Abstract
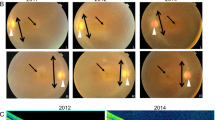
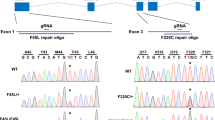
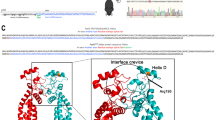
The murine rds (retinal degeneration slow) allele is a semidominant null allele that causes photoreceptor degeneration. The wild–type sequence at the rds locus encodes a photoreceptor disc membrane protein named peripherin/RDS. Mutations in the homologous human peripherin/RDS gene can cause autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa, but these are missense mutations or deletions of single codons. No obvious null alleles have been reported in humans, so that the human phenotype corresponding to rds is as yet unknown. Here we report a 2–basepair deletion in codon 25 of the human gene in a family with autosomal dominant retinitis punctata albescens, suggesting that this disease, rather than retinitis pigmentosa, is the comparable human phenotype.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arikawa, K., Molday, L.L., Molday, R.S. & Williams, D.S. Localization of peripherin/rds in the disk membranes of cone and rod photoreceptors: relationship to disk membrane morphogenesis and retinal degeneration. J. Cell Biol. 116, 659–667 (1992).
Connell, G.J. & Molday, R.S. Molecular cloning, primary structure, and orientation of the vertebrate photoreceptor cell protein peripherin in the rod outer segment disk membrane. Biochem. 29, 4691–4698 (1990).
Connell, G., Bascom, R., Molday, L., Reid, D., McInnes, R.R. & Molday, R.S. Photoreceptor peripherin is the normal product of the gene responsible for retinal degeneration in the rds mouse. Proc. natn Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 723–726 (1991).
Travis, G.H., Brennan, M.B., Danielson, P.E., Kozak, C.A. & Sutcliffe, J.G. Identification of a photoreceptor-specific mRNA encoded by the gene responsible for retinal degeneration slow (rds). Nature 338, 70–73 (1989).
Begy, C. & Bridges, C.D. Nucleotide and predicted protein sequence of rat retinal degeneration slow(rds). Nucl. Acids Res. 18, 3058 (1990).
Travis, G.H. et al. The human retinal degeneration slow (RDS) gene: chromosomal assignment and structure of the mRNA. Genomics 10, 733–739 (1991).
van Nie, R., Ivanyi, D. & Demant, P. A new H-2 linked mutation, rds, causing retinal degeneration in the mouse. Tissue Antigens 12, 106–108 (1978).
Travis, G.H., Groshan, K.R., Lloyd, M. & Bok, D. Complete rescue of photoreceptor dysplasia and degeneration in transgenic retinal degeneration slow (rds) mice. Neuron 9, 113–119 (1992).
Kajiwara, K., Hahn, L.B., Mukai, S., Travis, G.H., Berson, E.L. & Dryja, T.P. Mutations in the human retinal degeneration slow gene in autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Nature 354, 480–483 (1991).
Farrar, G.J. et al. A three-base-pair deletion in the peripherin-RDS gene in one form of retinitis pigmentosa. Nature 354, 478–480 (1991).
Orita, M. et al. Detection of polymorphisms of human DNA by gel electrophoresis as single-strand conformation polymorphisms. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. USA. 86, 2766–2770 (1989).
Berson, E.L. Retinitis pigmentosa and allied retinal diseases: electrophysiologic findings. Trans. Am. Acad. Ophthalmol. Otolaryngol. 81, 659–666 (1976).
Sandberg, M.A., Miller, S. & Berson, E.L. Rod electroretinograms in an elevated cyclic guanosine monophosphate-type human retinal degeneration. Invest. Ophthal. vis. Sci. 31, 2283–2287 (1990).
Lauber, H. Die sogenannte Retinitis punctata albescens. Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd. 48, 133–148 (1910).
Franceschetti, A., Francois, J. & Babel, J. Chorioretinal Heredodegenerations 229 (Charles C. Thomas, Springfield, Illinois, 1963).
Diem, M. Retinitis punctata albescens et pigmentosa. Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd. 53, 371–379 (1914).
Pillat, A. Tapetoretinal degeneration of the central fundus region. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 13, 1–12 (1930).
Wuestefeld, F. Zur Casuistik der Retinitis punctata albescens. Zeitschr. f. Augenheilk. 5, 110–115 (1901).
Ellis, D.S. & Heckenlively, J.R. Retinitis punctata albescens. Fundus appearance and functional abnormalities. Retina 3, 27–31 (1983).
Nettleship, E. A note on the progress of some cases of retinitis pigmentosa sine pigmento and of retinitis punctata albescens. Royal Lond. Ophthal. Hosp. Rep. 19, 123–129 (1914).
Kinniburgh, A.J., Maquat, L.E., Schedl, T., Rachmilewitz, E.A. & Ross, J. mRNA-deficient β° thalassemia results from a single nucleotide deletion. Nuc. Acids Res. 10, 5421–5427 (1982).
Sanyal, S., Chader, G. & Aguirre, G. in Retinal Degenerations: Experimental and Clinical Studies 239–256 (Alan R. Liss, New York, 1985).
Wataya, T. A histopathological study of retinitis punctata albescens. Jpn. J. clin. Ophthalmol. 14, 552–555 (1960).
Dryja, T.P., Hahn, L.B., Cowley, G.S., McGee, T.L. & Berson, E.L. Mutation spectrum of the rhodopsin gene among patients with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 9370–9374 (1991).
Sung, C.H. et al. Rhodopsin mutations in autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 6481–6485 (1991).
Inglehearn, C.F. et al. A completed screen for mutations of the rhodopsin gene in a panel of patients with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Hum. molec. Genet. 1, 41–45 (1992).
Sheffield, V.C., Fishman, G.A., Beck, J.S., Kimura, A.E. & Stone, E.M. Identification of novel rhodopsin mutations associated with retinitis pigmentosa by GC-clamped denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Am. J. hum. Genet. 49, 699–706 (1991).
Rosenfeld, P.J. et al. A null mutation in the rhodopsin gene causes rod photoreceptor dysfunction and autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Nature Genet. 1, 209–213 (1992).
Yandell, D.W. & Dryja, T.P. Detection of DNA sequence polymorphisms by enzymatic amplification and direct genomic sequencing. Am. J. hum. Genet. 45, 547–555 (1989).
Yandell, D.W. & Dryja, T.P. in Cold Spring Harbor Symposium Series: Cancer Cells 7 - Molecular Diagnostics of Human Cancer (eds Furth, M. & Greaves, M.) 223–227 (Cold Spring Harbor Press, New York, 1989).
Berson, E.L., Gouras, P. & Gunkel, R.D. Rod responses in retinitis pigmentosa, dominantly inherited. Arch. Ophthalmol. 80, 58–67 (1968).
Reichel, E., Bruce, A.M., Sandberg, M.A. & Berson, E.L. An electroretinographic and molecular genetic study of X-linked cone degeneration. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 108, 540–547 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kajiwara, K., Sandberg, M., Berson, E. et al. A null mutation in the human peripherin/RDS gene in a family with autosomal dominant retinitis punctata albescens. Nat Genet 3, 208–212 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0393-208
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0393-208
This article is cited by
-
A novel RLBP1 gene geographical area-related mutation present in a young patient with retinitis punctata albescens
Human Genomics (2017)
-
Diagnosis in a patient with fundus albipunctatus and atypical fundus changes
Documenta Ophthalmologica (2009)