Abstract
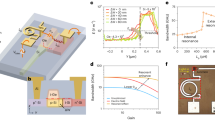
Developing an optical amplifier on silicon is essential for the success of silicon-on-insulator (SOI) photonic integrated circuits. Recently, optical gain with a 1-nm bandwidth was demonstrated using the Raman effect1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9, which led to the demonstration of a Raman oscillator10,11, lossless optical modulation12 and optically tunable slow light13. A key strength of optical communications is the parallelism of information transfer and processing onto multiple wavelength channels. However, the relatively narrow Raman gain bandwidth only allows for amplification or generation of a single wavelength channel. If broad gain bandwidths were to be demonstrated on silicon, then an array of wavelength channels could be generated and processed, representing a critical advance for densely integrated photonic circuits. Here we demonstrate net on/off gain over a wavelength range of 28 nm through the optical process of phase-matched four-wave mixing in suitably designed SOI channel waveguides. We also demonstrate wavelength conversion in the range 1,511–1,591 nm with peak conversion efficiencies of +5.2 dB, which represents more than 20 times improvement on previous four-wave-mixing efficiencies in SOI waveguides14,15,16,17. These advances allow for the implementation of dense wavelength division multiplexing in an all-silicon photonic integrated circuit. Additionally, all-optical delays18, all-optical switches19, optical signal regenerators20 and optical sources for quantum information technology21, all demonstrated using four-wave mixing in silica fibres, can now be transferred to the SOI platform.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Claps, R., Dimitropoulos, D., Raghunathan, V., Han, Y. & Jalali, B. Observation of stimulated Raman amplification in silicon waveguides. Opt. Express 11, 1731–1739 (2003)
Espinola, R. L., Dadap, J. I., Osgood, R. M. Jr, McNab, S. J. & Vlasov, Y. A. Raman amplification in ultrasmall silicon-on-insulator wire waveguides. Opt. Express 12, 3713–3718 (2004)
Liu, A., Rong, H., Paniccia, M., Cohen, O. & Hak, D. Net optical gain in a low loss silicon-on-insulator waveguide by stimulated Raman scattering. Opt. Express 12, 4261–4268 (2004)
Rong, H. et al. Raman gain and nonlinear optical absorption measurements in a low-loss silicon waveguide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 2196–2198 (2004)
Xu, Q., Almeida, V. R. & Lipson, M. Time-resolved study of Raman gain in highly confined silicon-on-insulator waveguides. Opt. Express 12, 4437–4442 (2004)
Liang, T. K. & Tsang, H. K. Efficient Raman amplification in silicon-on-insulator waveguides. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 3343–3345 (2004)
Boyraz, O. & Jalali, B. Demonstration of 11 dB fiber-to-fiber gain in a silicon Raman amplifier. Electron. Express 1, 429–434 (2004)
Xu, Q., Almeida, V. R. & Lipson, M. Demonstration of high Raman gain in a submicrometer-size silicon-on-insulator waveguide. Opt. Lett. 30, 35–37 (2005)
Jones, R. et al. Net continuous wave optical gain in a low loss silicon-on-insulator waveguide by stimulated Raman scattering. Opt. Express 13, 519–525 (2005)
Rong, H. et al. An all-silicon Raman laser. Nature 433, 292–294 (2005)
Rong, H. et al. A continuous-wave Raman silicon laser. Nature 433, 725–728 (2005)
Jones, R. et al. Lossless optical modulation in a silicon waveguide using stimulated Raman scattering. Opt. Express 13, 1716–1723 (2005)
Okawachi, Y. et al. All-optical slow-light on a photonic chip. Opt. Express 14, 2317–2322 (2006)
Fukuda, H. et al. Four-wave mixing in silicon wire waveguides. Opt. Express 13, 4629–4637 (2005)
Espinola, R. L., Dadap, J. I., Osgood, R. M. Jr, McNab, S. J. & Vlasov, Y. A. C-band wavelength conversion in silicon photonic wire waveguides. Opt. Express 13, 4341–4349 (2005)
Yamada, K. et al. All-optical efficient wavelength conversion using silicon photonic wire waveguide. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 18, 1046–1048 (2006)
Rong, H., Kuo, Y. H., Liu, A., Paniccia, M. & Cohen, O. High efficiency wavelength conversion of 10 Gb/s data in silicon waveguides. Opt. Express 14, 1182–1188 (2006)
Sharping, J. E. et al. All-optical, wavelength and bandwidth preserving, pulse delay based on parametric wavelength conversion and dispersion. Opt. Express 13, 7872–7877 (2005)
Lin, Q. et al. 40-Gb/s optical switching and wavelength multicasting in a two-pump parametric device. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 17, 2376–2378 (2005)
Ciaramella, E. & Trillo, S. All-optical reshaping via four-wave mixing in optical fibers. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 12, 849–851 (2000)
Li, X., Voss, P. L., Sharping, J. E. & Kumar, P. Optical-fiber source of polarization-entangled photons in the 1550 nm telecom band. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 053601 (2005)
Hansryd, J., Andrekson, A., Westlund, M., Li, J. & Hedekvist, P. Fiber-based optical parametric amplifiers and their applications. IEEE Select. Topics Quant. Electron. 8, 506–520 (2002)
Tsang, H. K. et al. Optical dispersion, two-photon absorption and self-phase modulation in silicon waveguides at 1.5 µm wavelength. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 416–418 (2002)
Dinu, M., Quochi, F. & Garcia, H. Third-order nonlinearities in silicon at telecom wavelengths. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 2954–2956 (2003)
Foster, M. A., Moll, K. D. & Gaeta, A. L. Optimal waveguide dimensions for nonlinear interactions. Opt. Express 12, 2880–2887 (2004)
Raghunathan, V., Claps, R., Dimitropoulos, D. & Jalali, B. Parametric Raman wavelength conversion in scaled silicon waveguides. J. Lightwave Technol. 23, 2094–2102 (2005)
Turner, A. C. et al. Tailored anomalous-group velocity dispersion in silicon channel waveguides. Opt. Express 14, 4357–4362 (2006)
Dimitropoulos, D., Raghunathan, V., Claps, R. & Jalali, B. Phase-matching and nonlinear optical processes in silicon waveguides. Opt. Express 12, 149–160 (2004)
Almeida, V. R., Panepucci, R. R. & Lipson, M. Nanotapers for compact mode conversion. Opt. Lett. 28, 1302–1304 (2003)
Liang, T. K. & Tsang, H. K. Role of free carriers from two-photon absorption in Raman amplification in silicon-on-insulator waveguides. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 2745–2747 (2004)
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge discussions with Y. Okawachi. This work was supported by the Center for Nanoscale Systems, supported by the NSF and the New York State Office of Science, Technology & Academic Research. M.A.F., J.E.S. and A.L.G. acknowledge support from the DARPA DSO Slow-Light Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Reprints and permissions information is available at npg.nature.com/reprintsandpermissions. The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foster, M., Turner, A., Sharping, J. et al. Broad-band optical parametric gain on a silicon photonic chip. Nature 441, 960–963 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04932
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04932
This article is cited by
-
A conformal mapping approach to broadband nonlinear optics on chip
Nature Photonics (2024)
-
Non-Hermitian topological phase transitions controlled by nonlinearity
Nature Physics (2024)
-
Broadband high-Q multimode silicon concentric racetrack resonators for widely tunable Raman lasers
Nature Communications (2022)
-
A photonic integrated continuous-travelling-wave parametric amplifier
Nature (2022)
-
Robust frequency-upconversion lasing operated at 400 K from inorganic perovskites microcavity
Nano Research (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.