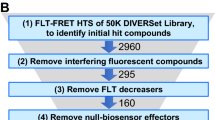
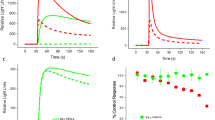
Abstract
The interaction of the N-type calcium channel β3 subunit with the α1B subunit alters the activation/inactivation kinetics and the maximal conductance of the channel. The defined protein-protein interaction of the human α1B and β3 subunits provides a target for small-molecule modulation of N-type channel activity. We describe a high throughput screen based on a counterseiection yeast two-hybrid assay, which was used to identify small molecules that disrupt α1B-β3 subunit interactions and inhibit N-type calcium channel activity. These small molecules may be a new class of calcium channel antagonists with therapeutic potential.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dunlap, K., Luebke, J.L, and Turner, T.J. 1995 Exocytotic Ca2+ channels in mammalian central neurons. Trends Neurosci. 18: 89–98.
Newcomb, R. and Palma, A. Effects of diverse omega-conopeptldes on the in vivo release of glutamic and gamma-aminobutyric acids. Brain Res. 638: 95–102. (1994).
Valentino, K., Newcomb, R., Gadbois, T., Singh, T., Bowersox, S., Bitner, S. et al. 1993. Selective N-type calcium channel antagonist protects against neuronal loss after global cerebral ischemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 7894–7897.
Qin, N., Platano, D., Olcese, R., Stefani, E., and Birnbaumer, L. 1997. Direct interaction of G β/γ with a C-terminal G β/γ-binding domain of the Ca2+ channel α1 subunit is responsible for channel inhibition by G protein-coupled receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 8866–8871.
Walker, D., Bichet, D., Campbell, K.P., and De Waard, M. 1998. A β4 isoform-specific interaction site in the carboxyl-terminal region of the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel α1 A subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 2361–2367.
Page, K.M., Canti, C., Stephens, G.J., Berrow, N.S., and Dolphin, A.C. 1998. Identification of the amino terminus of neuronal Ca2+ channel α1 submits α1B and α1E as an essential determinant of G-protein modulation. J. Neurosci. 18: 4815–4824.
Zamponi, G.W., Bourinet, E., Nelson, D., Nargeiot, J., and Snutch, T.P. 1997. Crosstalk between G-proteins and protein kinase C mediated by the calcium channel a1 subunit. Nature 385: 442–446.
De Waard, M., Liu, H., Walker, D., Scott, V.E., Scott, S., CA.et al. 1997. Direct binding of G-protein β/γ complex to voltage-dependent calcium channels. Nature. 385: 446–450.
Walker, D. and De Waard, M. 1998. Subunit interaction sites in voltage-dependent Ca+2 channels: role in channel function. Trends Neurosci. 21: 148–154.
Stea, A., Dubel, S.J., Pragnell, M., Leonard, J.P., Campbell, K., and Snutch, T.P. A β-subunit normalizes the electrophysiological properties of a cloned N-type Ca2+ channel α1,-subunit.Neuropharmacology 32: 1103–1116.
Anwyl, R. 1991. Modulation of vertebrate neuronal calcium channels by transmitters. Brain Res 16: 265–281.
Hille, B. 1994. Modulation of ion-channel function by G-protein-coupled receptors. Trends Neurosci. 17: 531–536.
De Waard, M., Pragnell, M., and Campbell, K. 1994. Ca2+ channel regulation by a conserved β subunit domain. Neuron 13: 495–593.
Pragnell, M., De Waard, M., Mori, Y., Tanabe, T., Snutch, T.P., and Campbell, K., 1997. Calcium channel β-subunit binds to conserved motif in the l-ll cytoplasmic linker. Nature 368: 67–70.
De Waard, M., Witcher, D.R., Pragnell, M., Liu, H., and Campbell, K. 1995. Properties of the α,-β anchoring site in voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 12056–12064.
Fields, S. and Song, O. 1989. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature 340: 245–256.
Bean, B.P. 1989. Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium currents by changes in channel voltage dependence. Nature 340: 153–155.
Mintz, I.M. and Bean, B.P. 1993. Block of calcium channels in rat neurons by synthetic omega-aga-iva. Neuropharmacology 32: 1161–1169.
Herlitze, S., Garcia, D.E., Mackie, K., Hille, B., Scheuer, T., and Catterall, W.A., 1996. Modulation of Ca2+ channels by G-protein βγ subunits. Nature 380: 258–261.
Ikeda, S.R. 1996. Voltage-dependent modulation of N-type calcium channels by G-protein βγ subunits. Nature 380: 255–258.
Huang, J. and Schreiber, S. 1997. A yeast genetic system for selection of small molecule inhibitors of protein-protein interaction in nanodroplets.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 13396–13401.
Vidal, M., Braun, P., Chen, E., Boeke, J.D., and Harlow, E. 1996. Genetic characterization of a mammalian protein-protein interaction by using a yeast reverse two-hybrid system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 10321–10326.
Leanna, M. and Hannick, M. 1996. The reverse two-hybrid system: a genetic scheme for selection against specific protein-protein interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 24: 3341–3347.
Shih, H-M. Godman, P.S., DeMaggis, A.J., Hollenberg, S.M., Goodman, K.H., and Hoekdstra, M.F. 1997. A positive genetic selection for disrupting protein-protein interactions: identification of CREB mutations that prevent association with the co-activator CBP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 13896–13901.
Manlatis, T., Fritsch, E.F., and Sambrook, J. 1992. Molecular cloning. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Finney, M. 1993. Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley & Sons, New York.
Ellinor, P.T., Zhang, J.F., Randall, A.D., Zhou, M., Schwarz, T.L., Tsien, R.W. et al. 1993. Functional expression of a rapidly inactivating neuronal calcium channel. Nature 363: 455–458.
Durfee, T., Becherer, K., Chen, P.-L., Yeh, S.-H., Yang, Y., Kilburn, A.E., Lee, W.-H., and Elledge, S.J., 1993. The retinoblastoma protein associates with the protein phosphatase type 1 catalytic subunit. Genes Dev. 7: 555–569.
Collin, T., Lory, P., Taviaux, S., Courtieu, C., Guilbault, P., Berta, P. et al. 1994. Cloning, chromosomal location and functional expression of the human voltage-dependent calcium channel β3 subunit. Eur. J. Biochem 220: 257–262.
Castellano, A., Wei, X., Birnbaumer, L., and Perez-Reyes, E., 1993. Cloning and expression of a third calcium channel β subunit. J. Biol. Chem 268: 3450–3455.
Hullin, R., Singer-Lahat, D., Freichel, M., Biel, M., Oascal, N., Hofmann, F. et al. 1992. Calcium channel β subunit heterogeneity: functional expression of cloned cDNA from heart, aorta and brain. EMBO J. 11: 885–890.
Harper, J.W., Adami, G.R., Wei, N., Kayomarsi, K., and Elledge, S.J. 1993. The p21 Cdk interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin dependent kinases. Cell 75: 805–816.
Elledge, S.J. and Davis, R.W. 1988. A family of versatile centromeric vectors designed for use in the sectoring-shuffle mutagenesis assay in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene 70: 303–312.
Kaufer, N.F., Fried, H.M., Schwindinger, W.F., Jasin, M., and Warner, J.R. Cyclohexlmide resistance in yeast; the gene and its protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 11: 3123–3235.
Yocum, R.R., Hanley, S., West, R., and Ptashne, M. 1984. Use of lacZ fusions to delimit regulatory elements of the inducible divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 4: 1985–1988.
Price, L., Kajkowski, E.M., Hadcock, J.R., Ozenberger, B.A., and Pausch, M.A. 1995. Functional coupling of a mammalian somatostatin receptor to the yeast pheromone response pathway. Mol. Cell Biol. 15: 6188–6195.
Hill, J.E., Myers, A.M., Koerner, T.J., and Tzagoloff, A. 1986. Yeast/E.coli shuttle vectors with multiple unique restriction sites. Yeast 2: 163–167.
Bai, C. and Elledge, S.J. 1997. Gene identification using the two-hybrid system. Methods Enzymol. 283: 141–156.
Ozenberger, B.A. and Young, K.H. 1995. Functional interacton of ligands and receptors o the hematopoietic superfamily n yeast. Mol. Endocrinol. 9: 1321–1329.
Rose, M.D. Winston, R. and Young, K.H. 1990. Methods in yeast genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbour, NY.
Plummer, M.R., Rittenhouse, A., Kanevsky, M., and Hess, P. 1991. Neurotransmitter modulation of calcium channels in rat sympathetic neurons. J. Neuroscience. 11: 2339–2348.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Young, K., Lin, S., Sun, L. et al. Identification of a calcium channel modulator using a high throughput yeast two-hybrid screen . Nat Biotechnol 16, 946–950 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1098-946
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1098-946
This article is cited by
-
Gγ recruitment systems specifically select PPI and affinity-enhanced candidate proteins that interact with membrane protein targets
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Identification of potential inhibitors based on compound proposal contest: Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes as a target
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Multiplex single-molecule interaction profiling of DNA-barcoded proteins
Nature (2014)
-
The Amino-terminal domain of tntegrin β3 functions as a transcriptional activator in yeast
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2006)
-
Identification of small-molecule inhibitors of interaction between the BH3 domain and Bcl-xL
Nature Cell Biology (2001)