Abstract
Replying to B. Heinemann et al. Nature 514, 10.1038/nature13688 (2014)
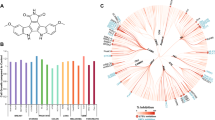
We welcome the accompanying Comment1 by Heinemann et al., in which the authors use an extensive panel of sensitive KDM assays to independently confirm our results2 that GSK-J1 is a potent KDM6 inhibitor. Additionally, Heinemann et al.1 demonstrate that GSK-J1 has some, albeit weaker, activity towards KDM5B and KDM5C, for which we only had preliminary data available at the time of our original publication. As our jumonji assay portfolio expands, we have continued to update the GSK-J1 activity profile on the SGC website (http://www.thesgc.org/chemical-probes/GSKJ1); this includes KDM5 inhibition activity by GSK-J1 similar to that reported by Heinemann. In conclusion, GSK-J1 remains the most selective KDM inhibitor yet disclosed and thus a valuable chemical tool.
Similar content being viewed by others
Main
Heinemann et al.1 also show a broader, weak micromolar KDM inhibitory activity of the ester pro-drug version of GSK-J1, GSK-J4. GSK-J4 is not itself a chemical tool for direct KDM inhibition, but was designed specifically to enable efficient intracellular delivery of GSK-J1 into macrophages. In our work, the intracellular conversion of ester pro-drug is complete within 15 min after which levels of intracellular GSK-J4 are negligible ([GSK-J4] = 150 nM; [GSK-J1] = 11.8 μM). This renders the activity profile of GSK-J4 irrelevant and the biological effects in macrophages will be exclusively driven by the activity of GSK-J1. For other cell systems, it is essential to assess the ability to convert GSK-J4 to GSK-J1 before conducting and interpreting biological studies.
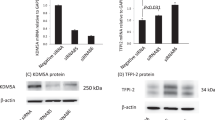
Despite the refinement of the selectivity profile of GSK-J1, our conclusion that KDM6 enzymatic activity is a key determinant of lipopolysaccharide responses in macrophages stands and was independently verified using short interfering RNA (siRNA) mediated knockdown of KDM6 enzymes. GSK-J1 remains a useful chemical probe for studying the catalytic function of KDM6 and the additional KDM5 activity may provide new opportunities for its use.
References
Heinemann, B. et al. Inhibition of demethylases by GSK-J1/J4. Nature 514, http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature13688 (2014)
Kruidenier, L. et al. A selective jumonji H3K27 demethylase inhibitor modulates the proinflammatory macrophage response. Nature 488, 404–408 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kruidenier, L., Chung, Cw., Cheng, Z. et al. Kruidenier et al. reply. Nature 514, E2 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13689
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13689
This article is cited by
-
A KDM6 inhibitor potently induces ATF4 and its target gene expression through HRI activation and by UTX inhibition
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
KDM6B is an androgen regulated gene and plays oncogenic roles by demethylating H3K27me3 at cyclin D1 promoter in prostate cancer
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
Therapeutic effect of a histone demethylase inhibitor in Parkinson’s disease
Cell Death & Disease (2020)
-
The great escape: tumour cell plasticity in resistance to targeted therapy
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.