Abstract
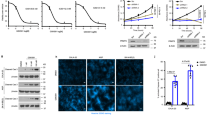
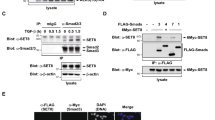
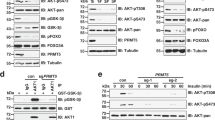
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) can undergo post-translational modifications, including phosphorylation, glycosylation and ubiquitylation, leading to diverse physiological consequences and modulation of its biological activity. There is increasing evidence that methylation may parallel other post-translational modifications in the regulation of various biological processes. It is still not known, however, whether EGFR is regulated by this post-translational event. Here, we show that EGFR Arg 1175 is methylated by an arginine methyltransferase, PRMT5. Arg 1175 methylation positively modulates EGF-induced EGFR trans-autophosphorylation at Tyr 1173, which governs ERK activation. Abolishment of Arg 1175 methylation enhances EGF-stimulated ERK activation by reducing SHP1 recruitment to EGFR, resulting in augmented cell proliferation, migration and invasion of EGFR-expressing cells. Therefore, we propose a model in which the regulatory crosstalk between PRMT5-mediated Arg 1175 methylation and EGF-induced Tyr 1173 phosphorylation attenuates EGFR-mediated ERK activation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bogdan, S. & Klambt, C. Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. Curr. Biol. 11, R292–R295 (2001).
Citri, A. & Yarden, Y. EGF–ERBB signalling: towards the systems level. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 505–516 (2006).
Hynes, N. E. & Lane, H. A. ERBB receptors and cancer: the complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 5, 341–354 (2005).
Linggi, B. & Carpenter, G. ErbB receptors: new insights on mechanisms and biology. Trends Cell Biol. 16, 649–656 (2006).
Paik, W. K., Paik, D. C. & Kim, S. Historical review: the field of protein methylation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 32, 146–152 (2007).
Bedford, M. T. Arginine methylation at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 120, 4243–4246 (2007).
Bachand, F. Protein arginine methyltransferases: from unicellular eukaryotes to humans. Eukaryot. Cell 6, 889–898 (2007).
Pahlich, S., Zakaryan, R. P. & Gehring, H. Protein arginine methylation: cellular functions and methods of analysis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1764, 1890–1903 (2006).
McBride, A. E. & Silver, P. A. State of the arg: protein methylation at arginine comes of age. Cell 106, 5–8 (2001).
Okabayashi, Y. et al. Tyrosines 1148 and 1173 of activated human epidermal growth factor receptors are binding sites of Shc in intact cells. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 18674–18678 (1994).
Rozakis-Adcock, M. et al. Association of the Shc and Grb2/Sem5 SH2-containing proteins is implicated in activation of the Ras pathway by tyrosine kinases. Nature 360, 689–692 (1992).
Batzer, A. G., Rotin, D., Urena, J. M., Skolnik, E. Y. & Schlessinger, J. Hierarchy of binding sites for Grb2 and Shc on the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol. Cell Biol. 14, 5192–5201 (1994).
Keilhack, H. et al. Phosphotyrosine 1173 mediates binding of the protein-tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 to the epidermal growth factor receptor and attenuation of receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 24839–24846 (1998).
Chang, B., Chen, Y., Zhao, Y. & Bruick, R. K. JMJD6 is a histone arginine demethylase. Science 318, 444–447 (2007).
Latham, J. A. & Dent, S. Y. Cross-regulation of histone modifications. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 14, 1017–1024 (2007).
Sims, R. J. 3rd & Reinberg, D. Is there a code embedded in proteins that is based on post-translational modifications? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 815–820 (2008).
Okutani, T. et al. Grb2/Ash binds directly to tyrosines 1068 and 1086 and indirectly to tyrosine 1148 of activated human epidermal growth factor receptors in intact cells. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 31310–31314 (1994).
Schulze, W. X., Deng, L. & Mann, M. Phosphotyrosine interactome of the ErbB-receptor kinase family. Mol. Syst. Biol. 1, 2005 0008 (2005).
You, M. & Zhao, Z. Positive effects of SH2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 on epidermal growth factor- and interferon-gamma-stimulated activation of STAT transcription factors in HeLa cells. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 23376–23381 (1997).
Tomic, S. et al. Association of SH2 domain protein tyrosine phosphatases with the epidermal growth factor receptor in human tumor cells. Phosphatidic acid activates receptor dephosphorylation by PTP1C. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 21277–21284 (1995).
Montano, X. Repression of SHP-1 expression by p53 leads to trkA tyrosine phosphorylation and suppression of breast cancer cell proliferation. Oncogene 28, 3787–3800 (2009).
Soler, C., Alvarez, C. V., Beguinot, L. & Carpenter, G. Potent SHC tyrosine phosphorylation by epidermal growth factor at low receptor density or in the absence of receptor autophosphorylation sites. Oncogene 9, 2207–2215 (1994).
Li, S., Couvillon, A. D., Brasher, B. B. & Van Etten, R. A. Tyrosine phosphorylation of Grb2 by Bcr/Abl and epidermal growth factor receptor: a novel regulatory mechanism for tyrosine kinase signaling. EMBO J. 20, 6793–6804 (2001).
Sini, P., Cannas, A., Koleske, A. J., Di Fiore, P. P. & Scita, G. Abl-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Sos-1 mediates growth-factor-induced Rac activation. Nat. Cell Biol. 6, 268–274 (2004).
Krause, C. D. et al. Protein arginine methyltransferases: evolution and assessment of their pharmacological and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol. Ther. 113, 50–87 (2007).
Anne, J. & Mechler, B. M. Valois, a component of the nuage and pole plasm, is involved in assembly of these structures, and binds to Tudor and the methyltransferase Capsuleen. Development 132, 2167–2177 (2005).
Peng, Y. et al. Androgen receptor coactivator p44/Mep50 in breast cancer growth and invasion. J. Cell Mol. Med. 14, 2780–2789 (2009).
Liu, Q. & Dreyfuss, G. In vivo and in vitro arginine methylation of RNA-binding proteins. Mol. Cell Biol. 15, 2800–2808 (1995).
Lee, J., Sayegh, J., Daniel, J., Clarke, S. & Bedford, M.T. PRMT8, a new membrane-bound tissue-specific member of the protein arginine methyltransferase family. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 32890–32896 (2005).
Chang, J. Y. et al. The tumor suppression activity of E1A in HER-2/neu-overexpressing breast cancer. Oncogene 14, 561–568 (1997).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institute of Health (RO1 109311 and PO1 099031), the National Breast Cancer Foundation, The Sister Institution Fund of China Medical University and Hospital/MD Anderson Cancer Center, and grants from the National Science Council (NSC 96-3111-B-039, NSC 95-2311-B-039-002 and NSC 99-2632-B-039-001), the National Health Research Institutes (NHRI-EX97-9603BC), and Department of Health (DOH97-TD-G-111-041, DOH97-TD-I-111-TM003 and DOH100-TD-C-111-005) of Taiwan. In memoriam, S. Lin-Guo for her courageous fight against breast cancer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J-M.H. carried out experimental design and most of the experimental work. J-M.H. and M-C.H. wrote the manuscript. C-K.C. conducted cell migration and invasion experiments. H-P.K. generated stable transfectants and carried out cell proliferation assays. C-T.C. conducted animal experiments. L-Y.L. and C-Y.L. generated antibodies. H-J.L., Y-N.W. and H-W.L. carried out sucrose gradient centrifugation and confocal microscopy analyses. M.L. and B.S. conducted immunoprecipitation assays. C-C.L. carried out mass spectrometry analyses. M.T.B. contributed to PRMT plasmids and reagents. C-H.T. and M-C.H. supervised the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 875 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, JM., Chen, CT., Chou, CK. et al. Crosstalk between Arg 1175 methylation and Tyr 1173 phosphorylation negatively modulates EGFR-mediated ERK activation. Nat Cell Biol 13, 174–181 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2158
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2158
This article is cited by
-
The disruptor of telomeric silencing 1-like (DOT1L) promotes peritoneal fibrosis through the upregulation and activation of protein tyrosine kinases
Molecular Biomedicine (2024)
-
Adriamycin induces cardiac fibrosis in mice via PRMT5-mediated cardiac fibroblast activation
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2023)
-
PRMT5 is a therapeutic target in choroidal neovascularization
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
PHGDH arginine methylation by PRMT1 promotes serine synthesis and represents a therapeutic vulnerability in hepatocellular carcinoma
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Autophagy dictates sensitivity to PRMT5 inhibitor in breast cancer
Scientific Reports (2023)