Abstract
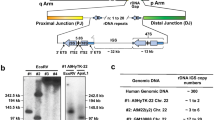
The pseudoautosomal boundaries are the interface between pseudoautosomal and sex chromosome–specific DNA sequences. We have isolated a gene, PBDX, from the human pseudoautosomal boundary region of Xp. The three exons at the 5′ end of PBDX are situated in the pseudoautosomal region immediately downstream of MIC2, whereas the other seven exons are in the X–speciflc region. Hence, PBDX is inherited in two modes: its 5′ end is pseudoautosomally inherited and its 3′ end is X–linked. The predicted amino acid sequence of the 540 bp coding region is 48% homologous to 12E7, the product of MIC2. By virtue of its position, PBDX becomes an excellent candidate for the XG blood group gene.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burgoyne, P.S. Genetic homology and crossing over in the X and Y chromosomes of mammals. Hum. Genet. 61, 85–90 (1982).
Ellis, N. & Goodfellow, P.N. The mammalian pseudoautosomal region. Trends Genet. 5, 406–410 (1989).
Cooke, H.J., Brown, W.R.A. & Rappold, G.A. Hypervariable telomeric sequences from the human sex chromosomes are pseudoautosomal. Nature 317, 687–692 (1985).
Simmler, M.-C. et al. Pseudoautosomal DNA sequences in the pairing region of the human sex chromosomes. Nature 317, 692–697 (1985).
Freije, D., Helms, C., Watson, M.S. & Donis-Keller, H. Identification of a second pseudoautosomal region near the Xq and Yq telomeres. Science 258, 1784–1787 (1992).
Rouyer, F. et al. A gradient of sex linkage in the pseudoautosomal region of the human sex chromsomes. Nature 319, 291–295 (1986).
Page, D.C. et al. Linkage, physcial mapping, and DNA sequence analysis of pseudoautsomal loci on the human X and Y chromosomes. Genomics 1, 243–256 (1987).
Brown, W.R.A. A physical map of the human pseudosutosomal region. EMBO J. 7, 2377–2385 (1988).
Petit, C., Levilliers, J. & Weissenbach, J. Physical mapping of the human pseudoautosomal region; comparison with the genetic linkage map. EMBO J. 7, 2369–2376 (1988).
Rappold, G.A. & Lehrach, H. A long range restriction map of the pseudoautosomal region by partial digest PFGE analysis from the telomere. Nucl. Acids Res. 16, 5361–5377 (1988).
Gabriel-Robez, O. et al. Deletion of the pseudoautosomal region and lack of sex-chromosome pairing at pachytene in two infertile men carrying an X;Y translocation. Cytogenet. cell Genet. 54, 38–42 (1990).
Mohandas, T.K. et al. Role of the psuedoautosomal region in sex-chromosome pairing during male meiosis: meiotic studies in a man with a deletion of distal Xp. Cell 51, 526–533 (1992).
Hassold, T.J., Sherman, S.L., Pettay, D., Page, D.C. & Jacobs, P.A. XY chromosome nondisjunction in man is associated with diminished recombination in the pseusoautosomal region. Am. J. hum. Genet. 49, 253–60 (1991).
Pritchard, C.A., Goodfellow, P.J. & Goodfellow, P.N. Mapping the limits of the human pseudoautosomal region and a candidate sequence for the male-determining gene. Nature 328, 273–275 (1987).
Ellis, N.A. et al. The pseudoautosomal boundary in man is defined by an Alu repeat sequence inserted on the Y chromosome. Nature 337, 81–84 (1989).
Ellis, N., Yen, P., Neiswanger, K., Shapiro, L.J. & Goodfellow, P.N. Evolution of the pseudoautosomal boundary in Old World monkeys and great apes. Cell 63, 977–986 (1990).
Ferguson-Smith, M.A., Sanger, R., Tippett, P., Aitken, D.A. & Boyd, E. A familial t(X;Y) translocation which assigns the Xg blood group locus to the region Xp22.3->pter. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 32, 273–274 (1982).
Yates, J.R.W. et al. Multipoint linkage analysis of steroid sulfatase (X-linked ichthyosis) and distal Xp markers. Genomics 1, 52–59 (1987).
Goodfellow, P.N. & Tippett, P. A human quantitative polymorphism related to Xg blood groups. Nature 289, 404–405 (1981).
Goodfellow, P.J., Pritchard, C.A., Tippett, P. & Goodfellow, P.N. Recombination between the X and Y chromosomes: implications for the relationship between MIC2, XG, and YG. Ann. hum. Genet. 51, 161–167 (1987).
von Heijne, G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J. molec. Biol. 184, 99–105 (1985).
Race, R.R. & Sanger, R. in Blood groups in man 578–593 (Oxford, Blackwell Scientific, 1975).
Banting, G.S., Pym, B., Darling, S.M. & Goodfellow, P.N. The MIC2 gene product: Epitope mapping and structural prediction analysis define an integral membrane protein. Molec. Immunol. 26, 181–188 (1989).
Gelin, C. et al. The E2 antigen, a 32 kd glycoprotein involved in T-cell adhesion processes, is the MIC2 gene product. EMBO J. 8, 3235–3239 (1989).
Yen, P.H. et al. The human X-linked steroid sulfatase gene and a Y-encoded pseudogene: evidence for an inversion of the Y chromosome during primate evolution. Cell 55, 1123–1135 (1988).
Fisher, E.M., Alitalo, T., Luoh, S.W., de la Chapelle, A. & Page, D.C. Human sex-chromosome-specific repeats within a region of pseudoautosomal/Yq homology. Genomics 7, 625–628 (1990).
Affara, N.A. et al. Regional assignment of Y-linked DNA probes by deletion mapping and their homology with X-chrornosome and autosomal sequences. Nucl. Acids Res. 14, 5353–5373 (1986).
Pritchard, C.A., Goodfellow, P.J. & Goodfellow, P.N. Isolation of a sequence which maps to the human sex determining region. Nucl. Acids Res. 15, 6159–6169 (1987).
Sinclair, A.H. et al. A gene from the human sex-determining region encodes a protein with homology to a conserved DNA-binding motif. Nature 346, 240–244 (1990).
Foley, G.E. et al. Continuous culture of human lymphoblasts from peripheral blood of a child with acute leukemia. Cancer 18, 522–529 (1965).
Feinberg, A.P. & Vogelstein, B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal. Biochem. 132, 6–13 (1983).
Ish-Horowicz, D. & Burke, J.F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucl. Acids Res. 9, 2989–2998 (1981).
Bimboim, H.C. & Doly, J. A rapid extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucl. Acids Res. 7, 1513–1523 (1979).
Grossberger, D. Minipreps of DNA from bacteriophage lambda. Nucl. Acids Res. 15, 6737 (1987).
Davis, R. et al. Rapid DNA isolations for enzymatic and hybridization analysis. Meth. Enzymol. 65, 404–411 (1980).
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. & Maniatis, T. in Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 7.19 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1989).
Tabor, S. & Richardson, C.C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified T7 DNA polymerase. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 84, 4767–4771 (1987).
Kreitman, M. & Landweber, L.F. A strategy for producing single-stranded DNA in the polyermase chain reaction. Gene Anal. Techn. 6, 84–88 (1989).
Andrews, P.W. et al. Pluripotent embryonal carcinoma clones derived from the human teratocarcinoma cell line Tera-2: differentiation in vivo and in vitro. Lab. Invest. 50, 147–162 (1984).
Lelias, J.-M. et al. cDNA cloning of a human mRNA preferentially expressed in hematopoietic cells and with homology to a GDP-dissociation inhibitor for the rho GTP-binding proteins. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 1479–1483 (1993).
Kozak, M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J. Cell Biol. 108, 229–241 (1989).
Wahle, E. The end of the message: 3′-end processing leading to polyadenylated messenger RNA. BioEssays 14, 113–118 (1992).
Dracopoli, N.C. et al. Genes controlling gp 25/30 cell-surface molecules map to chromosomes X and Y and escape X-inactivation. Am. J. hum. Genet. 37, 199–207 (1985).
Marcus, M., Trantravahi, R., Dev, J.G., Miller, D.A. & Miller, O.J. Human-mouse cell hybrid with human multiple Y chromosomes. Nature 262, 65–67 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ellis, N., Ye, TZ., Patton, S. et al. Cloning of PBDX, an MIC2-related gene that spans the pseudoautosomal boundary on chromosome Xp. Nat Genet 6, 394–400 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0494-394
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0494-394
This article is cited by
-
CD99 at the crossroads of physiology and pathology
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (2018)
-
A polymorphic pseudoautosomal boundary in the Carica papaya sex chromosomes
Molecular Genetics and Genomics (2015)
-
Tackling the characterization of canine chromosomal breakpoints with an integrated in-situ/in-silico approach: The canine PAR and PAB
Chromosome Research (2008)
-
CD99 plays a major role in the migration of monocytes through endothelial junctions
Nature Immunology (2002)
-
Characterization of the promoter region of human steriod sulfatase: A gene which escapes X inactivation
Somatic Cell and Molecular Genetics (1996)