Abstract
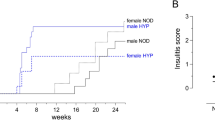
The BB rat is among the best models of insulin–dependent diabetes mellitus — with onset and pathogenesis closely resembling the human disease. One unusual feature is a severe T–cell lymphopenia, which appears to be inherited as a recessive trait controlled by a single gene, Lyp. Based on genetic analysis of several crosses, we show that development of diabetes involves at least three genes: Lyp, which is tightly linked to the neuropeptide Y (Npy) gene on chromosome 4, a gene linked to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) on chromosome 20, and a third unmapped gene for which the Fischer rat strain carries an allele conferring resistance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ekoe, J.-M. in Diabetes Mellitus (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1988).
Ellenberg and Rifkin's Diabetes Mellitus: Theory and Practice 4th ed (eds Rifkin, H., Porte, D. Jr.) (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1990).
Mordes, J.P., Desemone, J. & Rossini, A.A. The BB rat. Diabetes/Metabolism Rev. 3, 725–750 (1987).
Markholst, H., Eastman, S., Wilson, D., Andreasen, B.E. & Lernmark, A. Diabetes segregates as a single locus in crosses between inbred BB rats prone or resistant to diabetes. J. exp. Med. 174, 297–300 (1991).
Thomas, V.A. et al. Altered expression of diabetes in BB/Wor rats by exposure to viral pathogens. Diabetes 40, 255–259 (1991).
Like, A.A., Guberski, D.L. & Butler, L. Influence of environmental viral agents on frequency and tempo of diabetes mellitus in BB/Wor rats. Diabetes 40, 259–262 (1991).
Shyp, S., Tishon, A. & Oldstone, B.A. Inhibition of diabetes in BB rats by virus infection II. Effect of virus infection on the immune response to non-viral and viral antigens. J. Immunol 69, 501–507 (1990).
Jackson, R., Rassi, N., Crump, T., Haynes, B. & Eisenbarth, G.S. The BB diabetic rat. Profound T-cell lymphopenia. Diabetes 30, 887–889 (1981).
Elder, M.E. & Maclaren, N.K. Identification of profound peripheral T lymphocyte immunodeficiencies in the spontaneously diabetic BB rat. J. Immunol. 130, 1723–1731 (1983).
Yale, J.-F., Grose, M. & Marliss, E.B. Time course of the lymphopenia in BB rats. Relation to onset of diabetes. Diabetes 34, 955–959 (1985).
Plamondon, C., Kottis, V., Brideau, C., Metroz-Dayer, M.-D. & Poussier, P. Abnormal thymocyte maturation in spontaneously diabetic BB rats involves the deletion of CD4-8+ cells. J. Immunol. 144, 923–928 (1990).
Jackson, R.A. et al. Two genes required for diabetes in BB rat: evidence from cyclical intercrosses and backcrosses. J. exp. Med. 159, 1629–1636 (1984).
Guttmann, R.D., Colle, E., Michel, F. & Seemayer, T. Spontaneous diabetes mellitus syndrome in the rat. II. T lymphopenia and its association with clinical disease and pancreatic lymphocytic infiltration. J. Immunol. 130, 1732–1735 (1983).
Like, A.A., Guberski, D.L. & Butler, L. Diabetic BioBreeding/Worcester (BB/ Wor) rats need not be lymphopenic. J. Immunol. 136, 3254–3258 (1986).
Herold, K.C., Kastern, W., Markholst, H. & Lernmark, A. Derivation of non-lymphopenic BB rats with an intercross breeding. Autoimmunity 3, 83–93 (1989).
Colle, E. Genetic susceptibility to the development of spontaneous insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in the rat. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 57, 1–9 (1990).
Jacob, H.J. et al. Genetic mapping of a gene causing hypertension in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Cell 67, 213–224 (1991).
Levan, G. et al. The gene map of the norway rat (Rattus norvegicus) and comparative mapping with mouse and man. Genomics 10, 699–718 (1991).
Bahary, N., Zorich, G., Pachter, J.E., Liebel, R.L. & Friedman, J.M. Molecular genetic linkage maps of mouse chromosomes 4 and 6. Genomics 11, 33–47 (1991).
Colle, E., Guttmann, R.D. & Seemayer, T.A. Spontaneous diabetes mellitus syndrome in the rat. I. Association with the major histocompatability complex. J. exp. Med. 154, 1237–1242 (1981).
Colle, E., Guttmann, R.D., Seemayer, T.A. & Michel, F. Spontaneous diabetes mellitus syndrome in the rat. IV. Immunogenetic interactions of MHC and non-MHC components. Metabolism 32, 54–61 (1983).
Gunther, E. et al. Genetic analysis of susceptibility to diabetes mellitus in F2-hybrids between diabetes-prone BB and various MHC-recombinant congenic rat strains. J. Autoimmun. 4, 543–551 (1991).
Hattori, M. et al. The NOD mouse: recessive diabetogenic gene in the major histocompatability complex. Science 231, 733–735 (1986).
Thomson, G. et al. Genetic heterogeneity, modes of inheritance, and risk estimates for a joint study of Caucasians with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am. J. hum. Genet. 43, 799–816 (1988).
Wassmuth, R. & Lernmark, A. The genetics of susceptibility to diabetes. Clin. Immun. Immunopath. 53, 358–399 (1989).
Cornall, R.J. et al. Type 1 diabetes in mice is linked to the interleukin-1 receptor and Lsh/lty/Bcg genes on chromosome 1. Nature 353, 262–265 (1991).
Todd, J.A. et al. Genetic analysis of autoimmune type 1 diabetes mellitus in mice. Nature 351, 542–547 (1991).
Leiter, E.H. The genetics of diabetes susceptibility in mice. FASEB J. 3, 223–2241 (1989).
Sambrooke, J., Fritsch, E.F. & Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A laboratory manual 2nd edn (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1989).
Lander, E.S. et al. MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1, 174–181 (1987).
Fujii, H., Kakinuma, M., Yoshiki, T. & Natori, T. Polymorphism of class II gene of rat major histocompatability complex, RT1: partial sequence comparison of the first domain of the RT1. BB 1 alleles. Immunogenet. 33, 399–403 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jacob, H., Pettersson, A., Wilson, D. et al. Genetic dissection of autoimmune type I diabetes in the BB rat. Nat Genet 2, 56–60 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0992-56
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0992-56
This article is cited by
-
Model organism data evolving in support of translational medicine
Lab Animal (2018)
-
An orthologous non-MHC locus in rats and mice is linked to CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell proportion
Genes & Immunity (2017)
-
A novel Dock8 gene mutation confers diabetogenic susceptibility in the LEW.1AR1/Ztm-iddm rat, an animal model of human type 1 diabetes
Diabetologia (2015)
-
The intriguing mission of neuropeptide Y in the immune system
Amino Acids (2013)
-
Serum metabolite signature predicts the acute onset of diabetes in spontaneously diabetic congenic BB rats
Metabolomics (2011)