Abstract
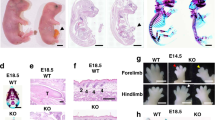
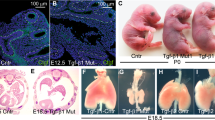
The genes Tlx1 (Hox11), Enx (Hox11L1, Tlx-2 ) and Rnx (Hox11L2, Tlx-3) constitute a family of orphan homeobox genes1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10. In situ hybridization has revealed considerable overlap in their expression within the nervous system, but Rnx is singularly expressed in the developing dorsal and ventral region of the medulla oblongata. Tlx1-deficient and Enx-deficient mice display phenotypes in tissues where the mutated gene is singularly expressed, resulting in asplenogenesis3,4 and hyperganglionic megacolon8, respectively. To determine the developmental role of Rnx, we disrupted the locus in mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells. Rnx-deficient mice developed to term, but all died within 24 hours after birth from a central respiratory failure. The electromyographic activity of intercostal muscles coupled with the C4 ventral root activity assessed in a medulla-spinal cord preparation revealed a high respiratory rate with short inspiratory duration and frequent apnea. Furthermore, a coordinate pattern existed between the abnormal activity of inspiratory neurons in the ventrolateral medulla and C4 motorneuron output, indicating a central respiratory defect in Rnx−/− mice. Thus, Rnx is critical for the development of the ventral medullary respiratory centre and its deficiency results in a syndrome resembling congenital central hypoventilation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hatano, M., Roberts, C.W.M., Minden, M., Crist, W.M. & Korsmeyer, S.J. Deregulation of a homeobox gene, HOX11, by the t(10;14) in T-cell leukemia. Science 253, 79–82 (1991).
Kennedy, M.A. et al. HOX11, a homeobox-containing T-cell oncogene on human chromosome 10q24. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 88, 8900 –8904 (1991).
Roberts, C.W.M., Shutter, J.R. & Korsmeyer, S.J. Hox11 controls the genesis of the spleen. Nature 368, 747–749 ( 1994).
Dear, T.N. et al. The Hox11 gene is essential for cell survival during spleen development . Development 121, 2909– 2915 (1995).
Dear, T.N., Sanchez-Garcia, I. & Rabbitts, T.H. The HOX11 gene encodes a DNA-binding nuclear transcriptional factor belonging to a distinct family of homeobox genes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 4431–4435 (1993).
Roberts, C.W.M., Sonder, A.M., Lumsden, A. & Korsmeyer, S.J. Developmental expression of Hox11 and specification of splenic cell fate. Am. J. Pathol. 146, 1089–1101 (1995).
Raju, K. et al. Characterization and developmental expression of Tlx-1, the murine homolog of HOX11. Mech. Dev. 44, 51–64 (1993).
Shirasawa, S. et al. Enx (Hox11L1)-deficient mice develop myenteric neuronal hyperplasia and megacolon. Nature Med. 3, 646– 650 (1997).
Masson, M., Greene, W.K. & Rabbitts, T.H. Optimal activation of an endogeneous gene by HOX11 requires the NH2-terminal 50 amino acids. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 3502–3508 ( 1998).
Logan, C., Wingate, R.J.T., McKay, I.J. & Lumsden, A. Tlx-1 and Tlx-3 homeobox gene expression in cranial sensory ganglia and hindbrain of the chick embryo: markers of patterned connectivity. J. Neurosci. 18, 5389–5402 (1998).
Bianchi, A.L., Denavit-Saubie, M. & Champagnat, J. Central control of breathing in mammals: neuronal circuitry, membrane properties and neurotransmitters. Am. Phys. Soc. 75, 1–45 (1995).
Suzue, T. Respiratory rhythm generation in the in vitro brain stem-spinal cord preparation of the neonatal rat. J. Physiol. 354, 173 –183 (1984).
Onimaru, H. Studies of the respiratory center using isolated brainstem-spinal cord preparations . Neurosci. Res. 21, 183– 190 (1995).
Arata, A., Onimaru, H. & Homma, I. Respiration-related neurons in the ventral medulla of newborn rats in vitro. Brain Res. Bull. 24, 599–604 (1990).
Rickling, J.C., Champagnat, J. & Denavit-Saubie, M. Electroresponsive properties and membrane potential trajectories of three types of inspiratory neurons in the newborn mouse brain stem in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 75, 795– 810 (1996).
Jacquin, T.D. et al. Reorganization of pontine rhythmogenic neuronal networks in Krox-20 knockout mice. Neuron 17, 747– 758 (1996).
Verloes, A. et al. Ondine-Hirschsprung syndrome (Haddad syndrome). Further delineation in two cases and review of the literature. Eur. J. Pediatr. 152, 75–77 (1993).
Mellins, R.B., Balfour, H.H., Turino, G.M. & Winters, R.W. Failure of automatic control of ventilation (Ondine's curse) report of an infant born with this syndrome and review of the literature. Medicine 49, 487–504 ( 1970).
Weese-Mayer, D.E., Silvestri, J.M., Marazita, M.L. & Hoo, J.J. Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome: inheritance and relation to sudden infant death syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 47, 360–367 (1993).
Bolk, S. et al. Endothelin-3 frameshift mutation in congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. Nature Genet. 13, 395– 396 (1996).
Amiel, J. et al. Mutations of the RET-GDNF signaling pathway in Ondine's curse . Am. J. Hum. Genet. 62, 715– 717 (1998).
Nakahara, S., Yokomori, K., Tamura, K., Oku, K. & Tsuchida, Y. Hirschsprung disease associated with Ondine's curse: a special subgroup? J. Pediatr. Surg. 30, 1481–1484 (1995).
Lumsden, A., Clarke, J.D.W., Keynes, R. & Fraser, S. Early phenotypic choices by neuronal precursors, revealed by clonal analysis of the chick embryo hindbrain. Development 120, 1581–1589 (1994).
McGinnis, W. & Krumlauf, R. Homeobox genes and axial patterning . Cell 68, 283–302 (1992).
Rubenstein, J.L.R. & Puelles, L. Homeobox gene expression during development of the vertebrate brain. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 29, 1–63 ( 1994).
Onimaru, H., Arata, A. & Homma, I. Primary respiratory rhythm generator in the medulla of brainstem-spinal cord preparation from newborn rat. Brain Res. 445, 314–324 ( 1988).
Onimaru, H. & Homma, I. Whole cell recordings from respiratory neurons in the medulla of brainstem-spinal cord preparations isolated from newborn rats. Plugers Arch. 420, 399– 406 (1992).
Acknowledgements
We thank D. Maher and E. Smith for preparation of this manuscript; and K. Ezure for encouragement and discussion. This research was supported in part by Grant-In-Aid for Exploratory Research from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (to A.A.) and Grant-In-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas (to S.S.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shirasawa, S., Arata, A., Onimaru, H. et al. Rnx deficiency results in congenital central hypoventilation. Nat Genet 24, 287–290 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/73516
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/73516
This article is cited by
-
Differential timing of granule cell production during cerebellum development underlies generation of the foliation pattern
Neural Development (2016)
-
Genomic and transcriptomic analyses match medulloblastoma mouse models to their human counterparts
Acta Neuropathologica (2014)
-
Hes-1 regulates the excitatory fate of neural progenitors through modulation of Tlx3 (HOX11L2) expression
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2012)
-
Genetic identification of an embryonic parafacial oscillator coupling to the preBötzinger complex
Nature Neuroscience (2009)