Abstract
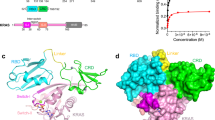
The activation of Ras by the guanine nucleotide-exchange factor Son of sevenless (Sos) constitutes the rate-limiting step in the transduction process that links receptor tyrosine kinases to Ras-triggered intracellular signalling pathways. A prerequisite for the function of Sos in this context is its ligand-dependent membrane recruitment, and the prevailing model implicates both the Sos carboxy-terminal proline-rich motifs and amino-terminal pleckstrin homology (PH) domain in this process. Here, we describe a previously unrecognized pathway for the PH domain-dependent membrane recruitment of Sos that is initiated by the growth factor-induced generation of phosphatidic acid via the signalling enzyme phospholipase D2 (PLD2). Phosphatidic acid interacts with a defined site in the Sos PH domain with high affinity and specificity. This interaction is essential for epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced Sos membrane recruitment and Ras activation. Our findings establish a crucial role for PLD2 in the coupling of extracellular signals to Sos-mediated Ras activation, and provide new insights into the spatial coordination of this activation event.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schlessinger, J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 103, 211–225 (2000).
Schlessinger, J. & Bar-Sagi, D. Activation of Ras and other signaling pathways by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 59, 173–179 (1994).
Wang, W. et al. The Grb2 binding domain of mSos1 is not required for downstream signal transduction. Nature Genet. 10, 294–300 (1995).
Karlovich, C. A. et al. In vivo functional analysis of the Ras exchange factor son of sevenless. Science 268, 576–579 (1995).
McCollam, L. et al. Functional roles for the pleckstrin and Dbl homology regions in the Ras exchange factor Son-of-sevenless. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 15954–15957 (1995).
Qian, X., Vass, W. C., Papageorge, A. G., Anborgh, P. H. & Lowy, D. R. N terminus of Sos1 Ras exchange factor: critical roles for the Dbl and pleckstrin homology domains. Mol. Cell Biol. 18, 771–778 (1998).
Byrne, J. L., Paterson, H. F. & Marshall, C. J. p21Ras activation by the guanine nucleotide exchange factor Sos, requires the Sos/Grb2 interaction and a second ligand-dependent signal involving the Sos N-terminus. Oncogene 13, 2055–2065 (1996).
Lemmon, M. A. & Ferguson, K. M. Signal-dependent membrane targeting by pleckstrin homology (PH) domains. Biochem. J. 350, 1–18 (2000).
Chen, R. H., Corbalan-Garcia, S. & Bar-Sagi, D. The role of the PH domain in the signal-dependent membrane targeting of Sos. EMBO J. 16, 1351–1359 (1997).
Zheng, J. et al. The solution structure of the pleckstrin homology domain of human SOS1. A possible structural role for the sequential association of diffuse B cell lymphoma and pleckstrin homology domains. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 30340–30344 (1997).
Kubiseski, T. J., Chook, Y. M., Parris, W. E., Rozakis-Adcock, M. & Pawson, T. High affinity binding of the pleckstrin homology domain of mSos1 to phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 1799–1804 (1997).
Karathanassis, D. et al. Binding of the PX domain of p47(phox) to phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate and phosphatidic acid is masked by an intramolecular interaction. EMBO J. 21, 5057–5068 (2002).
Stace, C. L. & Ktistakis, N. T. Phosphatidic acid- and phosphatidylserine-binding proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1761, 913–926 (2006).
Rizzo, M. A. et al. Phospholipase D and its product, phosphatidic acid, mediate agonist-dependent raf-1 translocation to the plasma membrane and the activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 1131–1139 (1999).
Park, J. W. Phosphatidic acid-induced translocation of cytosolic components in a cell-free system of NADPH oxidase: mechanism of activation and effect of diacylglycerol. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 229, 758–763 (1996).
Rebecchi, M., Boguslavsky, V., Boguslavsky, L. & McLaughlin, S. Phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C-delta 1: effect of monolayer surface pressure and electrostatic surface potentials on activity. Biochemistry 31, 12748–12753 (1992).
Fang, Y., Vilella-Bach, M., Bachmann, R., Flanigan, A. & Chen, J. Phosphatidic acid-mediated mitogenic activation of mTOR signaling. Science 294, 1942–1945 (2001).
de Rooij, J. & Bos, J. L. Minimal Ras-binding domain of Raf1 can be used as an activation-specific probe for Ras. Oncogene 14, 623–625 (1997).
Wang, X., Devaiah, S. P., Zhang, W. & Welti, R. Signaling functions of phosphatidic acid. Prog. Lipid Res. 45, 250–278 (2006).
Colley, W. C. et al. Phospholipase D2, a distinct phospholipase D isoform with novel regulatory properties that provokes cytoskeletal reorganization. Curr. Biol. 7, 191–201 (1997).
Slaaby, R., Jensen, T., Hansen, H. S., Frohman, M. A. & Seedorf, K. PLD2 complexes with the EGF receptor and undergoes tyrosine phosphorylation at a single site upon agonist stimulation. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 33722–33727 (1998).
Sung, T. -C. et al. Mutagenesis of Phospholipase D defines a superfamily including a trans-Golgi viral protein required for poxvirus pathogenicity. EMBO J. 16, 4519–4530 (1997).
Du, G., Huang, P., Liang, B. T. & Frohman, M. A. Phospholipase D2 localizes to the plasma membrane and regulates angiotensin II receptor endocytosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 15, 1024–1030 (2004).
Bogdan, S. & Klambt, C. Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. Curr Biol 11, R292–R295 (2001).
Luo, J. Q. et al. RalA interacts directly with the Arf-responsive, PIP2-dependent phospholipase D1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 235, 854–859 (1997).
Foster, D. A. & Xu, L. Phospholipase D in cell proliferation and cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 1, 789–800 (2003).
Malumbres, M. & Barbacid, M. RAS oncogenes: the first 30 years. Nature Rev. Cancer 3, 459–465 (2003).
Fiucci, G. et al. Changes in phospholipase D isoform activity and expression in multidrug-resistant human cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 85, 882–888 (2000).
Welsh, C. J., Yeh, G. C. & Phang, J. M. Increased phospholipase D activity in multidrug resistant breast cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 202, 211–217 (1994).
Zhao, Y. et al. Increased activity and intranuclear expression of phospholipase D2 in human renal cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 278, 140–143 (2000).
Rizzo, M. A., Shome, K., Watkins, S. C. & Romero, G. The recruitment of Raf-1 to membranes is mediated by direct interaction with phosphatidic acid and is independent of association with Ras. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 23911–23918 (2000).
Corbalan-Garcia, S., Margarit, S. M., Galron, D., Yang, S. S. & Bar-Sagi, D. Regulation of Sos activity by intramolecular interactions. Mol. Cell Biol. 18, 880–886 (1998).
Boykevisch, S. et al. Regulation of ras signaling dynamics by Sos-mediated positive feedback. Curr. Biol. 16, 2173–2179 (2006).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank members of the Bar-Sagi and Frohman laboratories, J. Kuriyan and H. Sondermann for helpful discussion, S. McLaughlin for help with the lipid vesicle binding assay and L. Taylor for help with image capturing and analysis. This work was supported by research grants from National Institutes of Health to D.B.-S. (CA55360 and CA28146), G.D. (GM071475) and M.A.F. (DK64166 and GM71520), and a Scientist Development Grant from the American Heart Association to G.D. (0430096N).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.Z. and D.B-S. conceived and designed the experiments. C.Z. performed the experiments. G.D. and M.A.F. designed, generated and provided PLD2 reagents. K.S. performed preliminary lipid-binding experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary figures S1, S2, S3 and S4 (PDF 249 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, C., Du, G., Skowronek, K. et al. Phospholipase D2-generated phosphatidic acid couples EGFR stimulation to Ras activation by Sos. Nat Cell Biol 9, 707–712 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1594
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1594
This article is cited by
-
The phospholipid transporter PITPNC1 links KRAS to MYC to prevent autophagy in lung and pancreatic cancer
Molecular Cancer (2023)
-
Crystal structure of plant PLDα1 reveals catalytic and regulatory mechanisms of eukaryotic phospholipase D
Cell Research (2020)
-
Role of phospholipase D in migration and invasion induced by linoleic acid in breast cancer cells
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2019)
-
RUNX1 positively regulates the ErbB2/HER2 signaling pathway through modulating SOS1 expression in gastric cancer cells
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Phospholipase D1 Signaling: Essential Roles in Neural Stem Cell Differentiation
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2018)