Abstract
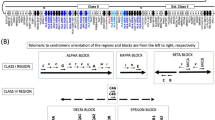
We discuss the genetic organization of the human major histocompatibility complex (the HLA region), and review recent advances in HLA typing achieved by analysis at the DNA level. The use of HLA Class II DNA probes, labelled either with 32P or non–radioactively, has revealed polymorphisms not detectable with conventional serologic typing reagents. These DNA polymorphisms, identified by restriction fragment length analyses, or by allele–specific oligonucleotide probes, have proved informative in transplantation tissue–typing, paternity determinations, and for disease susceptibility studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bodmer, W.F. 1984. The HLA System, 1984, p.11–22. In: Histocompatibility Testing. E. D. Albert, M. P. Baur, and W. R. Mayr (eds.). Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Trowsdale, J., Young, J.A.T., Kelly, A.P., Austin, P.J., Carson, S., Meunier, H., So, A., Erlich, H.A., Spielman, R.S., Bodmer, J., and Bodmer, W.F. 1985. Structure, sequence, and polymorphism in the HLA-D region. Immunological Reviews 85:5–43.
Korman, A.J., Boss, J.M., Spies, T., Sorrentino, R., Okada, K., and Strominger, J.L. 1985. Genetic complexity and expression of human Class II histocompatibility antigens. Immunological Reviews 85:45–86.
Rollini, P., Mach, B., and Gorski, J. 1985. Linkage map of three HLA-DRβ chain genes: Evidence for a recent duplication event. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:7197–7201.
Gorski, J., Tosi, R., Strubin, M., Rabourdin-Combe, C., and Mach, B. 1985. Serological and immunochemical analysis of the products of a single HLA-DRα and DRβ chain gene expressed in a mouse cell line after DNA-mediated cotransformation reveals that the β chain carries a known supertypic specificity. J. Exp. Med. 162:105–116.
Spies, T., Sorrentino, R., Boxx, J.M., Okada, K., and Strominger, J.L. 1985. Structural organization of the DR subregion of the human major histocompatibility complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:5165–5169.
Baur, M.P., Albert, E.D., and Mayr, W.R. 1984. The Central Data Analysis of the Ninth Workshop, p 37–51. In: Histocompatibility Testing. E. D. Albert, M. P. Baur, and W. R. Mayr (eds.). Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Erlich, H., Horn, G., Bugawan, T., and Scharf, S. 1986. The molecular analysis of HLA class II gene polymorphism. In: Perspectives in Immunogenetics and Histocompatibility, Volume 7. B. Schaecter et al.(ed.). Elsevier, in press.
Weyand, C.M., Goronzy, J., and Fathman, C.G. 1986. Human T-cell clones used to define functional epitopes on HLA class II molecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:762–766
Ryder, L.P., Svejgaard, A., and Dausset, J. 1982. Genetics of HLA disease association. Ann. Rev. Genet. 15:169–187.
Zmijewski, C.M. 1984. HLA and disease. CRC Critical Reviews in Clinical Lab. Sci. 20:285–370.
Reinsmoen, N.L. and Bach, F.H. 1982. Five HLA-D clusters associated with HLA-DR4. Hum. Immunol. 4:249–258.
Nepom, B.S., Nepom, G.T., Mickelson, E., Antonelli, P., and Hansen, J.S. 1983. Electrophoretic analysis of human HLA-DR antigens from HLA-DR4 homozygous cell lines: correlation between β-chain diversity and HLA-D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:6962–6966.
Trowsdale, J., Kelly, A., Lee, J., Carson, S., Austin, P., and Travers, P. 1984. Linkage map of two HLA-SBβ genes and two HLA-SBα-related genes: an intron in one of the SBβ genes contains a processed pseudogene. Cell 38:241–249.
Okada, K., Prentice, H.L., Boss, J.M., Levy, D.J., Kappes, D., Spies, T., Raghupathy, R., Mengler, R.A., Auffray, C., and Strominger, J.L. 1985. SB subregion of the human major histocompatibility complex: gene organization, allelic polymorphism and expression in transformed cells. EMBO J. 4:739–748.
Servenius, B., Gustafsson, K., Widmark, E., Emmoth, E., Anderson, G., Larhammer, D., Rask, L., and Peterson, P.A. 1984. Molecular map of the human HLA-SB (HLA-DP) region and sequence of an SBα (DPα) pseudogene. EMBO J. 3:3209–3214.
Erlich, H., Lee, J.S., Petersen, J.W., Bugawan, T., and DeMars, R. 1986. Molecular analysis of HLA class I and class II antigen loss mutants reveals a homozygous deletion of the DR, DQ, and part of the DP region: implications for class II gene order. Hum. Immunol. 16:205–219.
Bohme, J., Andersson, M., Hammerling, U., Andersson, G., Moller, E., Peterson, P.A., and Rask, L. 1985. HLA-DRβ genes vary in number between different DR specificities whereas the number of DQβ genes is constant. J. Immunol. 135:2149–2155.
Schwartz, D.C., and Cantor, C.R. 1984. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell 37:67–75.
Carle, G.F., Frank, M., and Olson, M.V. 1986. Electrophoretic separations of large DNA molecules by periodic inversion of the electric field. Science 232:65–68.
Hardy, D., Bell, J.D., Long, E.O., Lindsten, T., and McDevitt, H.O. 1986. Pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis mapping of the class II region of the human major histocompatibility complex. Nature, in press.
Stetler, D., Grumet, F.C., and Erlich, H. 1985. Polymorphic restriction endonuclease sites linked to the HLA-DRα gene: localization and use as genetic markers of insulin-dependent diabetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:8100–8104.
Cohen, D., Paul, P., Le Gall, I., Marcadet, A., Font, M.P., Cohen-Haguenauer, O., Sayagh, B., Cann, H., Lalouel, J.M., and Dausset, J. 1985. DNA polymorphism of HLA Class I and Class II Regions. Immunological Reviews 85:87–105.
Arnheim, N., Strange, C., and Erlich, H. 1985. Use of pooled DMA samples to detect linkage disequilibrium of polymorphic restriction fragments and human disease: studies of the HLA class II loci. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:6970–6974.
Wake, C.T., Long, E.O., and Mach, B. 1982. Allelic polymorphism and complexity of the genes for HLA-DRβ chains—direct analysis by DNA-DNA hybridization. Nature 300:372–374.
Andersson, M., Bohme, J., Andersson, G., Moller, E., Thorsby, E., Rask, L., and Peterson, P.A. 1984. Genomic hybridization with class II transplantation antigen cDNA probes as a complementary technique in tissue typing. Hum. Immunol. 11:57–67.
Stetler, D., Das, H., Nunberg, J.H., Saiki, R., Sheng-Dong, R., Mullis, K.B., Weissman, S.M., and Erlich, H.A. 1982. Isolation of a cDNA clone for the human HLA-DR antigen α chain by using a synthetic oligonucleotide as a hybridization probe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79:5966–5970.
Langer, P.R., Waldrop, A.A., and Ward, D.C. 1981. Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78:6633–6637.
Sheldon, E., Kellogg, D.A., Watson, R., Bloch, W., Levenson, C., and Erlich, H. 1986. The use of nonisotopic M13 probes for genetic analysis: application to HLA class II loci. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, in press.
Conner, B.J., Reyes, A.A., Morin, C., Itakura, K., Teplitz, R.L., and Wallace, R.B. 1983. Detection of sickle cell βS-globin allele by hybridization with synthetic oligonucleotides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:272–282.
Mullis, K., and Faloona, F. 1986. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase catalyzed chain reaction. Meth. Enzym., in press.
Saiki, R., Scharf, S., Faloona, F., Mullis, K., Horn, G., Erlich, H., and Arnheim, N. 1985. Enzymatic amplification of β-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science 230:1350–1354.
Saiki, R., Bugawan, T., Horn, G., Mullis, K., and Erlich, H.A. 1986. Genetic analysis of enzymatically amplified β-globin and HLA-DQα genomic DNA with allele specific oligonucleotide probes. Nature, in press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erlich, H., Sheldon, E. & Horn, G. HLA Typing Using DNA Probes. Nat Biotechnol 4, 975–981 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1186-975
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1186-975
This article is cited by
-
The distribution of HLA DQA1 and D1S80 (pMCT118) alleles and genotypes in the populations of Galicia and Central Portugal
International Journal of Legal Medicine (1993)
-
DRB1*LY10 — a newDRB1 allele and its haplotypic association
Immunogenetics (1990)
-
DNA polymorphism and the study of disease associations
Human Genetics (1988)