Abstract
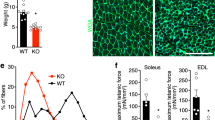
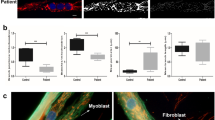
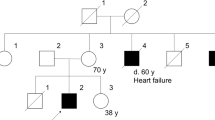
Mutations in the STA gene at the Xq28 locus have been found in patients with X-linked Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD). This gene encodes a hitherto unknown protein named ‘emerin’. To elucidate the subcellular localization of emerin, we raised two antisera against synthetic peptide fragments predicted from emerin cDNA. Using both antisera, we found positive nuclear membrane staining in skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscles in the normal controls and in patients with neuromuscular diseases other than EDMD. In contrast, a deficiency in immunofluorescent staining of skeletal and cardiac muscle from EDMD patients was observed. A 34 kD protein is immunoreactive with the antisera — the protein is equivalent to that predicted for emerin. Together, our findings suggest the specific deficiency of emerin in the nuclear membrane of muscle cells in patients with EDMD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Emery, A.H.E. & Dreifuss, F.E. Unusual type of benign X-linked muscular dystrophy. J. Neural. Neurosurg. Psychiatr. 29, 338–342 (1966).
Emery, A.H.E. Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy and other related disorders. Br. Med. Bull. 45, 772–787 (1989).
Dubowitz, V. Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. In Color Atlas of Muscle Disorders in Childhood (Year Book Medical Publishers, Chicago, 1989).
Hodgson, S.V., et al. A linkage study of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Hum. Genet. 74, 409–416 (1986).
Thomas, N.S.T., Williams, H., Elsas, L.J., Sarfarazi, M. & Harper, P.S. Localization of the gene for Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy to the distal long arm of the X-chromosome. J. Med. Genet. 23, 596–598 (1986).
Yates, J.R.W. et al. Emery–Dreifuss muscular dystrophy: localization to Xq27.3–qter confirmed by linkage to the factor VIII gene. J. Med. Genet. 23, 587–590 (1986).
Romeo, G. et al. Mapping of the Emery-Dreifuss gene through reconstruction of crossover points in two Italian pedigrees. Hum. Genet. 80, 59–62 (1988).
Cole, C.G. et al. Linkage of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy to the red/green cone pigment (RGCP) genes, proximal to factor VIII. Neuromusc. Disord. 2, 51–57 (1992).
Kress, W. et al. Multipoint linkage mapping of the Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy gene. Neuromusc. Disord. 2, 111–115 (1992).
Bione, S. et al. Identification of a novel X-linked gene responsible for Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Nature Genet. 8, 323–327 (1994).
Klauck, S.M., Wilgenbus, P., Yates, R.W., Muller, R. & Poustka, A. Identification of novel mutations in three families with Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 4, 1853–1857 (1995).
Bione, S. et al. Identification of new mutations in the Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy gene and evidence for genetic heterogeneity of the disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 4, 1859–1863 (1995).
Nigro, V. et al. SSCP detection of novel mutations in patients with Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy: definition of a small C-terminal region required for emerin function. Hum. Mol. Genet. 4, 2003–2004 (1995).
Bione, S. et al. Transcriptional organization of a 450-kb region of the human X chromosome in Xq28. Proc. Nail. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 10977–10981 (1993).
Hoffman, E.P., Brown, R.H. Jr. & Kunkel, L.M. Dystrophin: the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell. 51, 919–928 (1987).
Koenig, M., Monaco, A.P. & Kunkel, L.M. The complete sequence of dystrophin predicts a rod-shaped cytoskeletal protein. Cell. 53, 219–228 (1988).
Arahata, K. et al. Immunostaining of skeletal and cardiac muscle surface membrane with antibody against Duchenne muscular dystrophy peptide. Nature 333, 861–863 (1988).
Arahata, K. et al. Dystrophin diagnosis: Comparison of dystrophin abnormalities by immunofluorescence and immunoblot analyses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 7154–7158 (1989).
Arikawa-Hirasawa, E. et al. A severe muscular dystrophy patient with an internally deleted very short (110 kD) dystrophin: Presence of the binding site for dystrophin associated glycoprotein (DAG) may not be enough for physiological function of dystrophin. Neuromusc. Disord. 5, 429–438 (1995).
Arahata, K. et al. Preservation of the C-terminus of dystrophin molecule in the skeletal muscle from Becker muscular dystrophy. J. Neurol. Sci. 101, 148–156 (1991).
Koga, R. et al. Decreased myotonin-protein kinase in skeletal and cardiac muscles in myotonic dystrophy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Com. 202, 577–585 (1994).
de Duve, C., & Beaufay, H.A.,A short history of tissue fractionation. J. Cell Biol. 91, 293s–299s (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagano, A., Koga, R., Ogawa, M. et al. Emerin deficiency at the nuclear membrane in patients with Emery-Dreif uss muscular dystrophy. Nat Genet 12, 254–259 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0396-254
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0396-254
This article is cited by
-
Microtubule-based transport is essential to distribute RNA and nascent protein in skeletal muscle
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Muscular involvement and tendon contracture in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2Y: a mild adult phenotype and literature review
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2020)
-
Emerin anchors Msx1 and its protein partners at the nuclear periphery to inhibit myogenesis
Cell & Bioscience (2019)
-
Linker of nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton complex proteins in cardiomyopathy
Biophysical Reviews (2018)
-
Emerin plays a crucial role in nuclear invagination and in the nuclear calcium transient
Scientific Reports (2017)