Abstract
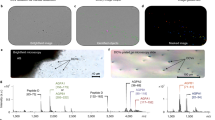
New sampling protocols combined with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) allow the assay of single dense core vesicles. Understanding the packaging of vesicles is important as vesicles are the quanta of information for intercellular communication. Using vesicles from the exocrine atrial gland of Aplysia californica as the model, a wide range of bioactive peptides are detected within each vesicle. Although the expression of the egg-laying hormone gene family of type 1 atrial gland cells has been previously examined, chemical characterization of individual 1–2 μm diameter vesicles demonstrates that products from several genes are colocalized. The mass sensitivity of MALDI MS can be further improved to enable the analysis of even smaller subcellular organelles.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kreiner, T., Sossin, W. & Scheller, R.H. Localization of Aplysianeurosecretory peptides to multiple populations of dense core vesicles. J. Cell Biol. 102, 769–782 (1986).
Mahon, A.C. et al. Structure and expression of the egg-laying hormone gene family in Aplysia. J. Neurosci. 5, 1872–1880 (1985).
Kurosky, A. et al. Expression and genetic variation of the Aplysia egg-laying hormone gene family in the atrial gland. Invertebrate Neurosci. 2, 261–271 (1997).
Rothman, B.S. et al. Isolation and primary structure of the califins, three biologically active egg-laying hormone-like peptides from the atrial gland of Aplysia californica. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 1616–1623 (1986).
Nagle, G.T., Painter, S.D., Blankenship, J.E., Dixon, J.D. & Kurosky, A. Evidence for the expression of three genes encoding homologous atrial gland peptides that cause egg laying in Aplysia. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 7853–7859 (1986).
Nagle, G.T., Painter, S.D., Blankenship, J.E. & Kurosky, A. Proteolytic processing of egg-laying hormone-related precursors in Aplysia. Identification of peptide regions critical for biological activity. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 9223–9237 (1988).
Nagle, G.T., van Heumen, W.R.A., El-Hamzawy, M.A. & Kurosky, A. Purification and characterization of Aplysia atrial gland secretory granules containing egg-laying prohormone-related peptides. Peptides 15, 101–108 (1994).
van Heumen, W.R.A., Nagle, G.T. & Kurosky, A. Ultrastructural localization of egg-laying prohormone-related peptides in the atrial gland of Aplysia californica. Cell Tiss. Res. 279, 13–24 (1995).
Chiu, D.T. et al. Probing single secretory vesicles with capillary electrophoresis. Science 279, 1190–1193 (1998).
Lillard, S.J. et al. Separation and characterization of amines from individual atrial gland vesicles of Aplysia californica. Anal. Chem. 70, 3517–3524 (1998).
Dreisewerd, K., Kingston, R., Geraerts, W.P.M. & Li, K.W. Direct mass spectrometric peptide profiling and sequencing of nervous tissues to identify peptide involved in male copulatory behavior in Lymnaea stagnalis. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Processes 169, 291–299 (1997).
Li, L. et al. Mass spectrometric survey of interganglionically transported peptides in Aplysia. Peptides 19, 1425–1433 (1998).
Redeker, V. Toullec, J. -Y., Vinh, J., Rossier, J. & Soyez, D. Combination of peptide profiling by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry and immunodetection on single glands or cells. Anal. Chem. 70, 1805–1811 (1998).
Jiménez, C.R. et al. Neuropeptide expression and processing as revealed by direct matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry of single neurons. J. Neurochem. 62, 404–407 (1994).
Garden, R.W., Moroz, L.L., Moroz, T.P., Shippy, S.A. & Sweedler, J.V. Excess salt removal with matrix rinsing: direct peptide profiling of neurons from marine invertebrates using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 31, 1126–1130 (1996).
Li, L., Golding, R.E. & Whittal, R.M. Analysis of single mammalian cell lysates by mass spectrometry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118, 11662–11663 (1996).
van Strien, F.J.C., Jesperson, S., van der Greef, J., Jenks, B.G. & Roubos, E.W. Identification of POMC processing products in single melanotrope cells by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. FEBS Lett. 379, 165–170 (1996).
Worster, B.M., Yeoman, M.S. & Benjamin, P.R. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometric analysis of the pattern of peptide expression in single neurons resulting from alternative mRNA splicing of the FMRFamide gene. Eur. J. Neurosci. 10, 3489–3507 (1998).
Chiu, D.T. & Zare, R.N. Assaying for peptides in individual Aplysia neurons with mass spectrometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 3338–3340 (1998).
Karas, M. & Hillenkamp, F. Laser desorption ionization of proteins with molecular masses exceeding 10,000 daltons. Anal. Chem. 60, 2299–2301 (1988).
Jespersen, S., Chaurand, P., van Strien, F.J.C., Spengler, B. & van der Greef, J. Direct sequencing of neuropeptides in biological tissue by MALDI-PSD mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 71, 660–666 (1999).
Li, L. Garden, R.W., Romanova E.V., Sweedler, J.V. In situ sequencing of peptides from biological tissues and single cells using MALDI-PSD/CID analysis. Anal. Chem. 71, 5451–5458 (1999).
Moore, S.K., Kauer, F.W., Begnoche, V.L. & Mayeri, E. A novel neuroactive peptide from the atrial gland of Aplysia. Soc. Neurosci. Abs. 22, 696 (1996).
Jespersen, S. et al. Attomole detection of proteins by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry with the use of picoliter vials. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 8, 581–584 (1994).
Solouki, T., Marto, J.A., White, F.M., Guan, S. & Marshall, A.G. Attomole biomolecule mass analysis by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance. Anal. Chem. 67, 4139–4144 (1995).
Allmaier, G. Picoliter to nanoliter deposition of peptide and protein solutions for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 11, 1567–1569 (1997).
Önnerfjord, P., Nilsson, J., Wallman, L., Laurell, T. & Marko-Varga, G. Picoliter sample preparation in MALDI-TOF MS using a micromachined silicon flow-through dispenser. Anal. Chem. 70, 4755–4760 (1998).
Zhang, H.Y., Andren, P.E. & Caprioli, R.M. Micro-preparation procedure for high-sensitivity matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 30, 1768–1771 (1995).
Toomre, D., Keller, P., White, J., Olivo, J. & Simons, K. Dual-color visualization of trans-Golgi network to plasma membrane traffic along microtubules in living cells. J. Cell Sci. 112, 21–33 (1999).
Hirschberg, K. et al. Kinetic analysis of secretory protein traffic and characterization of golgi to plasma membrane transport intermediates in living cells. J. Cell Biol. 143, 1485–1503 (1998).
Cauli, B. et al. Molecular and physiological diversity of cortical nonpyramidal cells. J. Neurosci. 17, 3894–3906 (1997).
Caprioli, R. M., Farmer, T. B. & Gile, J. Molecular imaging of biological samples: localization of peptides and proteins using MALDI-TOF MS. Anal. Chem. 69, 4751–4560 (1997).
Garden, R.W. & Sweedler, J.V. Heterogeneity within MALDI samples as revealed by mass spectrometric imaging, Anal. Chem. 71, 30–36 (2000).
Acknowledgements
We thank Gregg Nagle and Sherry Painter for insightful comments about atrial gland peptides, and we thank Christian Reilly for assistance with animal collection. This work is supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, and the Dreyfus Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubakhin, S., Garden, R., Fuller, R. et al. Measuring the peptides in individual organelles with mass spectrometry. Nat Biotechnol 18, 172–175 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/72622
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/72622
This article is cited by
-
MS-based proteomic analysis of cardiac response to hypoxia in the goldfish (Carassius auratus)
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Subcellular Peptide Localization in Single Identified Neurons by Capillary Microsampling Mass Spectrometry
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Nanomanipulation-Coupled Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/ Ionization-Direct Organelle Mass Spectrometry: A Technique for the Detailed Analysis of Single Organelles
Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry (2016)
-
Biomolecular Imaging with a C60-SIMS/MALDI Dual Ion Source Hybrid Mass Spectrometer: Instrumentation, Matrix Enhancement, and Single Cell Analysis
Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry (2014)
-
Mechanical Tension Modulates Local and Global Vesicle Dynamics in Neurons
Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering (2012)