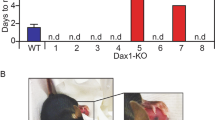
Abstract
Breeding the Y chromosome from certain Mus musculus domesticus strains onto the inbred laboratory mouse strain, C57BL/6J (B6), results in hermaphroditic progeny. This strain–dependent sex reversal suggests that there may be significant allelic variation in the murine sex determining gene, Sry. We have analysed the Sry genes from several domesttcus–type Y chromosomes and show that they encode smaller proteins than the molossinus–type alleles SryB6 and Sry129. We have also identified a polymorphic stretch of trinucleotide repeats that is unique to strains causing sex reversal and show that specific changes in the predicted polyglutamine amino acid sequence at this site are associated with different degrees of sex reversal.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eicher, E. M., Washburn, L.L., Whitney III, J.B. & Morrow, K.E. Mus poschiavinus Y chromosome in the C57BL/6J murine genome causes sex reversal. Science 217, 535–537 (1982).
Eicher, E.M. & Washburn, L.L. Inherited sex reversal in mice: Identification of a new primary sex-determining gene. J. exp. Zool. 228, 297–304 (1983).
Nagamine, C.M., Taketo, T. & Koo, G.C. Morphological development of the mouse gonad in tda-1 XY sex reversal. Differentiation 33, 214–222 (1987).
Nagamine, C.M., Taketo, T. & Koo, G.C. Studies on the genetics of tda-1 XY sex reversal in the mouse. Differentiation 33, 223–231 (1987).
Nagamine, C.M. et al. The musculus-type Y chromosome of the laboratory mouse is of Asian origin. Mamm. Genome 3, 84–91 (1992).
Tucker, P.K., Lee, B.K., Lundrigan, B.L. & Eicher, E.M. Geographic origin of the Y chromosomes in “old” inbred strains of mice. Mamm. Genome 3, 254–261 (1992).
Biddle, F.G., Eales, B.A. & Nishioka, Y. A DNA polymorphism from five inbred strains of the mouse identifies a functional class of domesticus-type Y chromosome that produces the same phenotypic distribution of gonadal hermaphrodites. Genome 34, 96–104 (1991).
Biddle, F.G. & Nishioka, Y. Assays of testis development in the mouse distinguish three classes of domesticus-type Y chromosome. Genome 30, 870–878 (1988).
Gubbay, J. et al. A gene mapping to the sex-determining region of the mouse Y chromosome is a member of a novel family of embryonically expressed genes. Nature 346, 245–250 (1990).
Koopman, P., Munsterberg, A., Capel, B., Vivian, N. & Lovell-Badge, R. Expression of a candidate sex-determining gene during mouse testis differentiation. Nature 348, 450–452 (1990).
Koopman, P., Gubbay, J., Vivian, N., Goodfellow, P. & Lovell-Badge, R. Male development of chromosomally female mice transgenic for Sry. Nature 351, 117–121 (1991).
Sinclair, A.H. et al. A gene from the human sex-determining region encodes a protein with homology to a conserved DNA-binding motif. Nature 346, 240–244 (1990).
Su, H. & Lau, Y.F.-C. Identification of the transcriptional unit, structural organization, and promoter sequence of the human sex-determining region Y (SRY) gene, using a reverse genetic approach. Am. J. hum. Genet. 52, 24–38 (1993).
Nasrin, N. et al. DNA-binding properties of the product of the testis-determining gene and a related protein. Nature 354, 317–320 (1991).
Harley, V.R. et al. DNA binding activity of recombinant SRY from normal males and XY females. Science 255, 453–456 (1992).
Gubbay, J. et al. Inverted repeat structure of the Sry locus in mice. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 7953–7957 (1992).
Mitchell, P.J. & Tjian, R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science 245, 371–378 (1989).
Kunieda, T. & Toyoda, Y. Nucleotide sequence of mouse Sry gene is different between Y chromosome originating from Mus musculus musculus and Mus musculus domesticus. Genomics 13, 236–237 (1992).
Graves, P.E. & Erickson, R.P. An amino acid change in the DNA-binding region of Sry found in Mus musculus domesticus and other species, does not explain C57BL/6J-YDom sex reversal. Biochem. Biophys. res. Commun. 185, 310–316 (1992).
Whitfield, L.S., Lovell-Badge, R. & Goodfellow, P. Rapid evolution of the mammalian sex-determining gene SRY. Nature 364, 713–715 (1993).
Tucker, P.K. & B.L., Lundrigan, Rapid evolution of the sex determining locus in Old World mice and rats. Nature 364, 715–717 (1993).
Giese, K., Cox, J. & Grosschedl, R. The HMG domain of lymphoid enhancer factor 1 bends DNA and facilitates assembly of functional nucleoprotein structures. Cell 69, 185–195 (1992).
Eicher, E.M. Primary sex determining genes in mice. In Prospects for Sexing Mammalian Sperm (eds Amann, R. P. & Seidel, G. E.) 121–135 (Colorado Associated University Press, Boulder, Colorado, 1982).
Brook, J. D. et al. Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: expansion of a trinucleotlde (CTG) repeat at the 3′ end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell 68, 799–808 (1992).
Fu, Y.-H. et al. An unstable triplet repeat in a gene related to myotonic muscular dystrophy. Science 255, 1256–1259 (1992).
LaSpada, A.R. et al. Androgen receptor gene mutations in X-linked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Nature 352, 77–79 (1991).
The Huntington's Disease Collaborative Research Group. A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington's disease chromosomes. Cell 72, 971–983 (1993).
Orr, H. et al. Expansion of an unstable trinucleotide CAG repeat in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. Nature Genet. 4, 221–226 (1993).
Koide, R. et al. Unstable expansion of a CAG repeat in hereditary dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy. Nature Genet. 6, 9–13 (1994).
Nagafuchi, S. et al. Expansion of an unstable CAG trinucleotide on chromosome 12p In dentatorubral and pallidoluysian atrophy. Nature Genet. 6, 14–18 (1994).
Coward, P. & Dasgupta, A., Cells are incapable of translating RNAs containing the poliovirus 5′ untranslated region: evidence for a translational inhibitor. J. Virol. 66, 286 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coward, P., Nagai, K., Chen, D. et al. Polymorphism of a CAG trinucleotide repeat within Sry correlates with B6.YDom sex reversal. Nat Genet 6, 245–250 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0394-245
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0394-245