 12.5% with strain B10.O20 (refs 6,7). QTL analysis of 222 (OcB-9 × O20) F2 mice revealed four new loci that influence susceptibility to lung cancer (Sluc genes). They are involved in two significant, partly counteracting interactions which mask their individual main effects: Sluc1 (on chromosome 19) interacts with Sluc2 (chromosome 2), and Sluc3 (chromosome 6) interacts with Sluc4 (chromosome 11). Together with the data of van Wezel et al, in the accompanying report8, our results indicate that interactions between tumour susceptibility genes are a common phenomenon which complicates their mapping.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Demant, P. & Hart, A.A.M. Recombinant congenic strains — a novel tool for analyzing genetic traits determined by more than one gene. Immunogenet., 24, 416–422 (1986).
Jansen, B.C. & Stam, P. High resolution of quantitative traits into multiple loci via interval mapping. Genetics 136, 1447–1455 (1994).
Jansen, R.C. Controlling the type I and type II errors in mapping quantitative trait loci. Genetics 138, 871–881 (1994).
Jansen, R.C. Complex plant traits: time for polygenic analysis. Trends Plant Sci. 1, 89–94 (1996).
Fijneman, R.J.A., Ophoff, R.A., Hart, A.A.M. & Demant, P. Kras-2 alleles, mutations, and lung tumour susceptibility in the mouse — an evaluation. Oncogene 9, 1417–1421 (1994).
Groot, P.C. et al. The recombinant congenic strains for analysis of multigenic traits: genetic composition. FASEB J. 6, 2826–2835 (1992).
Stassen, A.P.M., Groot, P.C., Eppig, J.T. & Demant, P. Genetic composition of the recombinant congenic strains. Mamm. Genome 7, 55–58 (1996).
van Wezel, T. et al. Gene interaction and single gene effects in colon tumour susceptibility in mice. Nature Genet. 14, 468–470 (1996).
Oomen, L.C.J.M., Demant, P, Hart, A.A.M. & Emmelot, P. Multiple genes in the H-2 complex affect differently the number and growth rate of transplacentally induced lung tumours in mice. Int. J. Cancer 31, 447–454 (1983).
Oomen, L.C.J.M., van der Vaik, M.A. & Demant, P. MHC and non-MHC genes in lung tumour susceptibility in the mouse: implications for the study of the different lung tumour types and their cell of origin. Exp. Lung Res. 17, 283–304 (1991).
Fijneman, R.J.A., Oomen, L.C.J.M., Snoek, M. & Demant, P. A susceptibility gene for alveolar lung tumours in the mouse maps between Hsp70.3 and G7 within the H2 complex. Immunogenet. 41, 106–109 (1995).
Ryan, J., Barker, P.E., Nesbitt, M.N. & Ruddle, F.H. KRAS2 as a genetic marker for lung tumour susceptibility in inbred mice. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 79, 1351–1357 (1987).
Gariboldi, M. et al. A major susceptibility locus to murine lung carcinogenesis maps on chromosome 6. Nature Genet. 3, 132–136 (1993).
Festing, M.F.W., Yang, A. & Malkinson, A.M. At least four genes and sex are associated with susceptibility to urethane-induced pulmonary adenomas in mice. Genet Res. 64, 99–106 (1994).
Manenti, G. et al. Genetic mapping of a pulmonary adenoma resistance locus (Par 1) in mouse. Nature Genet. 12, 455–457 (1996).
Devereux, T.R. et al. Assignment of a locus for mouse lung tumour susceptibility toproximal chromosome 19. Mamm. Genome 5, 749–755 (1994).
Paterson, A. et al. Resolution of quantitative traits into mendelian factors using a complete RFLP linkage map. Nature 335, 721–726 (1988).
Laird, P.W. et al. Simplified mammalian DNA isolation procedure. Nucl. Acid Res. 19, 4293 (1991).
Dietrich, W. et al. A genetic map of the mouse suitable for typing intraspecific crosses. Genetics 131, 423–447 (1992).
Dietrich, W.F. et al. A genetic map of the mouse with 4,006 simple sequence length polymorphisms. Nature Genet. 7, 220–245 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fijneman, R., de Vries, S., Jansen, R. et al. Complex interactions of new quantitative trait loci, Sluc1, Sluc2, Sluc3, and Sluc4, that influence the susceptibility to lung cancer in the mouse. Nat Genet 14, 465–467 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1296-465
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1296-465
This article is cited by
-
Quantitative trait loci for resistance to Flavobacterium psychrophilum in rainbow trout: effect of the mode of infection and evidence of epistatic interactions
Genetics Selection Evolution (2018)
-
Mice with different susceptibility to tick-borne encephalitis virus infection show selective neutralizing antibody response and inflammatory reaction in the central nervous system
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2013)
-
Increased drought tolerance and wider adaptability of qDTY 12.1 conferred by its interaction with qDTY 2.3 and qDTY 3.2
Molecular Breeding (2012)
-
Genetic influences on growth and body composition in mice: multilocus interactions
International Journal of Obesity (2009)
-
Genetic mapping of a new heart rate QTL on chromosome 8 of spontaneously hypertensive rats
BMC Medical Genetics (2007)