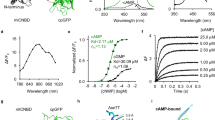
Abstract
Cyclic AMP controls several signalling cascades within cells, and changes in the amounts of this second messenger have an essential role in many cellular events. Here we describe a new methodology for monitoring the fluctuations of cAMP in living cells. By tagging the cAMP effector protein kinase A with two suitable green fluorescent protein mutants, we have generated a probe in which the fluorescence resonance energy transfer between the two fluorescent moieties is dependent on the levels of cAMP. This new methodology opens the way to the elucidation of the biochemistry of cAMP in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Simonds, W. F. G protein regulation of adenylate cyclase. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 20, 66–73 (1999).
Brandon, E. P., Idzerda, R. L. & McKnight, G. S. PKA isoforms, neural pathways, and behaviour: making the connection. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 7, 397–403 (1997).
Walsh, D. A. & Van-Patten, S. M. Multiple pathway signal transduction by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. FASEB J. 8, 1227–1236 (1994).
Meinkoth, J. L. et al. Signal transduction through the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 127, 179–187 (1993).
Lee, K. A. Transcriptional regulation by cAMP. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 3, 953–959 (1991).
Clegg, R. M. in Fluorescence Imaging Spectroscopy and Microscopy (eds Wang, X. F. & Herman, B.) 172–252 (Wiley, New York, 1996).
Adams, S. R., Harootunian, A. T., Buechler, Y. J., Taylor, S. S. & Tsien, R. Y. Fluorescence ratio imaging of cyclic AMP in single cells. Nature 349, 694–697 (1991).
Tsien, R. Y. The green fluorescent protein. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67, 509–544 (1998).
Adams, S. R., Bacskai, B. J., Taylor, S. S. & Tsien, R. Y. in Fluorescence and Luminescent Probes for Biological Activity 2nd edn (ed. Mason, W. T.) 156–172 (Academic, San Diego, 1999).
Zlokarnik, G. et al. Quantitation of transcription and clonal selection of single living cells with beta-lactamase as reporter. Science 279, 84–88 (1998).
Knighton, D. R. et al. Structure of a peptide inhibitor bound to the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science 253, 407–414 (1991).
Biondi, R. M., Baehler, P. J., Reymond, C. D. & Veron, M. Random insertion of GFP into the cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulatory subunit from Dictyostelium discoideum. Nucleic Acids Res. 26, 4946–4952 (1998).
Colledge, M. & Scott, J. D. AKAPs: from structure to function. Trends Cell Biol. 9, 216–221 (1999).
Griffin, B. A., Adams, S. R. & Tsien, R. Specific covalent labeling of recombinant protein molecules inside live cells. Science 281, 269–272 (1998).
Acknowledgements
We thank G. Ronconi and M. Santato for technical assistance. This work was supported by grants to T.P. from the Italian Association for Cancer Research (AIRC; grant number 98), from Telethon (grant 1226), from the CNR target project Biotechnology (grant 049), from the EU Programs Biotechnology (grants BIO4CT960382 and TMR FMRXCT960382), and from the Armenise Harvard Foundation, and to C.Y.C. and R.Y.T. from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to T.P.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaccolo, M., De Giorgi, F., Cho, C. et al. A genetically encoded, fluorescent indicator for cyclic AMP in living cells. Nat Cell Biol 2, 25–29 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/71345
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/71345
This article is cited by
-
Cardiac contraction and relaxation are regulated by distinct subcellular cAMP pools
Nature Chemical Biology (2024)
-
Expression and functions of adenylyl cyclases in the CNS
Fluids and Barriers of the CNS (2022)
-
A Novel Bioelectronic Reporter System in Living Cells Tested with a Synthetic Biological Comparator
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Optical approaches for single-cell and subcellular analysis of GPCR–G protein signaling
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2019)