Abstract
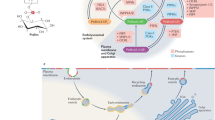
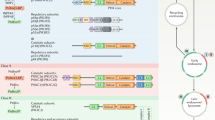
Phosphoinositides (PIs) undergo phosphorylation/dephosphorylation cycles through organelle-specific PI kinases and PI phosphatases that lead to distinct subcellular distributions of the individual PI species. Specific PIs control the correct timing and location of many trafficking events. Their ultimate mode of action is not always well defined, but it includes localized recruitment of transport machinery, allosteric regulation of PI-binding proteins and changes in the physical properties of the membrane.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Varnai, P. et al. Inositol lipid binding and membrane localization of isolated pleckstrin homology (PH) domains. Studies on the PH domains of phospholipase C delta 1 and p130. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 27412–27422 (2002).
Levine, T.P. & Munro, S. Targeting of Golgi-specific pleckstrin homology domains involves both PtdIns 4-kinase-dependent and -independent components. Curr. Biol. 12, 695–704 (2002).
Godi, A. et al. FAPPs control Golgi-to-cell surface membrane traffic by binding ARF and PtdIns(4)P. Nature Cell Biol. 6, 393–404 (2004).
Malecz, N. et al. Synaptojanin 2, a novel Rac1 effector that regulates clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Curr. Biol. 10, 1383–1386 (2000).
Godi, A. et al. ARF mediates recruitment of PtdIns-4-OH kinase-beta and stimulates synthesis of PtdIns(4,5)P2 on the Golgi complex. Nature Cell Biol. 1, 280–287 (1999).
Christoforidis, S. et al. Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinases are Rab5 effectors. Nature Cell Biol. 1, 249–252 (1999).
Donaldson, J.G. Multiple roles for Arf6: sorting, structuring, and signaling at the plasma membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 41573–41576 (2003).
Aikawa, Y. & Martin, T.F. ARF6 regulates a plasma membrane pool of phosphatidylinositol(4,5)bisphosphate required for regulated exocytosis. J. Cell Biol. 162, 647–659 (2003).
Simonsen, A. et al. EEA1 links PtdIns(3)K function to Rab5 regulation of endosome fusion. Nature 394, 494–498 (1998).
Cremona, O. & De Camilli, P. Phosphoinositides in membrane traffic at the synapse. J. Cell Sci. 114, 1041–1052 (2001).
Gaidarov, I., Smith, M.E., Domin, J. & Keen, J.H. The class II phosphoinositide 3-kinase C2alpha is activated by clathrin and regulates clathrin-mediated membrane trafficking. Mol. Cell 7, 443–449 (2001).
Kihara, A., Kabeya, Y., Ohsumi, Y. & Yoshimori, T. Beclin-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex functions at the trans-Golgi network. EMBO Rep. 2, 330–335 (2001).
De Matteis, M., Godi, A. & Corda, D. Phosphoinositides and the Golgi complex. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 14, 434–447 (2002).
Martin, T.F. PtdIns(4,5)P(2) regulation of surface membrane traffic. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 13, 493–499 (2001).
Botelho, R.J. et al. Localized biphasic changes in phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate at sites of phagocytosis. J. Cell Biol. 151, 1353–1368 (2000).
Vieira, O.V. et al. Distinct roles of class I and class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases in phagosome formation and maturation. J. Cell Biol. 155, 19–25 (2001).
Gillooly, D.J. et al. Localization of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate in yeast and mammalian cells. EMBO J. 19, 4577–4588 (2000).
Mishra, S.K. et al. Disabled-2 exhibits the properties of a cargo-selective endocytic clathrin adaptor. EMBO J. 21, 4915–4926 (2002).
Nishikawa, K. et al. Association of protein kinase Cmu with type II phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase and type I phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 23126–23133 (1998).
Hao, W. et al. Regulation of AP-3 function by inositides. Identification of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate as a potent ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 6393–6398 (1997).
Ford, M.G. et al. Curvature of clathrin-coated pits driven by epsin. Nature 419, 361–366 (2002).
Matsuoka, K. et al. COPtdInsI-coated vesicle formation reconstituted with purified coat proteins and chemically defined liposomes. Cell 93, 263–275 (1998).
Chaudhary, A. et al. Specific interaction of Golgi coatomer protein alpha-COP with phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 8344–8350 (1998).
Wang, Y.J. et al. Phosphatidylinositol 4 phosphate regulates targeting of clathrin adaptor AP-1 complexes to the Golgi. Cell 114, 299–310 (2003).
Mills, I.G. et al. EpsinR: an AP1/clathrin interacting protein involved in vesicle trafficking. J. Cell Biol. 160, 213–222 (2003).
Verstreken, P. et al. Synaptojanin is recruited by endophilin to promote synaptic vesicle uncoating. Neuron 40, 733–748 (2003).
Schuske, K.R. et al. Endophilin is required for synaptic vesicle endocytosis by localizing synaptojanin. Neuron 40, 749–762 (2003).
Terebiznik, M.R. et al. Elimination of host cell PtdIns(4,5)P(2) by bacterial SigD promotes membrane fission during invasion by Salmonella. Nature Cell Biol. 4, 766–773 (2002).
Rozelle, A.L. et al. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate induces actin-based movement of raft-enriched vesicles through WASP-Arp2/3. Curr. Biol. 10, 311–320 (2000).
Klopfenstein, D.R., Tomishige, M., Stuurman, N. & Vale, R.D. Role of phosphatidylinositol(4,5)bisphosphate organization in membrane transport by the Unc104 kinesin motor. Cell 109, 347–358 (2002).
Christoforidis, S., McBride, H.M., Burgoyne, R.D. & Zerial, M. The Rab5 effector EEA1 is a core component of endosome docking. Nature 397, 621–625 (1999).
Mayer, A. et al. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate regulates two steps of homotypic vacuole fusion. Mol. Biol. Cell 11, 807–817 (2000).
Boeddinghaus, C., Merz, A.J., Laage, R. & Ungermann, C. A cycle of Vam7p release from and PtdIns 3-P-dependent rebinding to the yeast vacuole is required for homotypic vacuole fusion. J. Cell Biol. 157, 79–89 (2002).
Godi, A. et al. ADP ribosylation factor regulates spectrin binding to the Golgi complex. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 8607–8612 (1998).
Randazzo, P.A., Nie, Z., Miura, K. & Hsu, V.W. Molecular aspects of the cellular activities of ADP-ribosylation factors. Sci. STKE 59, DOI: 10.1126/stke.2000.59.re1 (2000).
Zheng, J. et al. Identification of the binding site for acidic phospholipids on the pH domain of dynamin: implications for stimulation of GTPase activity. J. Mol. Biol. 255, 14–21 (1996).
Kutateladze, T. & Overduin, M. Structural mechanism of endosome docking by the FYVE domain. Science 291, 1793–1796 (2001).
Cheever, M.L. et al. Phox domain interaction with PtdIns(3)P targets the Vam7 t-SNARE to vacuole membranes. Nature Cell Biol. 3, 613–618 (2001).
Dumas, J.J. et al. Multivalent endosome targeting by homodimeric EEA1. Mol. Cell 8, 947–958 (2001).
Mao, Y. et al. Crystal structure of the VHS and FYVE tandem domains of Hrs, a protein involved in membrane trafficking and signal transduction. Cell 100, 447–456 (2000).
Misra, S. & Hurley, J.H. Crystal structure of a phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate-specific membrane-targeting motif, the FYVE domain of Vps27p. Cell 97, 657–666 (1999).
Bravo, J. et al. The crystal structure of the PX domain from p40(phox) bound to phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate. Mol. Cell 8, 829–839 (2001).
Itoh, T. et al. Role of the ENTH domain in phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding and endocytosis. Science 291, 1047–1051 (2001).
Ford, M.G. et al. Simultaneous binding of PtdIns(4,5)P2 and clathrin by AP180 in the nucleation of clathrin lattices on membranes. Science 291, 1051–1055 (2001).
Farsad, K. & De Camilli, P. Mechanisms of membrane deformation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15, 372–381 (2003).
Petiot, A., Faure, J., Stenmark, H. & Gruenberg, J. PtdIns3P signaling regulates receptor sorting but not transport in the endosomal pathway. J. Cell Biol. 162, 971–979 (2003).
Suchy, S.F., Olivos-Glander, I.M. & Nussabaum, R.L. Lowe syndrome, a deficiency of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 5-phosphatase in the Golgi apparatus. Hum. Mol. Genet. 4, 2245–2250 (1995).
Wishart, M.J. & Dixon, J.E. PTEN and myotubularin phosphatases: from 3-phosphoinositide dephosphorylation to disease. Trends Cell Biol. 12, 579–585 (2002).
Dang, H., Li, Z., Skolnik, E.Y. & Fares, H. Disease-related myotubularins function in endocytic traffic in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol. Biol. Cell 15, 189–196 (2004).
Naga Prasad, S.V. et al. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulates beta2-adrenergic receptor endocytosis by AP-2 recruitment to the receptor/beta-arrestin complex. J. Cell Biol. 158, 563–575 (2002).
Arico, S. et al. The tumor suppressor PTEN positively regulates macroautophagy by inhibiting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 35243–35246 (2001).
Walker, S.M., Downes, C.P. & Leslie, N.R. TPtdInsP: a novel phosphoinositide 3-phosphatase. Biochem. J. 360, 277–283 (2001).
Wu, Y. et al. PTEN 2, a Golgi-associated testis-specific homologue of the PTEN tumor suppressor lipid phosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 21745–21753 (2001).
Pendaries, C., Tronchere, H., Plantavid, M. & Payrastre, B. Phosphoinositide signaling disorders in human diseases. FEBS Lett. 546, 25–31 (2003).
Norris, F.A., Wilson, M.P., Wallis, T.S., Galyov, E.E. & Majerus, P.W. SopB, a protein required for virulence of Salmonella dublin, is an inositol phosphate phosphatase. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 14057–14059 (1998).
Vergne, I., Chua, J. & Deretic, V. Mycobacterium tuberculosis phagosome maturation arrest: selective targeting of PtdIns3P-dependent membrane trafficking. Traffic 4, 600–606 (2003).
Simonsen, A., Wurmser, A.E., Emr, S.D. & Stenmark, H. The role of phosphoinositides in membrane transport. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 13, 485–492 (2001).
Schu, P.V. et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase encoded by yeast VPS34 gene essential for protein sorting. Science 260, 88–91 (1993).
Fouraux, M.A. et al. Rabip4? is an effector of rab5 and rab4 and regulates transport through early endosomes. Mol. Biol. Cell 15, 611–624 (2004).
Xu, Y., Hortsman, H., Seet, L., Wong, S.H. & Hong, W. SNX3 regulates endosomal function through its PX-domain-mediated interaction with PtdIns(3)P. Nature Cell Biol. 3, 658–666 (2001).
Rudge, S.A., Anderson, D.M. & Emr, S.D. Vacuole size control: regulation of PtdIns(3,5)P2 levels by the vacuole-associated Vac14–Fig4 complex, a PtdIns(3,5)P2-specific phosphatase. Mol. Biol. Cell 15, 24–36 (2003).
Panaretou, C. & Tooze, S.A. Regulation and recruitment of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase on immature secretory granules is independent of ADP-ribosylation factor 1. Biochem. J. 363, 289–295 (2002).
Bankaitis, V.A., Aitken, J.R., Cleves, A.E. & Dowhan, W. An essential role for a phospholipid transfer protein in yeast Golgi function. Nature 347, 561–562 (1990).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank C. Berrie for reading the manuscript and E. Fontana for artwork preparation. This work has been supported in part by the Italian Association for Cancer Research, Telethon Italia, European Community and by the Italian Ministry of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matteis, M., Godi, A. PI-loting membrane traffic. Nat Cell Biol 6, 487–492 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb0604-487
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb0604-487
This article is cited by
-
Heparin and heparan sulfate proteoglycans promote HIV-1 p17 matrix protein oligomerization: computational, biochemical and biological implications
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Sec14l3 potentiates VEGFR2 signaling to regulate zebrafish vasculogenesis
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Protein kinase N controls a lysosomal lipid switch to facilitate nutrient signalling via mTORC1
Nature Cell Biology (2019)
-
Genetic variation and function of the HIV-1 Tat protein
Medical Microbiology and Immunology (2019)
-
Cyclophilin A enables specific HIV-1 Tat palmitoylation and accumulation in uninfected cells
Nature Communications (2018)