Abstract
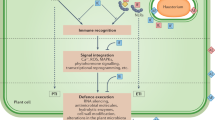
There are marked differences in the pattern of host gene expression in incompatible plant : microbial pathogen interactions compared with compatible interactions, associated with the elaboration of inducible defenses. Constitutive expression of genes encoding a chitinase or a ribosome-inactivating protein in transgenic plants confers partial protection against fungal attack, and a large repertoire of such antimicrobial genes has been identified for further manipulation. In addition, strategies are emerging for the manipulation of multigenic defenses such as lignin deposition and synthesis of phytoalexin antibiotics by overexpression of genes encoding rate determining steps, modification of transcription factors or other regulatory genes, and engineering production of novel phytoalexins by inter-species transfer of biosynthetic genes. The imminent cloning of disease resistance genes, further molecular dissection of stress signal perception and transduction mechanisms, and identification of genes that affect symptom development will provide attractive new opportunities for enhancing crop protection. Combinatorial integration of these novel strategies into ongoing breeding programs should make an important contribution to effective, durable field resistance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keen, N.T. 1990. Gene-for-gene complementarity in plant-pathogen interactions. Annu. Rev. Genet. 24: 447–463.
Keen, N.T. and Staskawicz, B. 1988. Host range determinants in plant pathogens and symbionts. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 42: 421–440.
Bennetzen, J.L. and Jones, J.D.G. 1992. Approaches and progress in the molecular cloning of plant disease resistance genes. In: Genetic Engineering: Principles and Methods, Vol 14. Setlow, J.K. (Ed.). Plenum Press, NY. In press.
Lamb, C.J., Lawton, M.A., Dron, M. and Dixon, R.A. 1989. Signals and transduction mechanisms for activation of plant defenses against microbial attack. Cell 56: 215–224.
Bowles, D.J. 1990. Defense-related proteins in higher plants. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 59: 873–907.
Dixon, R.A. and Lamb, C.J. 1990. Molecular communication in interactions between plants and microbial pathogens. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 41: 339–367.
Carr, J.P. and Klessig, D.F. 1989. The pathogenesis related proteins of plants, p. 65–109. In: Genetic Engineering: Principles and Methods, Vol 11. Setlow, J.K. (Ed.). Plenum Press, NY.
Lawton, M.A. and Lamb, C.J. 1987. Transcriptional activation of plant defense genes by fungal elicitor, wounding and infection. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7: 335–341.
Hedrick, S.A., Bell, J.N., Boller, T. and Lamb, C.J. 1988. Chitinase cDNA cloning and mRNA induction by fungal elicitor, wounding and infection. Plant Physiol. 86: 182–186.
Cramer, C.L., Ryder, T.B., Bell, J.N. and Lamb, C.J. 1985. Rapid switching of plant gene expression by fungal elicitor. Science 227: 1240–1243.
Bell, J.N., Dixon, R.A., Bailey, J.A., Rowell, P.M. and Lamb, C.J. 1984. Differential induction of chalcone synthase mRNA activity at the onset of phytoalexin accumulation in compatible and incompatible plant-pathogen interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81: 3384–3388.
Bell, J.N., Ryder, T.B., Wingate, V.P.M., Bailey, J.A. and Lamb, C.J. 1986. Differential accumulation of plant defense gene transcripts in a compatible and an incompatible plant-pathogen interaction. Mol. Cell. Biol. 6: 1615–1623.
Ku'c, J. 1982. Induced immunity to plant disease. BioScience 32: 854–860.
Ward, E.R., Uknes, S., Williams, S.C., Dincher, S.S., Wiederhold, D.L., Alexander, D., Métraux, J.-P. and Ryals, J.A. 1991. Coordinate gene activity in response to agents that induce systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 3: 1085–1094.
Smith, J.A., Hammerschmidt, R. and Fulbright, D.W. 1991. Rapid induction of systemic resistance in cucumber by Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 39: 79–94.
Dixon, R.A. and Harrison, M.J. 1990. Activation, structure and organization of genes involved in microbial defense in plants. Adv. Genet. 28: 165–234.
Mauch, F., Mauch-Mani, B. and Boller, T. 1988. Antifungal hydrolases in pea tissue. II. Inhibition of fungal growth by combinations of chitinase and β-1,3-glucanases. Plant Physiol. 88: 936–942.
Broglie, K., Chet, I., Holliday, M., Cressman, R., Biddle, P., Knowlton, C., Mauvais, C.J. and Broglie, R. 1991. Transgenic plants with enhanced resistance to the fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia solani. Science 254: 1194–1197.
Neuhaus, J.-M., Ahl-Goy, P., Hinz, U., Flores, U. and Meins, F. 1991. High-level expression of a tobacco chitinase gene in Nicotiana sylvestris. Susceptibility of transgenic tobacco plants to Cercospora nicotianae. Plant Mol. Biol. 16: 141–151.
Endo, Y., Tsurugi, K. and Ebert, R.F. 1988. The mechanism of action of barley toxin: a type 1 ribosome-inactivating protein with RNA N-glycosidase activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 954: 224–226.
Roberts, W.K. and Selitrennikoff, C.P. 1986. Isolation and partial characterization of two antifungal proteins from barley. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 880: 161–170.
Stirpe, F. and Hughes, R.C. 1989. Specificity of ribosome-inactivating proteins with RNA N-glycosidase activity. Biochem. J. 262: 1001–1002.
Leah, R., Tommerup, H., Svendsen, I. and Mundy, J. 1991. Biochemical and molecular characterization of three anti-fungal proteins from barley seed. J. Biol. Chem. 266: 1564–1573.
Logemann, J., Jach, G., Tommerup, H., Mundy, J. and Schell, J. 1992. Expression of a barley ribosome-inactivating protein leads to increased fungal protection in transgenic tobacco plants. Bio/Technology 10: 305–308.
Spooner, R. and Lord, J.M. 1990. Immunotoxins: status and prospects. TIBTECH 8: 189–193.
Cutt, J.R., Harpster, M.H., Dixon, D.C., Carr, J.P., Dunsmuir, P. and Klessig, D.F. 1989. Disease response to tobacco mosaic virus in transgenic tobacco plants that constitutively express the pathogenesis-related PR1b gene. Virology 173: 89–97.
Linthorst, H.J.M., Meuwissen, R.L.J., Kauffmann, S. and Bol, J.F. 1989. Constitutive expression of pathogenesis-related proteins PR-1, GRP, and PR-S in tobacco has no effect on virus infection. Plant Cell 1: 285–291.
Alexander, D., Goodman, R.M., Rella, M.G., Glascock, C., Weymann, K., Friedrich, L., Maddox, D., Ahl Goy, P., Luntz, T., Ward, E. and Ryals, J. 1992. Resistance to downy mildew in transgenic tobacco expressing pathogenesis-related protein 1a. Submitted.
Woloshuk, C.P., Meulenhoff, J.S., Sela-Buurlage, M., van den Elzen, P.J.M. and Cornelissen, B.J.C. 1991. Pathogenesis-induced proteins with inhibitory activity toward Phytophthora infestans. Plant Cell 3: 619–628.
Neale, A.D., Wahleithner, J.A., Lund, M., Bonnett, H.T., Kelly, A., Meeks-Wagner, D.R., Peacock, W.L. and Dennis, E.S. 1990. Chitinase, β-1,3-glucanase, osmotin and extensin are expressed in tobacco explants during flower formation. Plant Cell 2: 673–684.
Lotan, T., Ori, N. and Fluhr, R. 1989. Pathogenesis-related proteins are developmentally regulated in tobacco flowers. Plant Cell 1: 881–887.
Ori, N., Sessa, G., Lotan, T., Himmelhoch, S. and Fluhr, R. 1990. A major stylar matrix polypeptide (sp41) is a member of the pathogenesis-related proteins superclass. EMBO J. 9: 3429–3436.
De Jong, A.K., Cordewener, J., Lo Schiavo, F., Terzi, M., Vanderkerckhove, J., Van Kammen, A. and De Vries, S.C. 1992. A carrot somatic embryo mutant is rescued by chitinase. Plant Cell 4: 425–433.
Chrispeels, M.J. and Raikhel, N.V. 1991. Lectins, lectin genes and their role in plant defense. Plant Cell 3 1–9.
Broekaert, W.F., Van Parijs, J., Leyus, F., Joos, H. and Penmans, W.J. 1989. A chitin-binding lectin from stinging nettle rhizomes with antifungal properties. Science 245: 1100–1102.
Lerner, D.R. and Raikhel, N.V. 1992. The gene for stinging nettle lectin (Urtica dioica agglutinin) encodes both a lectin and a chitinase. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 11085–11091.
Howie, W., Newbigin, E., Joe, L., Penzes, E., Suslow, T. and Dunsmuir, P. 1992. Resistance to Rhizoctonia solani in transgenic tobacco. Abstract, Sixth Intl. Symp. Mol. Plant-Microb. Inter., Seattle.
Handelsman, J. and Parke, J.L. 1989. Mechanisms in biocontrol of soilborne plant pathogens, p. 27–610 In: Plant-Microbe Interactions: Molecular and Genetic Perspectives. Vol 3. Kosuge, T. and Nester, E.W. (Eds.). McGraw-Hill, NY
Nordeen, R.O. and Owens, L.D. 1992. Introduction of an antibacterial cecropin gene in tobacco plants. Plant Physiol. 99: Abstract S279.
Düring, K., Fladung, M. and Lörz, H. 1992. Antibacterial resistance of transgenic potato plants producing T4 lysozyme. Abstract, Sixth Intl. Symp. Mol. Plant-Microb. Inter., Seattle.
Dixon, R.A., Dey, P.M. and Lamb, C.J. 1983. Phytoalexins: Enzymology and molecular biology. Adv. Enzymol. Relat. Areas Mol. Biol. 55: 1–135.
Elkind, Y., Edwards, R., Mavandad, M., Hedrick, S.A., Ribak, O., Dixon, R.A. and Lamb, C.J. 1990. Abnormal development and down-regulation of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis in transgenic tobacco containing a heterologous phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87: 9057–9061.
Gunia, W., Hinderer, W., Wittkampf, U. and Barz, W. 1991. Elicitor induction of cytochrome P450 monooxygenases in cell suspension cultures of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) and their involvement in pterocarpan phytoalexin biosynthesis. Z. Naturforsch. 46C 58–66.
Lagrimini, L.M., Burkhart, W., Moyer, M. and Rothstein, S. 1987. Molecular cloning of complementary DNA encoding the lignin-forming peroxidase from tobacco: molecular analysis and tissue-specific expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84: 7542–7546.
Bradley, D.J., Kjellbom, P. and Lamb, C.J. 1992. Elicitor- and wound-induced oxidative cross-linking of a plant cell wall proline-rich protein: A novel, rapid defense response. Cell 70: 21–30.
Kolattukudy, P.E. 1992. Plant-fungal communication that triggers genes for breakdown and reinforcement of host defensive barriers, p. 65–83. In: Molecular Signals in Plant-Microbe Communication. Verma, D.P.S. (Ed.) CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Dittrich, H. and Kutchan, T.M. 1991. Molecular cloning, expression, and induction of berberine bridge enzyme, an enzyme essential to the formation of benzophenanthridine alkaloids in the response of plants to pathogenic attack. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 9969–9973.
Songstandt, D.D., De Luca, V., Brisson, N., Kurz, W.G.W. and Nessler, C.L. 1990. High levels of tryptamine accumulation in transgenic tobacco expressing tryptophan decarboxylase. Plant Physiol. 94: 1410–1413.
Dangl, J.L. 1991 Regulatory elements controlling developmental and stress-induced expression of phenylpropanoid genes, p. 78–83. In: Plant Gene Research, Vol. 8, Genes Involved in Plant Defense. Boller, T. and Meins, F. (Eds.). Springer-Verlag, NY.
Liang, X., Dron, M., Schmid, J., Dixon, R.A. and Lamb, C.J. 1989. Developmental and environmental regulation of a phenylalanine ammonia-lyase-β-glucuronidase gene fusion in transgenic tobacco plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 9284–9288.
Schmid, J., Doerner, P.W., Clouse, S.D., Dixon, R.A. and Lamb, C.J. 1990. Developmental and environmental regulation of a bean chalcone synthase promoter in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell 2: 619–631.
Zhu, Q., Doerner, P.W. and Lamb, C.J. 1992. Developmental and stress regulation of a rice chitinase gene promoter in transgenic tobacco. Plant J. In press.
van de Löcht, U., Meier, I., Hahlbrock, K. and Somssich, I. 1990. A 125 bp promoter fragment is sufficient for strong elicitor-mediated gene activation in parsley. EMBO J. 9: 2945–2950.
Dron, M., Clouse, S.D., Dixon, R.A., Lawton, M.A. and Lamb, C.J. 1988. Glutathione and fungal elicitor regulation of a plant defense gene promoter in electroporated protoplasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85: 6738–6742.
Lois, R., Dietrich, A., Hahlbrock, K. and Schulz, W. 1989. A phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene from parsley: Structure, regulation and identification of elicitor and light-responsive cis-acting elements. EMBO J. 8: 1641–1648.
Lawton, M.A., Clouse, S.D. and Lamb, C.J. 1990. Glutathione-elicited changes in chromatin structure within the promoter of the defense gene chalcone synthase. Plant Cell Rep. 8: 561–564.
Yu, L., Lamb, C.J. and Dixon, R.A. 1992. Purification and biochemical characterization of two proteins which bind to the H-box cis-element implicated in transcriptional activation of plant defense genes. Submitted.
Loake, G.J., Faktor, O., Lamb, C.J. and Dixon, R.A. 1992. Combination of H-box and G-box cis-elements is necessary for feedforward stimulation of a chalcone synthase promoter by the phenylpropanoid pathway intermediate p-coumaric acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. In press.
Katagiri, F. and Chua, N.-H. 1991. Plant transcription factors: present knowledge and future challenges. Trends Genet. 8 22–27.
VanEtten, H.D., Matthews, D.E. and Matthews, P.S. 1989. Phytoalexin detoxification: importance for pathogenicity and practical implications. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 27: 143–164.
Hain, R., Bieseler, B., Kindl, H., Schröder, G. and Stöcker, R. 1990. Expression of a stilbene synthase gene in Nicotiana tabacum results in synthesis of the phytoalexin resveratrol. Plant Mol. Biol. 15: 325–335.
Lois, A.F. and West, C.A. 1990. Regulation of expression of the casbene synthase gene during elicitation of castor bean seedlings with pectic fragments. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 276: 270–277.
Hohn, T.M. and Ohlrogge, J.B. 1991. Expression of a fungal sesquiterpene cyclase gene in transgenic tobacco. Plant Physiol. 97: 460–462.
Paiva, N.L., Edwards, R., Sun, Y., Hrazdina, G. and Dixon, R.A. 1991. Stress responses in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). XI. Molecular cloning and expression of alfalfa isoflavone reductase, a key enzyme of isoflavonoid phytoalexin biosynthesis. Plant Mol. Biol. 17: 653–667.
Tiemann, K., Inzé, D., van Montagu, M. and Barz, W. 1991. Pterocarpan phytoalexin biosynthesis in elicitor-challenged chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) cell cultures. Purification, characterization and cDNA cloning of NADPH : isoflavone oxidoreductase. Eur. J. Biochem. 200: 751–757.
Bless, W. and Barz, W. 1988. Isolation of pterocarpan synthase, the terminal enzyme of pterocarpan phytoalexin biosynthesis in cell suspension cultures of Cicer arietinum. FEBS Lett. 235: 47–50.
Sun, Y., Wu, Q., VanEtten, H.D. and Hrazdina, G. 1991. Stereoisomerism in plant disease resistance: induction and isolation of the 7,2′-dihydroxy-4′,5′ methylenedioxyisoflavone reductase, an enzyme introducing chirality during synthesis of isoflavonoid phytoalexins in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 284: 167–173.
Ingham, J.L., Keen, N.T. and Hymowitz, T. 1977. A new isoflavone phytoalexin from fungus-inoculated stems of Glycine wightii. Phyto-chemistry 16: 1943–1946.
Woodward, M.D. 1979. Phaseoluteone and other 5-hydroxyisoflavonoids from Phaseolus vulgaris. Phytochemistry 18: 363–365.
Turbek, C.S., Li, D., Choi, G.H., Schardl, C.I. and Smith, D.A. 1990. Induction and purification of kievitone hydratase from Fusarium solani f.sp. phaseoli. Phytochemistry 29: 2841–2846.
Lane, G.A., Sutherland, O.R.W. and Skipp, R.A. 1987. Isoflavonoids as insect feeding deterrents and antifungal components from roots of Lupinus augustifolius. J. Chem. Ecol. 13: 771–783.
Biggs, D.R.M., Welle, R., Visser, F.R. and Grisebach, H. 1987. Dimethylallylpyrophosphate : 3,9-dihydroxypterocarpan 10-dimethylallyl transferase from Phaseolus vulgaris. FEBS Lett. 220: 223–226.
Welle, R. and Grisebach, H. 1988. Induction of phytoalexin synthesis in soybean: enzymatic cyclization of prenylated pterocarpans to glyceollin isomers. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 263: 191–198.
Edwards, R. and Dixon, R.A. 1991. Isoflavone o-methyltransferase activities in elicitor-treated cell suspension cultures of Medicago sativa. Phytochemistry 30: 2597–2606.
Preisig, C.L., Matthews, D.E. and VanEtten, H.D. 1991. Purification and characterization of S-adenosyl-L-methionine : 6a-hydroxymaackiain 3-o-methyltransferase from Pisum sativum. Plant Physiol. 91: 559–566.
Bennetzen, J.L., Qin, M.-M., Ingels, S. and Ellingboe, A.H. 1988. Allele-specific and mutator-associated instability at the Rp1 disease resistance locus of maize. Nature 332: 369–370.
Hulbert, S.H. and Bennetzen, J.L. 1991. Recombination at the Rp1 locus of maize. Mol. Gen. Genet. 226: 377–382.
Kearney, B. and Staskawicz, B.J. 1990. Widespread distribution and fitness contribution of Xanthomonas campestris avirulence gene avrBs2. Nature 346: 385–387.
Keen, N.T. 1992. The molecular biology of disease resistance. Plant Mol. Biol. 19: 109–122.
Keen, N., Tamaki, S., Kobayashi, D., Gerhold, M., Shen, H., Gold, S., Lorang, J., Thordal-Christensen, H., Dahlbeck, D. and Staskawicz, B. 1990. Bacteria expressing avirulence gene D produce a specific elicitor of the soybean hypersensitive reaction. Mol. Plant-Microb. Inter. 3: 112–121.
van Kan, J.A.L., van den Ackerveken, G.F.J.M. and de Wit, P.J.G.M. 1991. Cloning and characterization of cDNA of avirulence gene avr9 of the fungal pathogen Cladosporium fulvum, causal agent of tomato leaf mold. Mol. Plant-Microb. Inter. 4: 52–59.
Debener, T., Lehnachers, H., Arnold, M. and Dangl, J.L. 1991. Identification and molecular mapping of a single Arabidopsis thaliana locus determining resistance to a phytopathogenic Pseudomonas syringae isolate. Plant J. 1: 289–302.
Dangl, J., Debener, T., Lehnackers, H., Ritter, C., Gerwin, M. and Vivian, A. 1992. Genetic approaches to an understanding of the HR in Arabidopsis thaliana: Towards cloning of the RPM1 resistance gene. Abstract S38, Sixth Intl. Symp. Plant-Microb. Inter., Seattle.
Sarfatti, M., Schaffer, M., Segal, G., Fluhr, R. and Zamir, D. 1991. Tomato recombinant inbreds direct a chromosome walk towards a Fusarium resistance gene. Abstract 1299, Intl. Soc. Plant Mol. Biol., Third Intl. Congr., Tucson.
Martin, G., Ganal, M. and Tanksley, S. 1992. Towards map-based cloning of the Pto resistance gene from tomato. Abstract 356, Intl. Symp. Plant Microb. Inter., Seattle.
Cosio, E.G., Frey, T. and Ebel, J. 1992. Identification of a high-affinity binding protein for a hepta-β-glucoside phytoalexin elicitor in soybean. Eur. J. Biochem. 204: 1115–1123.
Nespoulous, C., Huet, J.-C. and Pernollet, J.-C. 1992. Structure-function relationships of α and β elicitins, signal proteins involved in the plant-Phytophthora interaction. Planta 186: 551–557.
Pearce, G., Strydom, D., Johnson, S. and Ryan, C.A. 1991. A polypeptide from tomato leaves induces wound-inducible proteinase inhibitor proteins. Science 253: 895–898.
McGurl, B., Pearce, G., Orozco-Cardenas, M. and Ryan, C.A. 1992. Structure, expression, and antisense inhibition of the systemin precursor gene. Science 255: 1570–1573.
Raskin, I. 1992. Salicylate, a new plant hormone. Plant Physiol. 99: 799–803.
Chen, Z. and Klessig, D.F. 1991. Identification of a soluble salicylic acid-binding protein that may function in signal transduction in the plant disease-resistance response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 8179–8183.
Stab, M.R. and Ebel, J. 1987. Effects of Ca2+ on phytoalexin induction by fungal elicitor in soybean cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 257: 416–423.
Scheel, D., Colling, C., Hedrich, R., Kawalleck, P., Parker, J.E., Sacks, W.R., Somssich, I.E. and Hahlbrock, K. 1991. Signals in plant defense gene activation, p. 373–380. Adv. Mol. Genet. Plant-Microb. Inter. Vol 1. Hennecke, H. and Verma, D.P.S. (Eds.). Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Knight, M.R., Campbell, A.K., Smith, S.M. and Trewavas, A.J. 1991. Transgenic plant aequorin reports the effects of touch and cold-shock and elicitor on cytoplasmic calcium. Nature 352: 524–526.
Mathieu, Y., Kurkdjian, A., Xia, H., Guern, J., Koller, A., Spiro, M.D., O'Neill, M., Albersheim, P. and Darvill, A. 1991. Membrane responses induced by oligogalacturonides in suspension cultured tobacco cells. Plant J. 1: 333–343.
Farmer, E.E., Moloshok, T.D., Saxton, M.J. and Ryan, C.A. 1991. Oligosaccharide signaling in plants: Specificity of oligouronide-enhanced plasma membrane protein phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 266: 3140–3145.
Dietrich, A., Mayer, J.E. and Hahlbrock, K. 1990. Fungal elicitor triggers rapid, transient and specific protein phosphorylation in parsley cell suspension cultures. J. Biol. Chem. 265: 6360–6368.
Felix, G., Grosskopf, D.G., Regengass, M. and Boller, T. 1991. Rapid changes of protein phosphorylation are involved in transduction of the elicitor signal in plant cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 8831–8834.
Sutherland, M.W. 1991. The generation of oxygen radicals during host plant responses to infection. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 39: 79–94.
Apostol, I., Heinstein, P.F. and Low, P.S. 1989. Rapid stimulation of an oxidative burst during elicitation of cultured plant cells. Plant Physiol. 90: 109–116.
Sharma, Y.K., Sathasivan, K. and Mehdy, M.C. 1992. Positive and negative regulation of bean mRNA levels by fungal elicitor involves early cellular redox changes. Abstract P279, Sixth Intl. Symp. Plant-Microb. Inter., Seattle.
Baggiolini, M. and Wyman, M.P. 1990. Turning on the respiratory burst. Trends Biochem. Sci. 15 69–75.
Shapiro, B.M. 1991. The control of oxidant stress at fertilization. Science 252: 533–536.
Schreck, R., Rieber, P. and Bauerle, P.A. 1991. Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of the NF-KB transcription factor and HIV-1. EMBO J. 10: 2247–2258.
Sekizawa, Y. and Mase, S. 1981. Mode of controlling action of probenazole against rice blast disease with reference to the induced resistance mechanism in rice plants. J. Pesticide Sci. 6: 91–94.
Sekizawa, Y., Haga, M., Iwata, M., Hamamoto, A., Chihara, C. and Takino, Y. 1985. Probenazole and burst of respiration in rice leaf tissue infected with blast fungus. J. Pesticide Sci. 10: 225–231.
Métraux, J.P., Ahl Goy, P., Staub, T., Speich, J., Steinemann, A., Ryals, J. and Ward, E. 1991. Induced resistance in cucumber in response to 2,6-dichloroisonicotinic acid and pathogens, p. 432–439. In: Adv. Mol. Genet. Plant-Microb. Inter., Vol 1. Hennecke, H. and Verma, D.P.S. (Eds.). Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Yoshida, H., Konishi, K., Nakagawa, T., Sekido, S. and Yamaguchi, I. 1990. Characteristics of N-phenylsulfonyl-2-chloroisonicotinamide as an anti-rice blast agent. J. Pesticide Sci. 15: 199–203.
Uknes, S., Mauch-Mani, B., Moyer, M., Potter, S., Williams, S., Dincher, S., Chandler, D., Slusarenko, A., Ward, E. and Ryals, J. 1992. Acquired resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 4: 645–656.
Métraux, J.P., Signer, H., Ryals, J., Ward, E., Wyss-Benz, M., Gaudin, J., Raschdorf, K., Schmid, E., Blum, W. and Inverardi, B. 1990. Increase in salicylic acid at the onset of systemic acquired resistance in cucumber. Science 250: 1004–1006.
Yalpani, N., Silverman, P., Wilson, T.M.A., Kleier, D.A. and Raskin, I. 1991. Salicylic acid is a systemic signal and an inducer of pathogenesis-related proteins in virus-infected tobacco. Plant Cell 3: 809–818.
Bostock, R.M., Ku'c, J.A. and Laine, R.A. 1981. Eicosapentaenoic acid and arachidonic acids from Phytophthora infestans elicit fungitoxic sesquiterpenes in the potato. Science 212: 67–69.
Farmer, E.E. and Ryan, C.A. 1992. Octadecanoid-derived signals in plants. Trends Cell Biol. 2: 236–241.
Doerner, P.W., Stermer, B., Schmid, J., Dixon, R.A. and Lamb, C.J. 1990. Plant defense gene promoter-reporter gene fusions in transgenic plants: tools for identification of novel inducers. Bio/Technology 8: 845–848.
Yoder, O.C. 1980. Toxins in pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 18: 103–129.
De la Fuente, J.M., Mosqueda-Cano, G., Alvarez-Morales, A. and Herrera-Estrella, L. 1992. Expression of a bacterial phaseolotoxin-resistant ornithyl transcarbamylase in transgenic tobacco plants confers resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola. Bio/Technology 10: 905–909.
Anzai, H., Yoneyama, K. and Yamaguchi, I. 1989. Transgenic tobacco resistant to a bacterial disease by the detoxification of a pathogenic toxin. Mol. Gen. Genet. 219: 492–494.
Meeley, R.B., Johal, G.S., Briggs, S.P. and Walton, J.D. 1992. A biochemical phenotype for a disease resistance gene of maize. Plant Cell 4: 71–77.
Hahn, M.G., Bucheli, P., Cervone, F., Doares, S.H., O'Neill, R.A., Darvill, A.G. and Albersheim, P. 1989. The roles of cell wall constituents in plant-pathogen interactions, p. 131–181. In: Plant-Microbe Interactions, Vol 3. Nester, E. and Kosuge, T. (Eds.). MacMillan, NY.
Toubart, P., Desiderio, A., Salvi, G., Cervone, F., Daroda, L., De Lorenzo, G., Bergmann, C., Darvill, A.G. and Albersheim, P. 1992. Cloning and characterization of the gene encoding the endopolygalacturonase-inhibiting protein (PGIP) of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant J. 2: 367–373.
Cervone, F., Hahn, M.G., De Lorenzo, G., Darvill, A. and Albersheim, P. 1989. Host-pathogen interactions XXXIII. A plant protein converts a fungal pathogenicity factor into an elicitor of plant defense responses. Plant Physiol. 90: 542–548.
Bent, A.F., Innes, R.W., Ecker, J.R. and Staskawicz, B.J. 1992. Disease development in ethylene-insensitive Arabidopsis thaliana infected with virulent and avirulent Pseudomonas and Xanthomonas pathogens. Mol. Plant-Microb. Inter. In press.
Vögeli, U. and Chappell, J. 1990. Regulation of a sesquiterpene cyclase in cellulase-treated tobacco cell suspension cultures. Plant Physiol. 94: 1860–1866.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamb, C., Ryals, J., Ward, E. et al. Emerging Strategies for Enhancing Crop Resistance to Microbial Pathogens. Nat Biotechnol 10, 1436–1445 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1192-1436
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1192-1436
This article is cited by
-
Over-expression of Osmotin (OsmWS) gene of Withania somnifera in potato cultivar ‘Kufri Chipsona 1’ imparts resistance to Alternaria solani
Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC) (2020)
-
Generation of white mold disease-resistant sunflower plants expressing human lysozyme gene
Biologia plantarum (2006)
-
Flavonoid Biosynthetic Pathway and Cereal Defence Response: An Emerging Trend in Crop Biotechnoloy
Journal of Plant Biochemistry and Biotechnology (1999)