Abstract
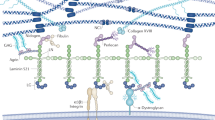
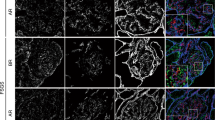
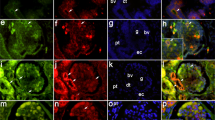
S–laminin/laminin β2, a homologue of the widely distributed laminin B1/β1 chain, is a major component of adult renal glomerular basement membrane (GBM). Immature GBM bears p1, which is replaced by β2 as development proceeds. In mutant mice that lack β2, the GBM remains rich in β1, suggesting that a feedback mechanism normally regulates GBM maturation. The β2–deficient GBM is structurally intact and contains normal complements of several collagenous and noncollagenous glycoproteins. However, mutant mice develop massive proteinuria due to failure of the glomerular filtration barrier. These results support the idea that laminin β chains are functionally distinct although they assemble to form similar structures. Laminin β2–deficient mice may provide a model for human congenital or idiopathic nephrotic syndromes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rohrbach, D.H. & Timpl, R., (eds) in Molecular and cellular aspects of basement membranes. (Academic Press, Inc., San Diego, 1993).
Burgeson, R.E. et al. A new nomenclature for laminins. Matrix Biol. 14, 209–211 (1994).
Timpl, R. & Brown, J.C. The laminins. Matrix Biol. 14, 275–281 (1994).
Hudson, B.G., Reeders, S.T. & Tryggvason, K. Type IV collagen: structure, gene organization, and role in human diseases. J. biol. Chem. 268, 26033–26036 (1993).
Sanes, J.R., Engvall, E., Butkowski, R. & Hunter, D.D. Molecular heterogeneity of basal laminae: Isoforms of laminin and collagen IV at the neuromuscular junction and elsewhere. J. Cell Biol. 111, 1685–1699 (1990).
Hunter, D.D., Shah, V., Merlie, J.P. & Sanes, J.R. A laminin-like adhesive protein concentrated in the synaptic cleft of the neuromuscular junction. Nature 338, 229–234 (1989).
Kleppel, M.M., Kashtan, C., Santi, P.A., Wieslander, J. & Michael, A.F. Distribution of familial nephritis antigen in normal tissue and renal basement membranes of patients with homozygous and heterozygous Alport familial nephritis. Lab. Invest. 61, 278–289 (1989).
Hostikka, S.L. et al. Identification of a distinct type IV collagen α chain with restricted kidney distribution and assignment of its gene to the locus of X chromosome-linked Alport syndrome. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 1606–1610 (1990).
Miner, J.H. & Sanes, J.R. Collagen IV α3, α4, and α5 chains in rodent basal laminae: sequence, distribution, association with laminins, and developmental switches. J. Cell Biol. 127, 879–891 (1994).
Ekblom, P. Renal development. in The kidney (eds Seldin, D. W. & Giebisch, G.) 475–501 (Raven Press, New York, 1992).
Reeves, W.H., Kanwar, Y.S. & Farquhar, M.G. Assembly of the glomerular filtration surface. J. Cell Biol. 85, 735–753 (1980).
Vehaskari, V.M. & Robson, A.M. Proteinnuria. in Pediatric kidney disease (ed. Edelman, Jr., C.M.) 531–551 (Little, Brown and Company, Boston, 1992).
Barker, D.F. et al. Identification of mutations in the COL4A5 collagen gene in Alport syndrome. Science 248, 1224–1227 (1990).
Mochizuki, T. et al. Identification of mutations in the β3(IV) and β4(IV) collagen genes in autosomal recessive Alport syndrome. Nature Genet. 8, 77–82 (1994).
Zhou, J. et al. Deletion of the paired α5(IV) and α6(IV) collagen genes in inherited smooth muscle tumors. Science 261, 1167–1169 (1993).
Kashtan, C.E., Sibley, R.K., Michael, A.F. & Vernier, R.L. Hereditary nephritis: Alport syndrome and thin glomerular basement membrane disease. in Renal pathology: with clinical and functional correlations, (eds C. C. Tisher & Brenner, B.M.) 1239–1266 (J.B. Lippincott Co., Philadelphia, 1994).
Noakes, P.G., Gautam, M., Mudd, J., Sanes, J.R. & Merlie, J.P. Aberrant differentiation of neuromuscular junctions in mice lacking s-laminin/laminin β2. Nature 374, 258–262 (1995).
Nash, M.A., Edelmann Jr., C.M., Bernstein, J. & Bamett, H.L. The nephrotic syndrome. in Pediatric kidney disease (ed. Edelman, Jr., C.M.) 1247–1251 (Little, Brown and Company, Boston, 1992).
Olson, J.L. The nephrotic syndrome. in Pathology of the kidney (ed. Heptinstall, R.H.) 779–869 (Little, Brown and Company, Boston, (1992).
Schnaper, H.W. & Robson, A.M. Nephrotic syndrome: minimal change disease, focal glomerulosclerosis, and related disorders. in Diseases of the kidney, (eds Schrier, R. W. & Gottschalk, C.W.) 1731–1766 (Little, Brown and Company, Boston, 1993).
Sorokin, L. & Ekblom, P. Development of tubular and glomerular cells of the kidney. Kidney Int. 41, 657–664 (1992).
Timpl, R. Proteoglycans of basement membranes. Experientia 49, 417–428 (1993).
Katz, A. et al. Renal entactin (nidogen): isolation, characterization and tissue distribution. Kidney Intl. 40, 643–652 (1991).
Fallen, J.R. & Hall, Z.W. Building synapses: agrin and dystroglycan stick together. Trends Neurosci 17, 469–473 (1994).
Desjardins, M. & Bendayan, M. Ontogenesis of glomerular basement membrane: structural and functional properties. J. Cell Biol. 113, 689–700 (1991).
Carlson, J.A. & Harrington, J.T. Laboratory evaluation of renal function. in Diseases of the kidney (edsSchrier,R. W. & Gottschalk,C.W.) 383–389 (Little, Brown and Company, Boston, (1993).
Scharer, K. & Gilli, G. Growth retardation in kidney disease. in Pediatric kidney disease, (ed. Edelman, Jr., C.M.) 593–596 (Little, Brown and Company, Boston, 1992).
McCluskey, R.T. Immunologic aspects of renal disease in Pathology of the kidney 4th edn (ed. Heptinstall, R.H.) 169–260 (Little, Brown, and Company, Boston, (1992).
Couser, W.G. Pathogenesis of glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 44, S19–S26 (1993).
Eddy, A. & Michael, A.F. Immune mechanisms of renal injury. in Pediatric kidney disease (ed. Edelman, Jr., C.M.) 329–397 (Little, Brown and Company, Boston, (1992).
Kashtan, C.E. & Kim, Y. Distribution of the α1 and α2 chains of collagen IV and of collagens V and VI in Alport syndrome. Kidney Int. 42, 115–126 (1992).
Sariola, H. et al. Dual origin of glomerular basement membrane. Develop. Biol. 101, 86–96 (1984).
Daniels, B.S. Increased albumin permeability in vitro following alterations of glomerular charge is mediated by the cells of the filtration barrier. J. Lab. clin. Med. 124, 224–230 (1994).
Sanes, J.R. Extracellular matrix molecules that influence neural development. Ann. Rev. Neurosci 12, 491–516 (1989).
Frenk, S., Antonowicz, I., Craig, J.M. & Metcoff, J. Experimental nephrotic syndrome in rats by aminonucleotide: renal lesions and body electrolyte compositions. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med. 89, 424–427 (1955).
Ogura, A. et al. Hereditary nephrotic syndrome with progression to renal failure in a mouse model (ICGN strain): clinical study. Nephron 68, 239–244 (1994).
Hudson, B.G. et al. The pathogenesis of Alport syndrome involves type IV collagen molecules containing the α3(IV) chain: evidence from anti-GBM nephritis after renal transplantation. Kidney Int. 42, 179–187 (1992).
Kestila, M. et al. Congenital nephrotic syndrome of the Finnish type maps to the long arm of chromosome 19. Am. J. hum. Genet. 54, 757–764 (1994).
Wewer, U.M. et al. Human β2 chain of laminin (formerly S chain): cDNA cloning, chromosomal localization, and expression in carcinomas. Genomics 24, 243–252 (1994).
Sunada, Y., Bernier, S.M., Kozak, C.A., Yamada, Y. & Campbell, K.P. Deficiency of merosin in dystrophic dy mice and genetic linkage of laminin M chain gene to dy locus. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 13729–13732 (1994).
Hong, X., Wu, X.-R., Wewer, U.M. & Engvall, E. Murine muscular dystrophy caused by a mutation in the laminin α2 (Lama2) gene. Nature Genet. 8, 297–302 (1994).
Pulkkinen, L. et al. Mutations in the γ2 chain gene (LAMC2) of kalinin/laminin 5 in the junctional forms of epidermolysis bullosa. Nature Genet. 6, 293–298 (1994).
Aberdam, D. et al. Herlitz's junctional epidermolysis bullosa is linked to mutations in the gene (LAMC2) for the γ2 subunit of nicein/kalinin (LAMININ-5). Nature Genet. 6, 299–304 (1994).
Sanes, J.R. Laminin, fibronectin and collagen in synaptic and extrasynaptic portions of muscle fiber basement membrane. J. Cell Biol. 93, 442–451 (1982).
Sugiyama, J., Bowen, D.C. & Hall, Z.W. Dystroglycan binds nerve and muscle agrin. Neuron 13, 103–115 (1994).
Kato, M., Koike, Y., Suzuki, S. & Kimata, K. Basement membrane proteoglycan in various tissues: characterization using monoclonal antibodies to the Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm mouse tumor low density heparan sulfate proteoglycan. J. Cell Biol. 106, 2203–2210 (1988).
Bender, B.L., Jaffe, R., Carlin, B. & Chung, A.E. Immunolocalization of entactin, a sulfated basement membrane component, in rodent tissues, and comparison with GP-2 (laminin). Am. J. Pathol. 103, 419–426 (1981).
Abrahamson, D.R. et al. Selective immunoreactivities of kidney basement membranes to monoclonal antibodies against laminin: localization of the end of the long arm and the short arms to discrete microdomains. J. Cell Biol. 109, 3477–3491 (1989).
Abrahamson, D.R. & St. John, P.L. Loss of laminin epitopes during glomerular basement membrane assembly in developing mouse kidneys. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 40, 1943–1953 (1992).
Martin, P.T., Ettinger, A.J. & Sanes, J.R. A synaptic localization domain in the synaptic cleft protein laminin β2 (s-laminin) Science (in the press).
Green, T.L., Hunter, D.D., Chan, W., Merlie, J.P. & Sanes, J.R. Synthesis and assembly of the synaptic cleft protein s-laminin by cultured cells. J. biol. Chem. 267, 2014–2022 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noakes, P., Miner, J., Gautam, M. et al. The renal glomerulus of mice lacking s–laminin/laminin β2: nephrosis despite molecular compensation by laminin β1. Nat Genet 10, 400–406 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0895-400
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0895-400
This article is cited by
-
Exogenous laminin exhibits a unique vascular pattern in the brain via binding to dystroglycan and integrins
Fluids and Barriers of the CNS (2022)
-
Complexities of the glomerular basement membrane
Nature Reviews Nephrology (2021)
-
Neurological involvement in monogenic podocytopathies
Pediatric Nephrology (2021)