Abstract
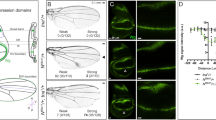
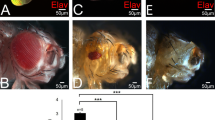
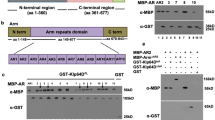
Inappropriate activation of downstream target genes by the oncoprotein β-catenin is implicated in development of numerous human cancers1,2. β-catenin and its fruitfly counterpart Armadillo act as a coactivator in the canonical Wnt/Wingless pathway by binding to Tcf/Lef transcription factors3,4,5,6. Here we report a conserved nuclear protein, named Chibby, which was identified in a screen for proteins that directly interact with the C-terminal region of β-catenin. In mammalian cultured cells we demonstrate that Chibby inhibits β-catenin-mediated transcriptional activation by competing with Lef-1 to bind to β-catenin. Inhibition of Drosophila Chibby by RNA interference results in segment polarity defects that mimick a wingless gain-of-function phenotype, and overexpression of the wingless target genes engrailed and Ultrabithorax. In addition, epistasis experiments indicate that chibby acts downstream of wingless and upstream of armadillo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller, J. R., Hocking, A. M., Brown, J. D. & Moon, R. T. Mechanism and function of signal transduction by the Wnt/β-catenin and Wnt/Ca2 + pathways. Oncogene 18, 7860–7872 (1999)
Polakis, P. Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes Dev. 14, 1837–1851 (2000)
Behrens, J. et al. Functional interaction of β-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature 382, 638–642 (1996)
Molenaar, M. et al. XTcf-3 transcription factor mediates β-catenin-induced axis formation in Xenopus embryos. Cell 86, 391–399 (1996)
Brunner, E., Peter, O., Schweizer, L. & Basler, K. pangolin encodes a Lef-1 homologue that acts downstream of Armadillo to transduce the Wingless signal in Drosophila. Nature 385, 829–833 (1997)
van de Wetering, M. et al. Armadillo coactivates transcription driven by the product of the Drosophila segment polarity gene dTCF. Cell 88, 789–799 (1997)
Peifer, M., Berg, S. & Reynolds, A. B. A repeating amino acid motif shared by proteins with diverse cellular roles. Cell 76, 789–791 (1994)
Hsu, S. C., Galceran, J. & Grosschedl, R. Modulation of transcriptional regulation by LEF-1 in response to Wnt-1 signaling and association with β-catenin. Mol. Cell Biol. 18, 4807–4818 (1998)
Hecht, A., Litterst, C. M., Huber, O. & Kemler, R. Functional characterization of multiple transactivating elements in β-catenin, some of which interact with the TATA-binding protein in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 18017–18025 (1999)
Broder, Y. C., Katz, S. & Aronheim, A. The Ras recruitment system, a novel approach to the study of protein- protein interactions. Curr. Biol. 8, 1121–1124 (1998)
Takemaru, K.-I. & Moon, R. T. The transcriptional coactivator CBP interacts with β-catenin to activate gene expression. J. Cell Biol. 149, 249–254 (2000)
Korinek, V. et al. Constitutive transcriptional activation by a β-catenin-Tcf complex in APC -/- colon carcinoma. Science 275, 1784–1787 (1997)
Yost, C. et al. The axis-inducing activity, stability, and subcellular distribution of β-catenin is regulated in Xenopus embryos by glycogen synthase kinase 3. Genes Dev. 10, 1443–1454 (1996)
Shtutman, M. et al. The cyclin D1 gene is a target of the β-catenin/LEF-1 pathway. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 5522–5527 (1999)
Noordermeer, J., Johnston, P., Rijsewijk, F., Nusse, R. & Lawrence, P. A. The consequences of ubiquitous expression of the wingless gene in the Drosophila embryo. Development 116, 711–719 (1992)
Peifer, M. & Wieschaus, E. The segment polarity gene armadillo encodes a functionally modular protein that is the Drosophila homolog of human plakoglobin. Cell 63, 1167–1176 (1990)
Lee, Y. S. & Carthew, R. W. Making a better RNAi vector for Drosophila: Use of intron spacers. Methods (in the press)
Elbashir, S. M. et al. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 411, 494–498 (2001)
Cadigan, K. M. & Nusse, R. Wnt signaling: a common theme in animal development. Genes Dev. 11, 3286–3305 (1997)
Sanson, B., Alexandre, C., Fascetti, N. & Vincent, J.-P. Engrailed and hedgehog make the range of wingless asymmetric in Drosophila embryos. Cell 98, 207–216 (1999)
Peifer, M., Sweeton, D., Casey, M. & Wieschaus, E. wingless signal and Zeste-white 3 kinase trigger opposing changes in the intracellular distribution of Armadillo. Development 120, 369–380 (1994)
Yu, X., Hoppler, S., Eresh, S. & Bienz, M. decapentaplegic, a target gene of the wingless signalling pathway in the Drosophila midgut. Development 122, 849–858 (1996)
Yu, X., Riese, J., Eresh, S. & Bienz, M. Transcriptional repression due to high levels of Wingless signalling. EMBO J. 17, 7021–7032 (1998)
Garcia-Rostan, G. et al. β-Catenin dysregulation in thyroid neoplasms. Am. J. Pathol. 158, 987–996 (2001)
Fukuchi, T. et al. β-Catenin mutation in carcinoma of the uterine endometrium. Cancer Res. 58, 3526–3528 (1998)
Andrews, N. C. & Faller, D. V. A rapid micropreparation technique for extraction of DNA-binding proteins from limiting numbers of mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 19, 2499 (1991)
Kennerdell, J. R. & Carthew, R. W. Use of dsRNA-mediated genetic interference to demonstrate that frizzled and frizzled2 act in the wingless pathway. Cell 95, 1017–1026 (1998)
Carthew, R. W. in Gene Silencing (ed. Hannon, G.) (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 2003)
Tautz, D. & Pfeifle, C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma 98, 81–85 (1988)
Acknowledgements
We thank R. Holmgren, R. Pestell, M. Waterman and DSHB for reagents; M. Peifer, J. Treisman and Bloomington Stock Center for fly stocks; R. Holmgren, F.-Q. Li and members of the Carthew and Moon laboratories for critically reading the manuscript. This work was supported by postdoctoral fellowships from the Japan Science and Technology Corporation and Uehara Memorial Foundation (to K.-I.T.), the Pew Charitable Trust (to R.W.C.), and by an NIH grant (to R.T.M.). R.T.M. is an Investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takemaru, KI., Yamaguchi, S., Lee, Y. et al. Chibby, a nuclear β-catenin-associated antagonist of the Wnt/Wingless pathway. Nature 422, 905–909 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01570
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01570
This article is cited by
-
Loss of the ciliary protein Chibby1 in mice leads to exocrine pancreatic degeneration and pancreatitis
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Wnt signaling in breast cancer: biological mechanisms, challenges and opportunities
Molecular Cancer (2020)
-
The Wnt/β-catenin/VASP positive feedback loop drives cell proliferation and migration in breast cancer
Oncogene (2020)
-
HOXC-AS1-MYC regulatory loop contributes to the growth and metastasis in gastric cancer
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2019)
-
Chibby suppresses aerobic glycolysis and proliferation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via the Wnt/β-catenin-Lin28/let7-PDK1 cascade
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.