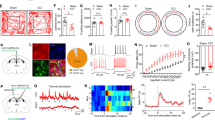
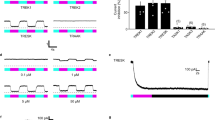
Abstract
Contrary to acute pain, chronic pain does not serve as a warning signal and must be considered as a disease per se. This pathology presents a sensory and psychological dimension at the origin of affective and cognitive disorders. Being largely refractory to current pharmacotherapies, identification of endogenous systems involved in persistent and chronic pain is crucial. The amygdala is a key brain region linking pain sensation with negative emotions. Here, we show that activation of a specific intrinsic neuromodulatory system within the amygdala associated with type 4 metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGlu4) abolishes sensory and affective symptoms of persistent pain such as hypersensitivity to pain, anxiety- and depression-related behaviors, and fear extinction impairment. Interestingly, neuroanatomical and synaptic analysis of the amygdala circuitry suggests that the effects of mGlu4 activation occur outside the central nucleus via modulation of multisensory thalamic inputs to lateral amygdala principal neurons and dorso-medial intercalated cells. Furthermore, we developed optogluram, a small diffusible photoswitchable positive allosteric modulator of mGlu4. This ligand allows the control of endogenous mGlu4 activity with light. Using this photopharmacological approach, we rapidly and reversibly inhibited behavioral symptoms associated with persistent pain through optical control of optogluram in the amygdala of freely behaving animals. Altogether, our data identify amygdala mGlu4 signaling as a mechanism that bypasses central sensitization processes to dynamically modulate persistent pain symptoms. Our findings help to define novel and more precise therapeutic interventions for chronic pain, and exemplify the potential of optopharmacology to study the dynamic activity of endogenous neuromodulatory mechanisms in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breivik H, Collett B, Ventafridda V, Cohen R, Gallacher D . Survey of chronic pain in Europe: prevalence, impact on daily life, and treatment. Eur J Pain 2006; 10: 287–333.
Johannes CB, Le TK, Zhou X, Johnston JA, Dworkin RH . The prevalence of chronic pain in United States adults: results of an Internet-based survey. J Pain 2010; 11: 1230–1239.
Nightingale S . The neuropathic pain market. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2012; 11: 101–102.
Bushnell MC, Ceko M, Low LA . Cognitive and emotional control of pain and its disruption in chronic pain. Nat Rev Neurosci 2013; 14: 502–511.
Basbaum AI, Bautista DM, Scherrer G, Julius D . Cellular and molecular mechanisms of pain. Cell 2009; 139: 267–284.
Latremoliere A, Woolf CJ . Central sensitization: a generator of pain hypersensitivity by central neural plasticity. J Pain 2009; 10: 895–926.
Goudet C, Magnaghi V, Landry M, Nagy F, RWt Gereau, Pin JP . Metabotropic receptors for glutamate and GABA in pain. Brain Res Rev 2009; 60: 43–56.
Goudet C, Chapuy E, Alloui A, Acher F, Pin JP, Eschalier A . Group III metabotropic glutamate receptors inhibit hyperalgesia in animal models of inflammation and neuropathic pain. Pain 2008; 137: 112–124.
Vilar B, Busserolles J, Ling B, Laffray S, Ulmann L, Malhaire F et al. Alleviating pain hypersensitivity through activation of type 4 metabotropic glutamate receptor. J Neurosci 2013; 33: 18951–18965.
Wang H, Jiang W, Yang R, Li Y . Spinal metabotropic glutamate receptor 4 is involved in neuropathic pain. Neuroreport 2011; 22: 244–248.
Davis MJ, Haley T, Duvoisin RM, Raber J . Measures of anxiety, sensorimotor function, and memory in male and female mGluR4(-)/(-) mice. Behav Brain Res 2012; 229: 21–28.
Davis MJ, Iancu OD, Acher FC, Stewart BM, Eiwaz MA, Duvoisin RM et al. Role of mGluR4 in acquisition of fear learning and memory. Neuropharmacology 2013; 66: 365–372.
Neugebauer V . Amygdala pain mechanisms. Handb Exp Pharmacol 2015; 227: 261–284.
Neugebauer V, Li W, Bird GC, Bhave G, Gereau RWt . Synaptic plasticity in the amygdala in a model of arthritic pain: differential roles of metabotropic glutamate receptors 1 and 5. J Neurosci 2003; 23: 52–63.
Jiang H, Fang D, Kong LY, Jin ZR, Cai J, Kang XJ et al. Sensitization of neurons in the central nucleus of the amygdala via the decreased GABAergic inhibition contributes to the development of neuropathic pain-related anxiety-like behaviors in rats. Mol Brain 2014; 7: 72.
Pekhletski R, Gerlai R, Overstreet LS, Huang XP, Agopyan N, Slater NT et al. Impaired cerebellar synaptic plasticity and motor performance in mice lacking the mGluR4 subtype of metabotropic glutamate receptor. J Neurosci 1996; 16: 6364–6373.
Pitsch J, Schoch S, Gueler N, Flor PJ, van der Putten H, Becker AJ . Functional role of mGluR1 and mGluR4 in pilocarpine-induced temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 2007; 26: 623–633.
De Bundel D, Zussy C, Espallergues J, Gerfen CR, Girault JA, Valjent E . Dopamine D2 receptors gate generalization of conditioned threat responses through mTORC1 signaling in the extended amygdala. Mol Psychiatry 2016; 21: 1545–1553.
Brabet I, Parmentier ML, De Colle C, Bockaert J, Acher F, Pin JP . Comparative effect of L-CCG-I, DCG-IV and gamma-carboxy-L-glutamate on all cloned metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes. Neuropharmacology 1998; 37: 1043–1051.
Gomeza J, Mary S, Brabet I, Parmentier ML, Restituito S, Bockaert J et al. Coupling of metabotropic glutamate receptors 2 and 4 to G alpha 15, G alpha 16, and chimeric G alpha q/i proteins: characterization of new antagonists. Mol Pharmacol 1996; 50: 923–930.
Trinquet E, Fink M, Bazin H, Grillet F, Maurin F, Bourrier E et al. D-myo-inositol 1-phosphate as a surrogate of D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-tris phosphate to monitor G protein-coupled receptor activation. Anal Biochem 2006; 358: 126–135.
Tamamaki N, Yanagawa Y, Tomioka R, Miyazaki J, Obata K, Kaneko T . Green fluorescent protein expression and colocalization with calretinin, parvalbumin, and somatostatin in the GAD67-GFP knock-in mouse. J Comp Neurol 2003; 467: 60–79.
Asede D, Bosch D, Luthi A, Ferraguti F, Ehrlich I . Sensory inputs to intercalated cells provide fear-learning modulated inhibition to the basolateral amygdala. Neuron 2015; 86: 541–554.
Pittolo S, Gomez-Santacana X, Eckelt K, Rovira X, Dalton J, Goudet C et al. An allosteric modulator to control endogenous G protein-coupled receptors with light. Nat Chem Biol 2014; 10: 813–815.
Goudet C, Vilar B, Courtiol T, Deltheil T, Bessiron T, Brabet I et al. A novel selective metabotropic glutamate receptor 4 agonist reveals new possibilities for developing subtype selective ligands with therapeutic potential. FASEB J 2012; 26: 1682–1693.
Sigurdsson T, Doyere V, Cain CK, LeDoux JE . Long-term potentiation in the amygdala: a cellular mechanism of fear learning and memory. Neuropharmacology 2007; 52: 215–227.
Pape HC, Pare D . Plastic synaptic networks of the amygdala for the acquisition, expression, and extinction of conditioned fear. Physiol Rev 2010; 90: 419–463.
Bienvenu TC, Busti D, Micklem BR, Mansouri M, Magill PJ, Ferraguti F et al. Large intercalated neurons of amygdala relay noxious sensory information. J Neurosci 2015; 35: 2044–2057.
Veinante P, Yalcin I, Barrot M . The amygdala between sensation and affect: a role in pain. J Mol Psychiatry 2013; 1: 9.
Harris KM, Weinberg RJ . Ultrastructure of synapses in the mammalian brain. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2012; 4: 5.
Gray EG . Axo-somatic and axo-dendritic synapses of the cerebral cortex: an electron microscope study. J Anat 1959; 93: 420–433.
Ohishi H, Akazawa C, Shigemoto R, Nakanishi S, Mizuno N . Distributions of the mRNAs for L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate-sensitive metabotropic glutamate receptors, mGluR4 and mGluR7, in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 1995; 360: 555–570.
Fremeau RT Jr, Voglmaier S, Seal RP, Edwards RH . VGLUTs define subsets of excitatory neurons and suggest novel roles for glutamate. Trends Neurosci 2004; 27: 98–103.
Barroso-Chinea P, Castle M, Aymerich MS, Lanciego JL . Expression of vesicular glutamate transporters 1 and 2 in the cells of origin of the rat thalamostriatal pathway. J Chem Neuroanat 2008; 35: 101–107.
Sah P, Lopez De Armentia M . Excitatory synaptic transmission in the lateral and central amygdala. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2003; 985: 67–77.
Lanuza E, Nader K, Ledoux JE . Unconditioned stimulus pathways to the amygdala: effects of posterior thalamic and cortical lesions on fear conditioning. Neuroscience 2004; 125: 305–315.
Duvarci S, Pare D . Amygdala microcircuits controlling learned fear. Neuron 2014; 82: 966–980.
Likhtik E, Popa D, Apergis-Schoute J, Fidacaro GA, Pare D . Amygdala intercalated neurons are required for expression of fear extinction. Nature 2008; 454: 642–645.
Busti D, Geracitano R, Whittle N, Dalezios Y, Manko M, Kaufmann W et al. Different fear states engage distinct networks within the intercalated cell clusters of the amygdala. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 5131–5144.
Jones CK, Bubser M, Thompson AD, Dickerson JW, Turle-Lorenzo N, Amalric M et al. The metabotropic glutamate receptor 4-positive allosteric modulator VU0364770 produces efficacy alone and in combination with L-DOPA or an adenosine 2 A antagonist in preclinical rodent models of Parkinson's disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2012; 340: 404–421.
Nakajima Y, Iwakabe H, Akazawa C, Nawa H, Shigemoto R, Mizuno N et al. Molecular characterization of a novel retinal metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR6 with a high agonist selectivity for L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate. J Biol Chem 1993; 268: 11868–11873.
Carr FB, Zachariou V . Nociception and pain: lessons from optogenetics. Front Behav Neurosci 2014; 8: 69.
Lalumiere RT . Optogenetic dissection of amygdala functioning. Front Behav Neurosci 2014; 8: 107.
Bahamonde MI, Taura J, Paoletta S, Gakh AA, Chakraborty S, Hernando J et al. Photomodulation of G protein-coupled adenosine receptors by a novel light-switchable ligand. Bioconjug Chem 2014; 25: 1847–1854.
Broichhagen J, Schonberger M, Cork SC, Frank JA, Marchetti P, Bugliani M et al. Optical control of insulin release using a photoswitchable sulfonylurea. Nat Commun 2014; 5: 5116.
Kokel D, Cheung CY, Mills R, Coutinho-Budd J, Huang L, Setola V et al. Photochemical activation of TRPA1 channels in neurons and animals. Nat Chem Biol 2013; 9: 257–263.
Schonberger M, Trauner D . A photochromic agonist for mu-opioid receptors. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2014; 53: 3264–3267.
Stein M, Middendorp SJ, Carta V, Pejo E, Raines DE, Forman SA et al. Azo-propofols: photochromic potentiators of GABA(A) receptors. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2012; 51: 10500–10504.
Mahan AL, Ressler KJ . Fear conditioning, synaptic plasticity and the amygdala: implications for posttraumatic stress disorder. Trends Neurosci 2012; 35: 24–35.
Herry C, Ferraguti F, Singewald N, Letzkus JJ, Ehrlich I, Luthi A . Neuronal circuits of fear extinction. Eur J Neurosci 2010; 31: 599–612.
Podkowa K, Rzezniczek S, Marciniak M, Acher F, Pilc A, Palucha-Poniewiera A . A novel mGlu4 selective agonist LSP4-2022 increases behavioral despair in mouse models of antidepressant action. Neuropharmacology 2015; 97: 338–345.
Kalinichev M, Le Poul E, Bolea C, Girard F, Campo B, Fonsi M et al. Characterization of the novel positive allosteric modulator of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 4 ADX88178 in rodent models of neuropsychiatric disorders. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2014; 350: 495–505.
Klak K, Palucha A, Branski P, Sowa M, Pilc A . Combined administration of PHCCC, a positive allosteric modulator of mGlu4 receptors and ACPT-I, mGlu III receptor agonist evokes antidepressant-like effects in rats. Amino Acids 2007; 32: 169–172.
Slawinska A, Wieronska JM, Stachowicz K, Palucha-Poniewiera A, Uberti MA, Bacolod MA et al. Anxiolytic- but not antidepressant-like activity of Lu AF21934, a novel, selective positive allosteric modulator of the mGlu(4) receptor. Neuropharmacology 2013; 66: 225–235.
Wieronska JM, Stachowicz K, Palucha-Poniewiera A, Acher F, Branski P, Pilc A . Metabotropic glutamate receptor 4 novel agonist LSP1-2111 with anxiolytic, but not antidepressant-like activity, mediated by serotonergic and GABAergic systems. Neuropharmacology 2010; 59: 627–634.
Todd AJ . Neuronal circuitry for pain processing in the dorsal horn. Nat Rev Neurosci 2010; 11: 823–836.
Han S, Soleiman MT, Soden ME, Zweifel LS, Palmiter RD . Elucidating an affective pain circuit that creates a threat memory. Cell 2015; 162: 363–374.
Neugebauer V, Galhardo V, Maione S, Mackey SC . Forebrain pain mechanisms. Brain Res Rev 2009; 60: 226–242.
Pare D, Quirk GJ, Ledoux JE . New vistas on amygdala networks in conditioned fear. J Neurophysiol 2004; 92: 1–9.
Maren S . Synaptic mechanisms of associative memory in the amygdala. Neuron 2005; 47: 783–786.
Phelps EA, LeDoux JE . Contributions of the amygdala to emotion processing: from animal models to human behavior. Neuron 2005; 48: 175–187.
Dobi A, Sartori SB, Busti D, Van der Putten H, Singewald N, Shigemoto R et al. Neural substrates for the distinct effects of presynaptic group III metabotropic glutamate receptors on extinction of contextual fear conditioning in mice. Neuropharmacology 2013; 66: 274–289.
Palazzo E, Fu Y, Ji G, Maione S, Neugebauer V . Group III mGluR7 and mGluR8 in the amygdala differentially modulate nocifensive and affective pain behaviors. Neuropharmacology 2008; 55: 537–545.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Nicola Romanò, Sophie Laffray, Emmanuel Bourinet, André Calas and Etienne Gontier for research assistance and helpful discussions, and Ebba L. Lagerqvist for critical reading of the manuscript. Cell-based pharmacological assays were performed on the ARPEGE (Pharmacology-Screening-Interactome) platform at the Institute de Génomique Fonctionnelle. We acknowledge financial support from the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR-12-NEUR-0003 and ANR-13-BSV1-006 to CG), the ERANET Neuron LIGHTPAIN project (to AL, JG and J-PP), the Fundació La Marató de TV3 (110230, 110231, 110232, to JG, AL and CG), the Fondation Recherche Médicale (FRM team DEQ20130326522 to J-PP), the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (FA, J-PP and CG), the Catalan government (2012 BEI_ 00597 to XG-S and 2014SGR-0109 to AL), the Federation of European Biochemical Societies and the Spanish Government (CTQ2014-57020-R to AL and SAF2014-58396-R to JG), the Beatriu de Pinós program of Agència de Gestió d'Ajuts Universitaris i de Recerca (AGAUR, to XR), the Charitable Hertie Foundation (to IE), the Werner Reichardt Centre for Integrative Neuroscience at the University of Tuebingen, an Excellence Cluster funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, EXC 307, to IE), and the Austrian Science Fund (Fonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung, Sonderforschungsbereich grant F44-17-B23 and W012060-10 to FF).
Author contributions
CZ conceived, performed and analyzed behavioral pharmacology, immunofluorescence microscopy and immediate early gene experiments, and wrote the paper. XGS designed and synthesized optogluram, characterized photoisomerization, and performed and analyzed cell-based pharmacological experiments. XR performed and analyzed cell-based pharmacological experiments. DDB performed and analyzed behavioral pharmacology experiments. SF performed immunofluorescence and electron microscopy experiments. DB and DA performed and analyzed classical and optogenetic-based electrophysiological experiments. FM performed and analyzed cell-based pharmacological experiments. FA designed and synthesized LSP4-2022. JG supervised and analyzed pharmacological experiments. EV supervised and designed behavioral experiments. IE supervised and designed electrophysiology experiments. FF supervised and designed neuroanatomy experiments. J-PP analyzed pharmacological results, designed experiments and analyzed activity data. AL conceived and supervised the project, planned experiments, designed compounds. CG conceived and supervised the project, designed and analyzed results and wrote the paper. All authors made comments and corrections to the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
AL, JG, XG-S, XR, CG and J-PP have filed a patent application for photochromic allosteric modulators of metabotropic glutamate receptors. FA, CG and J-PP have filed a patent application for the antihyperalgesic activity of hypophosphorous acid derivatives. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zussy, C., Gómez-Santacana, X., Rovira, X. et al. Dynamic modulation of inflammatory pain-related affective and sensory symptoms by optical control of amygdala metabotropic glutamate receptor 4. Mol Psychiatry 23, 509–520 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.223
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.223
This article is cited by
-
The emergence of molecular systems neuroscience
Molecular Brain (2022)
-
Effects of a psychedelic 5-HT2A receptor agonist on anxiety-related behavior and fear processing in mice
Neuropsychopharmacology (2022)
-
Facilitating mGluR4 activity reverses the long-term deleterious consequences of chronic morphine exposure in male mice
Neuropsychopharmacology (2021)
-
Optical control of neuronal ion channels and receptors
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2019)
-
The molecular neurobiology of chronic pain–induced depression
Cell and Tissue Research (2019)