Abstract
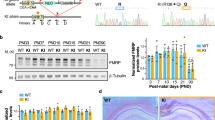
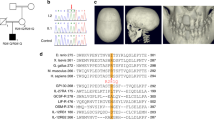
We demonstrate here the importance of interleukin signalling pathways in cognitive function and the normal physiology of the CNS. Thorough investigation of an MRX critical region in Xp22.1–21.3 enabled us to identify a new gene expressed in brain that is responsible for a non-specific form of X-linked mental retardation. This gene encodes a 696 amino acid protein that has homology to IL-1 receptor accessory proteins. Non-overlapping deletions and a nonsense mutation in this gene were identified in patients with cognitive impairment only. Its high level of expression in post-natal brain structures involved in the hippocampal memory system suggests a specialized role for this new gene in the physiological processes underlying memory and learning abilities.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moser, H.W., Ramey, C.T. & Leonard, C.O. Principles and Practice of Medical Genetics (eds Emery, A.E.H. & Rimoin, D.L.) (Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, 1983).
Hagberg, B. & Kyllerman, M. Epidemiology of mental retardation. A Swedish survey. Brain Dev. 5, 441– 449 (1983).
Lubs, H.A. et al. XLMR genes: update 1998. Am. J. Med. Genet. 64, 147–157 (1998).
Gedeon, A.K., Donnelly, A.J., Mulley, J.C., Kerr, B. & Turner, G. How many X-linked genes for non-specific mental retardation (MRX) are there? Am. J. Med. Genet. 64, 158–162 (1996).
des Portes, V. et al. X-linked nonspecific mental retardation (MRX) linkage studies in 25 unrelated families: the European XLMR consortium. Am. J. Med. Genet. 85, 263–265 (1999).
Gecz, J., Gedeon, A., Sutherland, G. & Mulley, J. Identification of the gene FMR2, associated with FRAX-E mental retardation. Nature Genet. 13, 105– 108 (1996).
Billuart, P. et al. Oligophrenin 1, a novel gene encoding a rho-GAP protein involved in X-linked non-specific mental retardation. Nature 392, 923–926 (1998).
Allen, K.M. et al. PAK3 mutation in nonsyndromic X-linked mental retardation. Nature Genet. 20, 25–30 (1998).
Hall, A. RhoGTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science 279, 509–514 (1998).
D'Adamo, P. et al. Mutations in GDI1 are responsible for X-linked mental retardation. Nature Genet. 19, 134– 139 (1998).
Bienvenu. T. et al. Non-specific X-linked semidominant mental retardation by mutations in a Rab GDP-dissociation inhibitor. Hum. Mol. Genet. 7, 1311–1315 ( 1998).
Südhof, T.C. Function of Rab3 GDP-GTP exchange. Neuron 18, 519–522 (1997).
Novick, P. & Zerial, M. The diversity of Rab proteins in vesicle transport. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 9, 496–504 (1997).
Castillo, P.E. et al. Rab3 is essential for mossy fibre long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 388, 590– 593 (1997).
Fries, M.H. et al. Mental retardation locus in Xp21 chromosome microdeletion. Am. J. Med. Genet. 46, 363– 368 (1993).
Raeymaekers, P. et al. A form of non-specific mental retardation is probably caused by a microdeletion in a Belgian family. Am J. Med. Genet. 64, 16 (1996).
Billuart, P. et al. Identification by STS PCR screening of a microdeletion in Xp21.3–22.1 associated with non-specific mental retardation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 5, 977–979 (1996).
des Portes, V. et al. Inherited microdeletion in Xp21.3–22.1 involved in non-specific mental retardation. Clin. Genet. 53 , 136–141 (1998).
Solovyev, V.V., Salsmov, A.A. & Lawrence, C.B. Predicting internal exons by oligonucleotide composition and discriminant analysis of spliceable open reading frame. Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 5156–5163 (1994).
Huang, I., Gao, X., Li, S. & Cao, Z. Recruitment of IRAK to the interleukin 1 receptor complex requires interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 12829 –12832 (1997).
Greenfeder, S.A. et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a second subunit of the interleukin 1 receptor complex. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 13757–13765 (1995).
Kozak, M. An analysis of 5′-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 15, 8125– 8148 (1987).
Sims, J.E. et al. cDNA expression cloning of the IL-1 receptor, a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Science 241, 585–589 (1988).
Kopp, E.B. & Medzhitov, R. The toll-receptor family and control of innate immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 11, 13–18 (1999).
Kocsis, B. & Vertes, R.P. Characterization of neurons of the supramammillary nucleus and mammillary body that discharge rhythmically with the hippocampal θ rhythm in the rat. J. Neurosci. 14, 7040–7052 (1994).
Milner, B., Squire, L.R. & Kandel, E.R. Cognitive neuroscience and the study of memory. Neuron 20, 445–468 ( 1998).
Tsien, J.Z., Huerta, P.T. & Tonegawa, S. The essential role of hippocampal CA1 NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic plasticity in spatial memory. Cell 87, 1327–1338 (1996).
Bliss, T.V.P. & Collingridge, L.G. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361 , 31–39 (1993).
Ninomiya-Tsuji, J. et al. The kinase TAK1 can activate the NIK-IκB as well as the MAP kinase cascade in the IL-1 signalling pathway. Nature 398, 252–256 ( 1999).
Dinarello, C.A. Biologic basis for interleukin-1 in disease. Blood 87, 2095–2147 (1996).
Cao, Z., Henzel, W.J. & Cao, X. IRAK: a kinase associated with the interleukin-1 receptor. Science 271, 1128–1131 (1996).
Crumeyrolle-Arias, M. et al. Radioimagers as an alternative to film autoradiography for in situ quantitative analysis of 125I-ligand receptor binding and pharmacological studies. Histochem. J. 28, 801–809 (1996).
Bianchi, M., Sacerdote, P. & Panerai, A.E. Cytokines and cognitive functions in mice. Biol. Signals Recept. 7, 45–54 (1998).
Katsuki, H. et al. Interleukin-1 inhibits long-term potentiation in the CA3 region of mouse hippocampal slices. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 181, 323–326 (1990).
Rada, P. et al. Interleukin-1β decreases acethylcholine measured by microdialysis in the hippocampus of freely moving rats. Brain Res. 550, 287–290 (1991).
Cassel, J.C. & Jeltsch, H. Serotonergic modulation of cholinergic function in the central nervous system: cognitive implications. Neuroscience 69, 1–41 ( 1995).
Da Silva, J., Pierrat, B., Mary, J.L. & Lesslauer, W. Blockade of p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway inhibits inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression in mouse astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 28373–28380 (1997).
Ferrero, G.B. et al. An integrated physical map and genetic map of a 35 Mb region on chromosome Xp22.3–Xp21.3. Hum. Mol. Genet. 4, 1821–1827 (1995).
Lehrach, H. et al. Hybridization fingerprinting in genome mapping and sequencing. Genome Analysis Vol 1: Genetic and Physical Mapping (eds Davies, K.E. & Tilghman, S.M.) 39–81 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 1990).
Muscatelli, F. et al. Mutations in the DAX-1 gene give rise to both X-linked adrenal hypoplasia congenita and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Nature 372, 672–676 ( 1994).
Acknowledgements
We thank patients and family members for participation; F. Francis, V. des Portes and M. Catala for helpful discussions; F. Fauchereau, G. Friocourt and P. Chaffey for their contributions; and the Sanger Centre and Baylor College of Medicine for making available PAC and BAC sequencing data. This work was supported in part by grants from INSERM, including an APEX program number 4X007E, the Association Française contre les Myopathies and The Fondation Jérôme Lejeune.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carrié, A., Jun, L., Bienvenu, T. et al. A new member of the IL-1 receptor family highly expressed in hippocampus and involved in X-linked mental retardation. Nat Genet 23, 25–31 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/12623
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/12623
This article is cited by
-
Innate immunity at the crossroads of healthy brain maturation and neurodevelopmental disorders
Nature Reviews Immunology (2021)
-
The IL-1 family of cytokines and receptors in rheumatic diseases
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2019)
-
Loss of SETDB1 decompacts the inactive X chromosome in part through reactivation of an enhancer in the IL1RAPL1 gene
Epigenetics & Chromatin (2018)
-
Mechanisms of splicing-dependent trans-synaptic adhesion by PTPδ–IL1RAPL1/IL-1RAcP for synaptic differentiation
Nature Communications (2015)
-
The hippocampo-amygdala control of contextual fear expression is affected in a model of intellectual disability
Brain Structure and Function (2015)