Abstract
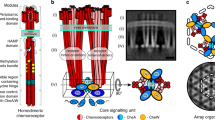
Coliform bacteria detect chemical attractants by means of a membrane-associated cluster of receptors and signalling molecules. We have used recently determined molecular structures, in conjunction with plastic models generated by three-dimensional printer technology, to predict how the proteins of the complex are arranged in relation to the plasma membrane. The proposed structure is a regular two-dimensional lattice in which the cytoplasmic ends of chemotactic-receptor dimers are inserted into a hexagonal array of CheA and CheW molecules. This structure creates separate compartments for adaptation and downstream signalling, and indicates a possible basis for the spread of activity within the cluster.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dixon, J. S. Evaluation of the CASP2 docking section. Proteins 1 (suppl.), 198–204 ( 1997).
Skawinsky, W. J. et al. The application of stereolithography to the fabrication of accurate molecular models. J. Mol. Graphics 13, 126–135 (1995).
Bailey, M. J., Schulten, K. & Johnson, J. E. The use of solid physical models for the study of macromolecular assembly. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 8, 202–208 (1998).
Maddock, J. R. & Shapiro, L. Polar location of the chemoreceptor complex in the Escherichia coli cell. Science 259, 1717–1723 (1993).
Eisenbach, M. Control of bacterial chemotaxis. Mol. Microbiol. 20 , 903–910 (1996).
Falke, J. J., Bass, R. B., Butler, S. L., Chervitz, S. A. & Danielson, M. A. The two-component signaling pathway of bacterial chemotaxis: a molecular view of signal transduction by receptors, kinases, and adaptation enzymes. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 13, 457–512 ( 1997).
Armitage, J. P. Bacterial tactic responses. Adv. Micro. Phys. 41, 229–289 (1999).
Bilwes, A. M., Alex, L. A., Crane, B. R. & Simon, M. I. Structure of CheA, a signal-transducing histidine kinase. Cell 96, 131–141 ( 1999).
McEvoy, M. M., Hausrath, A. C., Randolph, G. B., Remington, S. J. & Dahlquist, F. W. Two binding modes reveal flexibility in kinase/response regulator interactions in the bacterial chemotaxis pathway. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 7333–7338 (1998).
Morrison, T. B. & Parkinson, J. S. Liberation of an interaction domain from the phosphotransfer region of CheA, a signaling kinase of Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 91, 5485–5489 (1994).
Bourret, R. B., Davagnino, J. & Simon, M. I. The carboxy-terminal portion of the CheA kinase mediates regulation of autophosphorylation by transducer and CheW. J. Bacteriol. 175, 2097–2101 ( 1993).
Morrison, T. B. & Parkinson, J. S. A fragment liberated from the Escherichia coli CheA kinase that blocks stimulatory, but not inhibitory, chemoreceptor signaling. J. Bacteriol. 179, 5543–5550 (1997).
Liu, J. & Parkinson, J. S. Genetic evidence for interaction between CheW and Tsr proteins during chemoreceptor signaling by Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 173, 4941– 4951 (1991).
Lee, B. & Richards, F. M. The interpretation of protein structures: estimation of static accessibility. J. Mol. Biol. 55, 379–400 (1971).
Kim, K. K., Yokota, H. & Kim, S.-H. Four-helical-bundle structure of the cytoplasmic domain of a serine chemotaxis receptor. Nature 400, 787–792 (1999).
Koradi, R., Billeter, M. & Wüthrich, K. MOLMOL: a program for display and analysis of macromolecular structures. J. Mol. Graphics 14, 51– 55 (1996).
Bass, R. B., Coleman, M. D. & Falke, J. J. Signaling domain of the aspartate receptor is a helical hairpin with a localized kinase docking surface: cysteine and disulfide scanning studies. Biochemistry 38, 9317– 9327 (1999).
Le Moual, H. & Koshland, D. E. Jr Molecular evolution of the C-terminal cytoplasmic domain of a superfamily of bacterial receptors involved in taxis. J. Mol. Biol. 261, 568 –585 (1996).
Gegner, J. A., Graham, D. R., Roth, A. F. & Dahlquist, F. W. Assembly of an MCP receptor, CheW, and kinase CheA complex in the bacterial chemotaxis signal transduction pathway. Cell 70, 975–982 (1992).
Scharf, B. E., Fahrner, K. A. & Berg, H. C. CheZ has no effect on flagellar motors activated by CheY13DK106YW. J. Bacteriol. 180, 5123–5128 (1998).
DeFranco, A. L. & Koshland, D. E. Jr Molecular cloning of chemotaxis genes and overproduction of gene products in the bacterial sensing system. J. Bacteriol. 147, 390– 400 (1981).
Hazelbauer, G. L. & Harayama, S. Sensory transduction in bacterial chemotaxis. Int. Rev. Cytol. 81, 33–70 (1983).
Li, G. & Weis, R. M. Covalent modification regulates ligand binding to receptor complexes in the chemosensory system of Escherichia coli. Cell 100, 357– 365 (2000).
Bray, D. & Bourret, R. B. Computer analysis of the binding reactions leading to a transmembrane receptor-linked multiprotein complex involved in bacterial chemotaxis. Mol. Biol. Cell 6 , 1367–1380 (1995).
Liu, Y., Levit, M., Lurz, R., Surette, M. G. & Stock, J. B. Receptor-mediated protein kinase activation and the mechanism of transmembrane signaling in bacterial chemotaxis. EMBO J. 16, 7231–7240 ( 1997).
Borkovich, K. A., Alex, L. A. & Simon, M. I. Attenuation of sensory receptor signaling by covalent modification. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 6756–6760 (1992).
Hazelbauer, G. L., Park, C. & Nowlin, D. M. Adaptational “crosstalk” and the crucial role of methylation in chemotactic migration by Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 86, 1448– 1452 (1989).
Subbaramaiah, K. & Simms, S. A. Photolabeling of CheR methyltransferase with S-adenosyl-L-methionine (AdoMet). Studies on the AdoMet binding site. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 8636–8642 (1992).
Wu, J., Li, J., Li, G., Long, D. G. & Weis, R. M. The receptor binding site for the methyltransferase of bacterial chemotaxis is distinct from the sites of methylation. Biochemistry 35, 4984–4993 (1996).
Barnakov, A. N., Barnakova, L. A. & Hazelbauer, G. L. Efficient adaptational demethylation of chemoreceptors requires the same enzyme-docking site as efficient methylation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 10667– 10672 (1999).
Li, J., Swanson, R. V., Simon, M. I. & Weis, R. M. The response regulators CheB and CheY exhibit competitive binding to the kinase CheA. Biochemistry 34, 14626– 14636 (1995).
Segall, J. E., Manson, M. D. & Berg, H. C. Signal processing times in bacterial chemotaxis. Nature 296, 855–857 ( 1982).
Khan, S., Amoyaw, K., Spudich, J. L., Reid, G. P. & Trentham, D. R. Bacterial chemoreceptor signaling probed by flash photorelease of a caged serine. Biophys. J. 62, 67–68 (1992).
Bray, D., Levin, M. D. & Morton-Firth, C. J. Receptor clustering as a cellular mechanism to control sensitivity. Nature 393, 85– 88 (1998).
Duke, T. A. J. & Bray, D. Heightened sensitivity of a lattice of membrane receptors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 10104–10108 (1999).
Hazelbauer, G. L. & Engström, P. Parallel pathways for transduction of chemotactic signals in Escherichia coli. Nature 283, 98–100 ( 1980).
Feng, X., Baumgartner, J. W. & Hazelbauer, G. L. High- and low-abundance chemoreceptors in Escherichia coli: differential activities associated with closely related cytoplasmic domains. J. Bacteriol. 179, 6714– 6720 (1997).
Weerasuriya, S., Schneider, B. M. & Manson, M. D. Chimeric chemoreceptors in Escherichia coli: signaling properties of Tar–Tap and Tap–Tar Hybrids. J. Bacteriol. 180, 914–920 (1998).
Humphrey, W., Dalke, A. & Schulten, K. VMD — visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graphics 14, 33–38 (1996).
Sayle, R. & Milner-White, E. J. RasMol: biomolecular graphics for all. Trends Biochem. Sci. 20, 374 (1995).
Guex, N. & Peitsch, M.C. SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: an environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 18, 2714–2723 ( 1997).
Merritt, E. A. & Bacon, D. J. Raster3D: photorealistic molecular graphics. Methods Enzymol. 277, 505–524 (1997).
Acknowledgements
We thank F. W. Dahlquist, A. M. Bilwes and S. H. Kim for atomic coordinates of chemotaxis proteins, and F. W. Dahlquist for criticism of the manuscript. T.S.S. was supported by a Glaxo International Scholarship and an ORS Award from CVCP. N.L.N. was supported by an EMBO long-term fellowship. This work was supported by a grant from the UK Medical Research Council (to D.B.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimizu, T., Le Novère, N., Levin, M. et al. Molecular model of a lattice of signalling proteins involved in bacterial chemotaxis. Nat Cell Biol 2, 792–796 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/35041030
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35041030
This article is cited by
-
Current progress in hepatic tissue regeneration by tissue engineering
Journal of Translational Medicine (2019)
-
3D bioprinting of tissues and organs
Nature Biotechnology (2014)
-
50 years of allosteric interactions: the twists and turns of the models
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2013)
-
A phenylalanine rotameric switch for signal-state control in bacterial chemoreceptors
Nature Communications (2013)
-
Overview of Mathematical Approaches Used to Model Bacterial Chemotaxis I: The Single Cell
Bulletin of Mathematical Biology (2008)