Abstract
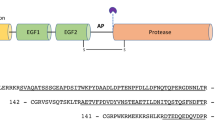
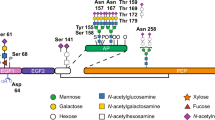
Human Protein C (HPC), an antithrombotic factor with potential clinical utility, is a vitamin K-dependent protein that has several complex post-translational modifications. In an effort to define the functional roles of these modifications, recombinant HPC (rHPC) was expressed in and characterized from 3 adenovirus-transformed cell lines. The rHPC in crude culture medium from the 3 cell lines displayed anticoagulant activities that were either higher, slightly lower or much lower than that of plasma HPC. The rHPC from each cell line was purified and characterized using a novel, but simple chromatographic method, termed “pseudo-affinity”, capable of resolving molecules differing by only very slight modifications. We demonstrate the critical dependence of full γ-carboxylation on the function of this protein. In addition, our data indicate that both the γ-carboxyglutamate and glycosyl contents affect the functional activities of rHPC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Esmon, C.T. 1989. The role of Protein C and thrombomodulin in the regulation of blood coagulation. J. Biol. Chem. 264: 4743–4746.
Stenflo, J. 1988. The biochemistry of Protein C, p. 21–53. In: Protein C and Related Proteins. Bertina, R. M. (Ed.). Churchill Livingstone, New York.
Suttie, J.W. 1986. Report of workshop on expression of vitamin K- dependent proteins in bacterial and mammalian cells. Thrombosis Res. 44: 129–134.
Foster, D.C., Rudinski, M.S., Schach, B.G., Berkner, K.L., Kumar, A.A., Hagen, F.S., Sprecher, C.A., Insley, M.Y. and Davie, E.W. 1987. Propeptide of human Protein C is necessary for gamma-carboxylation. Biochem. 26: 7003–7011.
Suttie, J.W., Hoskins, J.A., Engelke, J., Hopfgartner, A., Ehrlich, H., Bang, N.U. Belagaje, R.M., Schoner, B. and Long, G.L. 1987. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase: possible role of the substrate “Propeptide” as an intracellular recognition site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84: 634–637.
Stenflo, J., Holme, E., Lindstedt, S., Chandramouli, N., Tsai-Huang, L.H., Tam, J.P. and Merrifield, R.B. 1989. Hydroxylation of aspartic acid in domains homologous to the epidermal growth factor precursor is catalysed by a 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 444–447.
Derian, C.K., VanDusen, W., Prysiecki, C.T., Walsh, P.N., Berkner, K.L., Kaufman, R.J. and Friedman, P.A. 1989. Inhibitors of 2-ketoglutarate-deendent dioxygenase block aspartyl beta-hydroxylation of recombinant human Factor IX in several mammalian expression system. J. Biol. chem. 264: 6615–6618.
Gronke, R.S., VanDusen, W.J., Garsky, V.M., Jacobs, J.W., Sardana, M.K., Stern, A.M. and Friedman, P.A. 1989. Aspartyl-beta-hydroxylase: In vitro hydroxylation of a synthetic peptide based on the structure of the first growth factor-like domain of human factor IX. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 3609–3613.
Ohlin, A., Landes, G., Bourdon, P., Oppenheimer, C., Wydro, R. and Stenflo, J. 1988. Beta-hydroxyaspartic acid in the first epidermal growth factor-like domain of Protein C. J. Biol. Chem. 263: 19240–19248.
Rees, D.J.G., Jones, I.M., Handford, P.A., Walter, S.J., Esnouf, M.P. Smith, K.J. and Brownlee, G.G. 1988. The role of beta-hydroxyaspartate and adjacent carboxylate residues in the first EGF domain of human Factor IX. EMBO J. 7: 2053–2061.
Stenflo, J. and Fernlund, P. 1982. Amino acid sequence of the heavy chain of bovine Protein C. J. Biol. chem. 257: 12180–12190.
Titani, K., Kumar, S., Takio, K., Ericsson, L.H., Wade, R.D., Ashida, K., Walsh, K.A., Chopek, M.W., Sadler, J.E. and Fujikawa, K. 1986. Amino acid sequence of human von Willebrand Factor. Biochem. 25: 3171–3184.
Yan, S.C., Grinnell, B.W. and Wold, F. 1989. Posttranslational modifications of proteins: some problems left to solve. Trends in Biological Sci. 14: 264–268.
Grinnell, B.W., Berg, D.T., Walls, J. and Yan, S.B. 1987. Transactivated expression of fully gamma-carboxylated recombinant human Protein C, an antithrombotic factor. Bio/Technology 5: 1189–1192.
Berg, D.T., Walls, J.D. and Grinnell, B.W. 1988. A variant enhancer/regulatory region from a cloned human prototype BK virus genome. Nuc. Acids Res. 16: 9057.
Beckman, R.J., Schmidt, R.J., Santerre, R.F., Plutzky, J., Crabtree, G.R. and Long, G.L. 1985. The structure and evolution of a 461 amino acid human Protein C precursor and its messenger RNA, based upon the DNA sequence of cloned human liver cDNAs. Nuc. Acids Res. 13: 5233–5247.
Grinnell, B.W., Berg, D.T. and Walls, J. 1986. Activation of the adenovirus and BK virus late promotors: Effects of the BK virus enhancer and trans-acting viral early proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 6: 3596–3605.
Kuwada, M. and Katayama, K. 1983. An improved method for the determination of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid in proteins, bone and urine. Anal. Biochem. 131: 173–179.
Alvarez-Coque, M.C.G., Hernandez, M.J.M., Camanas, R.M.V. and Fernandez, C.M. 1989. Formation and instability of o-phthalaldehyde derivatives of amino acids. Anal. Biochem. 178: 1–7.
de Monitgny, P., Stobaugh, J.F., Givens, R.S., Carlson, R.G., Srinivasachar, K., Sternson, L.A. and Higuchi, T. 1987. Reversed-phase HPLC separation of dimethylaminoazobenzene sulfonyl and dimethylaminoazobenzene thiohydantoin-amino acid derivatives for amino acid analysis and microsequencing studies at the pmole level. Anal. Chem. 59: 1096–1101.
Hardy, M.R., Townsend, R.R. and Lee, Y.C. 1988. Monosaccharide analysis of glycoconjugates by anion exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection. Anal. Biochem. 170: 54–62.
Laemmli, U.K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685.
Bradford, M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive methhod for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254.
Stenflo, J. 1976. A new vitamin K-dependent protein. J. Biol. Chem. 251: 355–363.
Johnson, A.E., Esmon, N.L., Laue, T.M. and Esmon, C.T. 1983. Structural changes required for activation of protein C are induced by Ca2+ binding to a high affinity site that does not contain gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 258: 5554–5560.
Kisiel, W. and Davie, E.W. 1981. Protein C. Meth. Enzymol. 80: 320–332.
Borowski, M., Furie, B.C., Goldsmith, G.H. and Furie, B. 1985. Metal and phospholipid binding properties of partially carboxylated human prothrombin variants. J. Biol. Chem. 260: 9258–9264.
Fernlund, P. and Stenflo, J. 1982. Amino acid sequence of the light chain of bovine Protein C. J. Biol. Chem. 257: 12170–12179.
Green, E.D. and Baenziger, J.U. 1988. Asparagine-linked oligosaccharides on lutropin, follitropin and thyrotropin. J. Biol. Chem. 263: 25–35.
Defize, L.H.K., Arndl-Jovin, D.J., Jovin, T.M., Boonstra, J., Meisenhelder, J., Hunter, T., de Hey, H.T. and de Laat, S.W. 1988. A 431 cell variants lacking the blood group A antigen display increased high affinity epidermal growth factor-receptor number, protein-tyrosine kinase activity, and receptor turnover. J. Cell Biol. 107: 939–949.
Miletich, J.P. and Broze, G.J. 1988. Human beta-Protein C is not glycosylated at the fourth N-linked site. Blood 72: 371a.
Hau, L. and Salem, H.H. 1988. The effect of enzymatic removal of sialic acids on the functional properties of Protein C. Thrombosis & Haemostasis 60: 267–270.
Kaufman, R.J., Wasley, L.C., Furie, B.C., Furie, B. and Shoemaker, C.B. 1986. Expression, purification and characterization of recombinant gamma-carboxylated Factor IX synthesized in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J. Biol. Chem. 261: 9622–9628.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, S., Razzano, P., Chao, Y. et al. Characterization and Novel Purification of Recombinant Human Protein C from Three Mammalian Cell Lines. Nat Biotechnol 8, 655–661 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0790-655
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0790-655