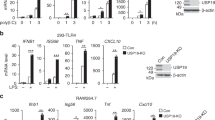
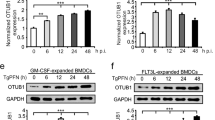
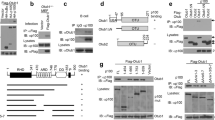
Abstract
The non-canonical NF-κB pathway forms a major arm of NF-κB signalling that mediates important biological functions, including lymphoid organogenesis, B-lymphocyte function, and cell growth and survival1,2,3. Activation of the non-canonical NF-κB pathway involves degradation of an inhibitory protein, TNF receptor-associated factor 3 (TRAF3), but how this signalling event is controlled is still unknown1,2. Here we have identified the deubiquitinase OTUD7B as a pivotal regulator of the non-canonical NF-κB pathway. OTUD7B deficiency in mice has no appreciable effect on canonical NF-κB activation but causes hyperactivation of non-canonical NF-κB. In response to non-canonical NF-κB stimuli, OTUD7B binds and deubiquitinates TRAF3, thereby inhibiting TRAF3 proteolysis and preventing aberrant non-canonical NF-κB activation. Consequently, the OTUD7B deficiency results in B-cell hyper-responsiveness to antigens, lymphoid follicular hyperplasia in the intestinal mucosa, and elevated host-defence ability against an intestinal bacterial pathogen, Citrobacter rodentium. These findings establish OTUD7B as a crucial regulator of signal-induced non-canonical NF-κB activation and indicate a mechanism of immune regulation that involves OTUD7B-mediated deubiquitination and stabilization of TRAF3.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dejardin, E. The alternative NF-κB pathway from biochemistry to biology: pitfalls and promises for future drug development. Biochem. Pharmacol. 72, 1161–1179 (2006)
Sun, S. C. The noncanonical NF-κB pathway. Immunol. Rev. 246, 125–140 (2012)
Razani, B., Reichardt, A. D. & Cheng, G. Non-canonical NF-κB signaling activation and regulation: principles and perspectives. Immunol. Rev. 244, 44–54 (2011)
Senftleben, U. et al. Activation of IKKα of a second, evolutionary conserved, NF-κB signaling pathway. Science 293, 1495–1499 (2001)
Xiao, G., Harhaj, E. W. & Sun, S. C. NF-κB-inducing kinase regulates the processing of NF-κB2 p100. Mol. Cell 7, 401–409 (2001)
Liao, G., Zhang, M., Harhaj, E. W. & Sun, S. C. Regulation of the NF-κB-inducing kinase by tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3-induced degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 26243–26250 (2004)
Vallabhapurapu, S. et al. Nonredundant and complementary functions of TRAF2 and TRAF3 in a ubiquitination cascade that activates NIK-dependent alternative NF-κB signaling. Nature Immunol. 9, 1364–1370 (2008)
Zarnegar, B. J. et al. Noncanonical NF-κB activation requires coordinated assembly of a regulatory complex of the adaptors cIAP1, cIAP2, TRAF2 and TRAF3 and the kinase NIK. Nature Immunol. 9, 1371–1378 (2008)
Coornaert, B., Carpentier, I. & Beyaert, R. A20: central gatekeeper in inflammation and immunity. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 8217–8221 (2009)
Harhaj, E. W. & Dixit, V. M. Regulation of NF-κB by deubiquitinases. Immunol. Rev. 246, 107–124 (2012)
Evans, P. C. et al. Isolation and characterization of two novel A20-like proteins. Biochem. J. 357, 617–623 (2001)
Lee, E. G. et al. Failure to regulate TNF-induced NF-κB and cell death responses in A20-deficient mice. Science 289, 2350–2354 (2000)
Häcker, H. et al. Specificity in Toll-like receptor signalling through distinct effector functions of TRAF3 and TRAF6. Nature 439, 204–207 (2006)
Oganesyan, G. et al. Critical role of TRAF3 in the Toll-like receptor-dependent and -independent antiviral response. Nature 439, 208–211 (2006)
Bremm, A., Freund, S. M. & Komander, D. Lys11-linked ubiquitin chains adopt compact conformations and are preferentially hydrolyzed by the deubiquitinase Cezanne. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 17, 939–947 (2010)
Enesa, K. et al. NF-κB suppression by the deubiquitinating enzyme Cezanne: a novel negative feedback loop in pro-inflammatory signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 7036–7045 (2008)
Hooper, L. V. & Macpherson, A. J. Immune adaptations that maintain homeostasis with the intestinal microbiota. Nature Rev. Immunol. 10, 159–169 (2010)
Dohi, T. et al. Elimination of colonic patches with lymphotoxin beta receptor-Ig prevents Th2 cell-type colitis. J. Immunol. 167, 2781–2790 (2001)
Gommerman, J. L. & Browning, J. L. Lymphotoxin/light, lymphoid microenvironments and autoimmune disease. Nature Rev. Immunol. 3, 642–655 (2003)
Lorenz, R. G., Chaplin, D. D., McDonald, K. G., McDonough, J. S. & Newberry, R. D. Isolated lymphoid follicle formation is inducible and dependent upon lymphotoxin-sufficient B lymphocytes, lymphotoxin β receptor, and TNF receptor I function. J. Immunol. 170, 5475–5482 (2003)
Bouskra, D. et al. Lymphoid tissue genesis induced by commensals through NOD1 regulates intestinal homeostasis. Nature 456, 507–510 (2008)
Wang, Y. et al. Lymphotoxin beta receptor signaling in intestinal epithelial cells orchestrates innate immune responses against mucosal bacterial infection. Immunity 32, 403–413 (2010)
Xie, P., Stunz, L. L., Larison, K. D., Yang, B. & Bishop, G. A. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3 is a critical regulator of B cell homeostasis in secondary lymphoid organs. Immunity 27, 253–267 (2007)
Xu, Y., Cheng, G. & Baltimore, D. Targeted disruption of TRAF3 leads to postnatal lethality and defective T-dependent immune responses. Immunity 5, 407–415 (1996)
Xie, P., Kraus, Z. J., Stunz, L. L., Liu, Y. & Bishop, G. A. TNF receptor-associated factor 3 is required for T cell-mediated immunity and TCR/CD28 signaling. J. Immunol. 186, 143–155 (2011)
Kayagaki, N. et al. DUBA: a deubiquitinase that regulates type I interferon production. Science 318, 1628–1632 (2007)
Chang, M., Jin, W. & Sun, S. C. Peli1 facilitates TRIF-dependent Toll-like receptor signaling and proinflammatory cytokine production. Nature Immunol. 10, 1089–1095 (2009)
Evans, P. C. et al. A novel type of deubiquitinating enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 23180–23186 (2003)
Reiley, W., Zhang, M., Wu, X., Graner, E. & Sun, S.-C. Regulation of the deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD by IκB kinase γ-dependent phosphorylation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 3886–3895 (2005)
Anders, R. A., Subudhi, S. K., Wang, J., Pfeffer, K. & Fu, Y. X. Contribution of the lymphotoxin β receptor to liver regeneration. J. Immunol. 175, 1295–1300 (2005)
Lomada, D., Liu, B., Coghlan, L., Hu, Y. & Richie, E. R. Thymus medulla formation and central tolerance are restored in IKKα−/− mice that express an IKKα transgene in keratin 5+ thymic epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 178, 829–837 (2007)
Morrison, M. D., Reiley, W., Zhang, M. & Sun, S. C. An atypical tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor-binding motif of B cell-activating factor belonging to the TNF family (BAFF) receptor mediates induction of the noncanonical NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 10018–10024 (2005)
Hassink, G. C. et al. The ER-resident ubiquitin-specific protease 19 participates in the UPR and rescues ERAD substrates. EMBO Rep. 10, 755–761 (2009)
Reiley, W. W. et al. Deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD negatively regulates the ubiquitin-dependent kinase Tak1 and prevents abnormal T cell responses. J. Exp. Med. 204, 1475–1485 (2007)
Ota, N. et al. IL-22 bridges the lymphotoxin pathway with the maintenance of colonic lymphoid structures during infection with Citrobacter rodentium . Nature Immunol. 12, 941–948 (2011)
Acknowledgements
We thank Z. Chen and P. Evans for expression vectors and J. Browning and Biogen for the anti-LTβR antibody. We also thank the personnel from the flow cytometry, DNA analysis, animal facility, and histology core facilities at The MD Anderson Cancer Center for technical assistance. This study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (AI057555, AI064639 and GM84459 to S.-C.S.; CA137059 to T.Z.; T32CA009598 to G.C.B.) and the Sister Institution Network Fund of MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.H. designed the study, performed experiments, analysed data and wrote part of the manuscript; G.C.B., J.-H.C., N.P.-O., J.J., A.Z., Y. X., X.C. and M.C. contributed to the performance of the experiments, Y.-X.F. contributed critical reagents; C.Z. and T.Z. were involved in the supervision of N.P.-O. and A.Z., respectively, and the discussion of results; and S.-C.S. designed the research and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Figures 1-20 and Supplementary Table 1. (PDF 8125 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, H., Brittain, G., Chang, JH. et al. OTUD7B controls non-canonical NF-κB activation through deubiquitination of TRAF3. Nature 494, 371–374 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11831
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11831
This article is cited by
-
RRS1 knockdown inhibits the proliferation of neuroblastoma cell via PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway
Pediatric Research (2022)
-
OTUD6B-associated intellectual disability: novel variants and genetic exclusion of retinal degeneration as part of a refined phenotype
Journal of Human Genetics (2022)
-
OTUD6A promotes prostate tumorigenesis via deubiquitinating Brg1 and AR
Communications Biology (2022)
-
Regulation of osteoclast-mediated bone resorption by microRNA
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
OTUD5 promotes innate antiviral and antitumor immunity through deubiquitinating and stabilizing STING
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.