Abstract
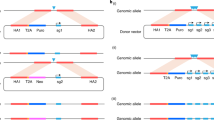
We describe a novel gene targeting strategy for the genetic analysis of essential genes in mammalian cells and its use to study the role of the cell cycle control gene CDC2 in human cells. A cell line (HT2-19) was generated in which endogenous CDC2 gene expression and cell viability depend on the presence of an inducer in the growth medium. In the absence of inducer, HT2-19 cells undergo extensive DNA rereplication and apoptosis. Rereplication is indicative of a role for human CDC2 in a control mechanism, previously undetected in mammalian cells, that prevents premature entry into S-phase.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Capecchi, M.R. Altering the genome by homologous recombination. Science 244, 1288–1292 (1989).
Porter, A.C.G. Designer genomes. Technique 1, 53–65 (1989).
Forsburg, S.L. & Nurse, P. Cell cycle regulation in the yeasts Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 7, 227–256 (1991).
Norbury, C. & Nurse, P. Animal cell cycles and their control. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 61, 441–470 (1992).
Nigg, E.A. Cyclin-dependent protein kinases: key regulators of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Bioessays 17, 471–480 (1995).
Morgan, D.O. Principles of CDK regulation Nature 374, 131–134 (1995).
Nurse, P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature 344, 503–508 (1990).
Broek, D. Bartlett, R. Crawford, K. & Nurse, P. Involvement of p34cdc2 in establishing the dependency of S phase on mitosis. Nature 349, 388–393 (1991).
Hayles, J. Fisher, D. Woollard, A. & Nurse, P. Temporal order of S phase and mitosis in fission yeast is determined by the state of the p34cdc2-mitotic B cyclin complex. Cell 78, 813–822 (1994).
D'Urso, G. & Nurse, P. Checkpoints in the cell cycle of fission yeast. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 5, 12–16 (1995).
Correa Bordes, J. & Nurse, P. p25rum1 orders S phase and mitosis by acting as an inhibitor of the p34cdc2 mitotic kinase. Cell 83, 1001–1009 (1995).
Dahmann, C. Diffley, J.F. & Nasmyth, K.A. S-phase-promoting cyclin-dependent kinases prevent re-replication by inhibiting the transition of replication origins to a pre-replicative state. Curr. Biol. 5, 1257–1269 (1995).
Girard, F. Strausfeld, U. Fernandez, A. & Lamb, N.J. Cyclin A is required for the onset of DNA replication in mammalian fibroblasts. Cell 67, 1169–1179 (1991).
Pagano, M. et al. Regulation of the cell cycle by the cdk2 protein kinase in cultured human fibroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 121, 101–111 (1993).
Tsai, L.H. Lees, E. Faha, B. Harlow, E. & Riabowol, K. The cdk2 kinase is required for the G1-to-S transition in mammalian cells. Oncogene 8, 1593–1602 (1993).
Hunter, T. & Pines, J. Cyclins and cancer. II: Cyclin D and CDK inhibitors come of age. Cell 79, 573–582 (1994).
Th'ng, J.P. et al. The FT210 cell line is a mouse G2 phase mutant with a temperature-sensitive CDC2 gene product. Cell 63, 313–324 (1990).
Hamaguchi, J.R. et al. Requirement for p34cdc2 kinase is restricted to mitosis in the mammalian cdc2 mutant FT210. J. Cell Biol. 117, 1041–1053 (1992).
Riabowol, K. Draetta, G. Brizuela, L. Vandre, D. & Beach, D. The cdc2 kinase is a nuclear protein that is essential for mitosis in mammalian cells. Cell 57, 393–401 (1989).
Furukawa, Y. Piwnica Worms, H. Ernst, T.J. Kanakura, Y. & Griffin, J.D. cdc2 gene expression at the G1 to S transition in human T lymphocytes. Science 250, 805–808 (1990).
Hu, M.C. & Davidson, N. The inducible lac operator-represser system is functional in mammalian cells. Cell 48, 555–566 (1987).
Figge, J. Wright, C. Collins, C.J. Roberts, T.M. & Livingston, D.M. Stringent regulation of stably integrated chloramphenicol acetyl transferase genes by E. coli lac represser in monkey cells. Cell 52, 713–722 (1988).
Brown, M. et al. lac repressor can regulate expression from a hybrid SV40 early promoter containing a lac operator in animal cells. Cell 49, 603–612 (1987).
Itzhaki, J.E. & Porter, A.C. Targeted disruption of a human interferon-inducible gene detected by secretion of human growth hormone. Nucl. Acids Res. 19, 3835–3842 (1991).
Itzhaki, J.E. et al. Targeted breakage of a human chromosome mediated by cloned human telomeric DNA. Nature Genet. 2, 283–287 (1992).
Porter, A.C. & Itzhaki, J.E. Gene targeting in human somatic cells. Complete inactivation of an interferon-inducible gene. Eur. J. Biochem. 218, 273–281 (1993).
Valancius, V. & Smithies, O. Testing an “in-out” targeting procedure for making subtle genomic modifications in mouse embryonic stem cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 11, 1402–1408 (1991).
Rasheed, S. Nelson Rees, W.A. Toth, E.M. Arnstein, P. & Gardner, M.B. Characterization of a newly derived human sarcoma cell line (HT-1080). Cancer 33, 1027–1033 (1974).
Tang, F.J. Ts'o, P.O. & Lesko, S.A. Simultaneous in situ detection of beta-interferon mRNA and DNA in the same cell. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 37, 697–701 (1989).
Darzynkiewicz, Z. et al. Features of apoptotic cells measured by flow cytometry. Cytometry 13, 795–808 (1992).
Shi, L. et al. Premature p34cdc2 activation required for apoptosis. Science 263, 1143–1145 (1994).
Ongkeko, W. Ferguson, D.J. Harris, A.L. & Norbury, C. Inactivation of Cdc2 increases the level of apoptosis induced by DNA damage. J. Cell Sci. 108, 2897–2904 (1995).
Lazebnik, Y.A. Cole, S. Cooke, C.A. Nelson, W.G. & Earnshaw, W.C. Nuclear events of apoptosis in vitro in cell-free mitotic extracts: a model system for analysis of the active phase of apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 123, 7–22 (1993).
Norbury, C. MacFarlane, M. Fearnhead, H. & Cohen, G.M. Cdc2 activation is not required for thymocyte apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 202, 1400–1406 (1994).
Oberhammer, F.A. Hochegger, K. Froschl, G. Tiefenbacher, R. & Pavelka, M. Chromatin condensation during apoptosis is accompanied by degradation of lamin A+B, without enhanced activation of cdc2 kinase. J. Cell Biol. 126, 827–837 (1994).
Wyborski, D.L. & Short, J.M. Analysis of inducers of the E. coli lac repressor system in mammalian cells and whole animals. Nucl. Acids Res. 19, 4647–4653 (1991).
Gossen, M. et al. Transcriptional activation by tetracyclines in mammalian cells. Science 268, 1766–1769 (1995).
Welch, P.J. & Wang, J.Y. Coordinated synthesis and degradation of cdc2 in the mammalian cell cycle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 3093–3097 (1992).
Kuhn, R. Schwenk, F. Aguet, M. & Rajewsky, K. Inducible gene targeting in mice. Science 269, 1427–1429 (1995).
Hayashi, S. A Cdc2 dependent checkpoint maintains diploidy in Drosophila. Development 122, 1051–1058 (1996).
Adachi, Y & Laemmli, U.K Study of the cell cycle-dependent assembly of the DNA pre-replication centres in Xenopus egg extracts. EMBO J. 13, 4153–4164 (1994).
Rao, P.N. & Johnson, R.T. Mammalian cell fusion: studies on the regulation of DNA synthesis and mitosis. Nature 225, 159–164 (1970).
King, R.W. Jackson, P.K. & Kirschner, M.W. Mitosis in transition. Cell 79, 563–571 (1994).
Waldman, T. Lengauer, C. Kinzler, K.W. & Vogelstein, B. Uncoupling of S phase and mitosis induced by anticancer agents in cells lacking p21. Nature 381, 713–716 (1996).
Herzinger, T. et al. Ultraviolet B irradiation-induced G2 cell cycle arrest in human keratinocytes by inhibitory phosphorylation of the cdc2 cell cycle kinase. Oncogene 11, 2151–2156 (1995).
Lock, R.B. & Ross, W.E. Inhibition of p34cdc2 kinase activity by etoposide or irradiation as a mechanism of G2 arrest in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cancer Res. 50, 3761–3766 (1990).
Lock, R.B. Inhibition of p34cdc2 kinase activation, p34cdc2 tyrosine dephosphorylation, and mitotic progression in Chinese hamster ovary cells exposed to etoposide. Cancer Res. 52, 1817–1822 (1992).
Tsao, Y.P. D'Arpa, P. & Liu, L.F. The involvement of active DNA synthesis in camptothecin-induced G2 arrest: altered regulation of p34cdc2/cyclin B. Cancer Res. 52, 1823–1829 (1992).
Cross, S.M. et al. A p53-dependent mouse spindle checkpoint. Science 267, 1353–1356 (1995).
Bruno, S. Ardelt, B. Skierski, J.S. Traganos, F. & Darzynkiewicz, Z. Different effects of staurosporine, an inhibitor of protein kinases, on the cell cycle and chromatin structure of normal and leukemic lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 52, 470–473 (1992).
Traganos, F. Gong, J. Ardelt, B. & Darzynkiewicz, Z. Effect of staurosporine on MOLT-4 cell progression through G2 and on cytokinesis. J. Cell Physiol 158, 535–544 (1994).
Usui, T. et al. Uncoupled cell cycle without mitosis induced by a protein kinase inhibitor, K-252a. Cell Biol. 115, 1275–1282 (1991).
Handeli, S. & Weintraub, H. The ts41 mutation in Chinese hamster cells leads to successive S phases in the absence of intervening G2, M, and G1. Cell 71, 599–611 (1992).
Zhang, Y Wang, Z. & Ravid, K. The cell cycle in polyploid megakaryocytes is associated with reduced activity of cyclin B1-dependent cdc2 kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 4266–4272 (1996).
Yoshida, M. & Beppu, T. Reversible arrest of proliferation of rat 3Y1 fibroblasts in both the G1 and G2 phases by trichostatin A. Exp. Cell Res. 177, 122–131 (1988).
Yoshida, M. et al. Effects of leptomycin B on the cell cycle of fibroblasts and fission yeast cells. Exp. Cell Res. 187, 150–156 (1990).
Sleigh, M.J. A nonchromatographic assay for expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene in eucaryotic cells. Anal. Biochem. 156, 251–256 (1986).
Mulligan, R.C. & Berg, P. Selection for animal cells that express the Escherichia coli gene coding for xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78, 2072–2076 (1981).
Sadler, J.R. Sasmor, H. & Betz, J.L. A perfectly symmetric lac operator binds the lac repressor very tightly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80, 6785–6789 (1983).
Southern, P.J. & Berg, P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J. Mol. Appl. Genet. 1, 327–341 (1982).
Fieck, A. Wyborski, D.L. & Short, J.M. Modifications of the E. coli Lac repressor for expression in eukaryotic cells: effects of nuclear signal sequences on protein activity and nuclear accumulation. Nucl. Acids Res. 20, 1785–1791 (1992).
Dalton, S. Cell cycle regulation of the human cdc2 gene. EMBO J. 11, 1797–1804 (1992).
Kelly, J.M. et al. Characterization of a human gene inducible by alpha- and beta-interferons and its expression in mouse cells. EMBO J. 5, 1601–1606 (1986).
Harlow, E. & Lane, D. A Laboratory Manual (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 1988)
Norbury, C. Blow, J. & Nurse, P. Regulatory phosphorylation of the p34cdc2 protein kmase in vertebrates. EMBO J. 10, 3321–3329 (1991).
Nusse, M. Beisker, W. Hoffmann, C. & Tarnok, A. Flow cytometric analysis of G1-and G2/M-phase subpopulations in mammalian cell nuclei using side scatter and DNA content measurements. Cytometry 11, 813–821 (1990).
Draetta, G. & Beach, D. Activation of cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis in human cells: cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and subunit rearrangement. Cell 54, 17–26 (1988).
Morla, A.O. Draetta, G. Beach, D. & Wang, J.Y. Reversible tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2: dephosphorylation accompanies activation during entry into mitosis. Cell 58, 193–203 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Itzhaki, J., Gilbert, C. & Porter, A. Construction by gene targeting in human cells of a ‘conditional’ CDC2 mutant that rereplicates its DNA. Nat Genet 15, 258–265 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0397-258
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0397-258
This article is cited by
-
The lethal response to Cdk1 inhibition depends on sister chromatid alignment errors generated by KIF4 and isoform 1 of PRC1
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Deciphering c-MYC-regulated genes in two distinct tissues
BMC Genomics (2011)
-
SP600125 suppresses Cdk1 and induces endoreplication directly from G2 phase, independent of JNK inhibition
Oncogene (2010)
-
Defining the role of Emi1 in the DNA replication–segregation cycle
Chromosoma (2008)
-
Stringent and reproducible tetracycline-regulated transgene expression by site-specific insertion at chromosomal loci with pre-characterised induction characteristics
BMC Molecular Biology (2007)