Abstract
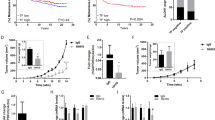
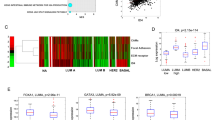
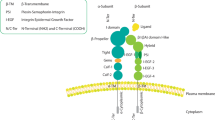
Integrins, receptors for extracellular matrix ligands, are critical regulators of the invasive phenotype1. Specifically, the α6β4 integrin has been linked with epithelial cell motility, cellular survival and carcinoma invasion, hallmarks of metastatic tumours2,3,4. Previous studies have also shown that antagonists of the NFAT (nuclear factor of activated T-cells) family of transcription factors5,6 exhibit strong anti-tumour-promoting activity7. This suggests that NFAT may function in tumour metastasis. Here, we investigate the involvement of NFAT in promoting carcinoma invasion downstream of the α6β4 integrin. We provide evidence that both NFAT1, and the recently identified NFAT5 isoform, are expressed in invasive human ductal breast carcinomas and participate in promoting carcinoma invasion using cell lines derived from human breast and colon carcinomas. NFAT1 and NFAT5 activity correlates with the expression of the α6β4 integrin. In addition, the transcriptional activity of NFAT5 is induced by α6β4 clustering in the presence of chemo-attractants, resulting in enhanced cell migration. These observations show that NFATs are targets of α6β4 integrin signalling and are involved in promoting carcinoma invasion, highlighting a novel function for this family of transcription factors in human cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark, E. A. & Brugge, J. S. Science 268, 233–239 (1995).
Mercurio, A. M. & Rabinovitz, I. Semin. Cancer Biol. 11, 129–141 (2001).
Shaw, L. M., Rabinovitz, I., Wang, H. H., Toker, A. & Mercurio, A. M. Cell 91, 949–960 (1997).
Trusolino, L., Bertotti, A. & Comoglio, P. M. Cell 107, 643–654 (2001).
Crabtree, G. R. J Biol Chem 276, 2313–2316 (2000).
Rao, A., Luo, C. & Hogan, P. G. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 15, 707–747 (1997).
Jiang, H., Yamamoto, S., Nishikawa, K. & Kato, R. Carcinogenesis 14, 67–71 (1993).
Rabinovitz, I. & Mercurio, A. M. J. Cell Biol. 139, 1873–1884 (1997).
Macian, F., Garcia-Rodriguez, C. & Rao, A. EMBO J. 19, 4783–4795 (2000).
Feske, S., Draeger, R., Peter, H. H., Eichmann, K. & Rao, A. J. Immunol. 165, 297–305 (2000).
Okamura, H. et al. Mol. Cell 6, 539–550 (2000).
Northrop, J. P. et al. Nature 369, 497–502 (1994).
Aramburu, J. et al. Science 285, 2129–2133 (1999).
Milan, D., Griffith, J., Su, M., Price, E. R. & McKeon, F. Cell 79, 437–447 (1994).
O'Keefe, S. J., Tamura, J., Kincaid, R. L., Tocci, M. J. & O'Neill, E. A. Nature 357, 692–694 (1992).
Lopez-Rodriguez, C., Aramburu, J., Rakeman, A. S. & Rao, A. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 7214–7219 (1999).
Lopez-Rodriguez, C. et al. Immunity 15, 47–58 (2001).
John, A. & Tuszynski, G. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 7, 14–23 (2001).
Graef, I. A., Chen, F. & Crabtree, G. R. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 11, 505–512 (2001).
de la Pompa, J. L. et al. Nature 392, 182–186 (1998).
Boss, V., Abbott, K. L., Wang, X. F., Pavlath, G. K. & Murphy, T. J. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 19664–19671 (1998).
Plyte, S. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 14350–14358 (2001).
Koukoulis, G. K. et al. Am. J. Pathol. 139, 787–799 (1991).
Tagliabue, E. et al. Clin. Cancer Res. 4, 407–410 (1998).
Miyakawa, H. et al. Am. J. Physiol. 274, F753–F761 (1998).
Miyakawa, H., Woo, S. K., Dahl, S. C., Handler, J. S. & Kwon, H. M. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 2538–2542 (1999).
Trama, J., Lu, Q., Hawley, R. G. & Ho, S. N. J. Immunol. 165, 4884–4894 (2000).
Acknowledgements
We thank N. Clipstone for generously providing expression plasmids for NFAT. We also thank C. Ferran, A. Mercurio, T. Tani, H. Turner and members of the Toker and Kinet laboratories for insightful discussions. This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health to A.T. (CA82695 and DK64854), A.R. (CA42471) and L.M.S. (CA81325), the U.S. Department of Defense to L.M.S., a fellowship from the Association Pour la Recherche Contre le Cancer to S.J. and fellowships from the Cancer Research Institute and the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society to C.L.-R.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jauliac, S., López-Rodriguez, C., Shaw, L. et al. The role of NFAT transcription factors in integrin-mediated carcinoma invasion. Nat Cell Biol 4, 540–544 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb816
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb816
This article is cited by
-
Lysine methylation promotes NFAT5 activation and determines temozolomide efficacy in glioblastoma
Nature Communications (2023)
-
SAFB2 Inhibits the Progression of Breast Cancer by Suppressing the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway via NFAT5
Molecular Biotechnology (2023)
-
The prognostic and immunological role of FKBP1A in an integrated muti-omics cancers analysis, especially lung cancer
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2023)
-
A novel FBW7/NFAT1 axis regulates cancer immunity in sunitinib-resistant renal cancer by inducing PD-L1 expression
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2022)
-
The chromosome 21 kinase DYRK1A: emerging roles in cancer biology and potential as a therapeutic target
Oncogene (2022)