Abstract
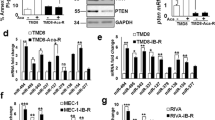
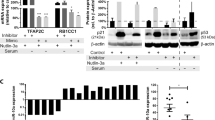
The lymph node (LN) is the site of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cell activation and proliferation. Aberrant microRNA (miRNA) expression has been shown to have a role in CLL pathogenesis; however, a comparison of miRNA expression between CLL cells in the LN and the peripheral blood (PB) has previously not been reported. On the basis of the analysis of 17 paired LN and PB samples from CLL patients, we identify a panel of miRNAs that are increased in LN CLL cells correlating with an activation phenotype. When evaluated in CLL cells from 38 patients pre and post treatment with ibrutinib, a subset of these miRNAs (miR-22, miR-34a, miR-146b and miR-181b) was significantly decreased in response to ibrutinib. A concomitant increase in putative miRNA target transcripts (ARID1B, ARID2, ATM, CYLD, FOXP1, HDAC1, IBTK, PTEN and SMAD4) was also observed. Functional studies confirmed targets of ibrutinib-responsive miRNAs to include messenger RNA transcripts of multiple tumor suppressors. Knockdown of endogenous miR-34a and miR146b resulted in increased transcription of tumor suppressors and inhibition of cell proliferation. These findings demonstrate that ibrutinib downregulates the expression of a subset of miRNAs related to B-cell activation leading to increased expression of miRNA targets including tumor suppressors and a reduction in cell proliferation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campo E, Swerdlow SH, Harris NL, Pileri S, Stein H, Jaffe ES . The 2008 WHO classification of lymphoid neoplasms and beyond: evolving concepts and practical applications. Blood 2011; 117: 5019–5032.
Herishanu Y, Katz BZ, Lipsky A, Wiestner A . Biology of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in different microenvironments: clinical and therapeutic implications. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 2013; 27: 173–206.
Zhang S, Kipps TJ . The pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Annu Rev Pathol 2014; 9: 103–118.
Fegan C, Pepper C . Apoptosis deregulation in CLL. Adv Exp Med Biol 2013; 792: 151–171.
Herishanu Y, Perez-Galan P, Liu D, Biancotto A, Pittaluga S, Vire B et al. The lymph node microenvironment promotes B-cell receptor signaling, NF-kappaB activation, and tumor proliferation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2011; 117: 563–574.
Burger JA, Tedeschi A, Barr PM, Robak T, Owen C, Ghia P et al. Ibrutinib as initial therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2015; 373: 2425–2437.
Wiestner A . The role of B-cell receptor inhibitors in the treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2015; 100: 1495–1507.
Byrd JC, Furman RR, Coutre SE, Flinn IW, Burger JA, Blum KA et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2013; 369: 32–42.
Herman SE, Mustafa RZ, Gyamfi JA, Pittaluga S, Chang S, Chang B et al. Ibrutinib inhibits BCR and NF-kB signaling and reduces tumor proliferation in tissue-resident cells of patients with CLL. Blood 2014; 123: 3286–3295.
Farooqui MZH, Valdez J, Martyr S, Aue G, Saba N, Niemann CU et al. Ibrutinib for previously untreated and relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with Tp53 aberrations: a phase 2, single-arm trial. Lancet Oncol 2015; 16: 169–176.
de Claro RA, McGinn KM, Verdun N, Lee SL, Chiu HJ, Saber H et al. FDA approval: ibrutinib for patients with previously treated mantle cell lymphoma and previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 2015; 21: 3586–3590.
Cheng S, Ma J, Guo A, Lu P, Leonard JP, Coleman M et al. BTK inhibition targets in vivo CLL proliferation through its effects on B-cell receptor signaling activity. Leukemia 2014; 28: 649–657.
Herman SE, Niemann CU, Farooqui M, Jones J, Mustafa RZ, Lipsky A et al. Ibrutinib-induced lymphocytosis in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: correlative analyses from a phase II study. Leukemia 2014; 28: 2188–2196.
Bartel DP . MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009; 136: 215–233.
Croce CM . Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 2009; 10: 704–714.
Rossi S, Shimizu M, Barbarotto E, Nicoloso MS, Dimitri F, Sampath D et al. microRNA fingerprinting of CLL patients with chromosome 17p deletion identify a miR-21 score that stratifies early survival. Blood 2010; 116: 945–952.
Dufour A, Palermo G, Zellmeier E, Mellert G, Duchateau-Nguyen G, Schneider S et al. Inactivation of Tp53 correlates with disease progression and low miR-34a expression in previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients. Blood 2013; 121: 3650–3657.
Mraz M, Chen L, Rassenti LZ, Ghia EM, Li H, Jepsen K et al. miR-150 influences B-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia by regulating expression of GAB1 and FOXP1. Blood 2014; 124: 84–95.
Mraz M, Malinova K, Kotaskova J, Pavlova S, Tichy B, Malcikova J et al. miR-34a, miR-29c and miR-17-5p are downregulated in CLL Patients with TP53 abnormalities. Leukemia 2009; 23: 1159–1163.
Yeh YY, Ozer HG, Lehman AM, Maddocks K, Yu L, Johnson AJ et al. Characterization of CLL exosomes reveals a distinct microRNA signature and enhanced secretion by activation of BCR signaling. Blood 2015; 125: 3297–3305.
Zhu DX, Zhu W, Fang C, Fan L, Zou ZJ, Wang YH et al. miR-181a/B significantly enhances drug sensitivity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells via targeting multiple anti-apoptosis genes. Carcinogenesis 2012; 33: 1294–1301.
Mraz M, Pospisilova S, Malinova K, Slapak I, Mayer J . MicroRNAs in chronic lymphocytic leukemia pathogenesis and disease subtypes. Leuk Lymphoma 2009; 50: 506–509.
Li S, Moffett HF, Lu J, Werner L, Zhang H, Ritz J et al. MicroRNA expression profiling identifies activated B cell status in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. PLoS One 2011; 6: e16956.
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Shimizu M et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 13944–13949.
Degheidy HA, Gadalla SM, Farooqui MZ, Abbasi F, Arthur DC, Bauer SR et al. Bcl-2 level as a biomarker for 13q14 deletion in CLL. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2013; 84: 237–247.
Negrini M, Cutrona G, Bassi C, Fabris S, Zagatti B, Colombo M et al. microRNAome expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: comparison with normal B-cell subsets and correlations with prognostic and clinical parameters. Clin Cancer Res 2014; 20: 4141–4153.
Calin GA, Ferracin M, Cimmino A, Di Leva G, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE et al. A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 1793–1801.
Mraz M, Kipps TJ . MicroRNAs and B cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 2013; 54: 1836–1839.
Pede V, Rombout A, Vermeire J, Naessens E, Mestdagh P, Robberecht N et al. CLL cells respond to B-cell receptor stimulation with a microRNA/mRNA signature associated with MYC activation and cell cycle progression. PLoS One 2013; 8: e60275.
Wang W, Corrigan-Cummins M, Hudson J, Maric I, Simakova O, Neelapu SS et al. MicroRNA profiling of follicular lymphoma identifies microRNAs related to cell proliferation and tumor response. Haematologica 2012; 97: 586–594.
Luo X, Zhang J, Wang H, Du Y, Yang L, Zheng F et al. PolyA RT-PCR-based quantification of microRNA by using universal TaqMan probe. Biotechnol Lett 2012; 34: 627–633.
Wang W, Corrigan-Cummins M, Barber EA, Saleh LM, Zingone A, Ghafoor A et al. Aberrant levels of miRNAs in bone marrow microenvironment and peripheral blood of myeloma patients and disease progression. J Mol Diagn 2015; 17: 669–678.
Kubiczkova L, Kryukov F, Slaby O, Dementyeva E, Jarkovsky J, Nekvindova J et al. Circulating serum microRNAs as novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for multiple myeloma and monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Haematologica 2014; 99: 511–518.
Daibata M, Kubonishi I, Eguchi T, Yano S, Ohtsuki Y, Miyoshi I . The establishment of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen-positive (SP-50B) and Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen-negative (SP-53) cell lines with t(11;14)(q13;q32) chromosome abnormality from an intermediate lymphocytic lymphoma. Cancer 1989; 64: 1248–1253.
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW . NIH image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 2012; 9: 671–675.
Foa R, Del Giudice I, Guarini A, Rossi D, Gaidano G . Clinical Implications of the Molecular Genetics of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Haematologica 2013; 98: 675–685.
Wang Y, Zhang LL, Champlin RE, Wang ML . Targeting Bruton's tyrosine kinase with ibrutinib in B-cell malignancies. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2015; 97: 455–468.
Elter T, Hallek M, Engert A . Fludarabine in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2006; 7: 1641–1651.
Genovese G, Ergun A, Shukla SA, Campos B, Hanna J, Ghosh P et al. microRNA regulatory network inference identifies miR-34a as a novel regulator of TGF-β signaling in glioblastoma. Cancer Discov 2012; 2: 736–749.
Lal A, Thomas MP, Altschuler G, Navarro F, O'Day E, Li XL et al. Capture of microRNA-bound mRNAs identifies the tumor suppressor miR-34a as a regulator of growth factor signaling. PLoS Genet 2011; 7: e1002363.
Qiao P, Li G, Bi W, Yang L, Yao L, Wu D . microRNA-34a inhibits epithelial mesenchymal transition in human cholangiocarcinoma by targeting Smad4 through transforming growth factor-beta/Smad pathway. BMC Cancer 2015; 15: 469.
Geraldo MV, Yamashita AS, Kimura ET . MicroRNA miR-146b-5p regulates signal transduction of TGF-β by repressing SMAD4 in thyroid cancer. Oncogene 2012; 31: 1910–1922.
Wu MY, Fu J, Xiao X, Wu J, Wu RC . MiR-34a regulates therapy resistance by targeting HDAC1 and HDAC7 in breast cancer. Cancer Lett 2014; 354: 311–319.
Zhao J, Lammers P, Torrance CJ, Bader AG . TP53-independent function of miR-34a via HDAC1 and p21(CIP1/WAF1.). Mol Ther 2013; 21: 1678–1686.
Brizova H, Kalinova M, Krskova L, Mrhalova M, Kodet R . A novel quantitative PCR of proliferation markers (Ki-67, topoisomerase Ilalpha, and TPX2): an immunohistochemical correlation, testing, and optimizing for mantle cell lymphoma. Virchows Arch 2010; 456: 671–679.
Herman SE, Gordon AL, Hertlein E, Ramanunni A, Zhang X, Jaglowski S et al. Bruton tyrosine kinase represents a promising therapeutic target for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and is effectively targeted by PCI-32765. Blood 2011; 117: 6287–6296.
Palacios F, Prieto D, Abreu C, Ruiz S, Morande P, Fernandez-Calero T et al. Dissecting chronic lymphocytic leukemia microenvironment signals in patients with unmutated disease: microRNA-22 regulates phosphatase and tensin homolog/AKT/FOXO1 pathway in proliferative leukemic cells. Leuk Lymphoma 2015; 56: 1560–1565.
Palacios F, Abreu C, Prieto D, Morande P, Ruiz S, Fernandez-Calero T et al. Activation of the PI3k/AKT pathway by microRNA-22 results in CLL B-cell proliferation. Leukemia 2015; 29: 115–125.
Andrade TA, Evangelista AF, Campos AH, Poles WA, Borges NM, Camillo CM et al. A microRNA signature profile in EBV+ diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly. Oncotarget 2014; 5: 11813–11826.
Zenz T, Mohr J, Eldering E, Kater AP, Buhler A, Kienle D et al. miR-34a as part of the resistance network in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2009; 113: 3801–3808.
Fabbri M, Bottoni A, Shimizu M, Spizzo R, Nicoloso MS, Rossi S et al. Association of a microRNA/TP53 feedback circuitry with pathogenesis and outcome of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. JAMA 2011; 305: 59–67.
Ruiz-Lafuente N, Alcaraz-Garcia MJ, Sebastian-Ruiz S, Garcia-Serna AM, Gomez-Espuch J, Moraleda JM et al. IL-4 up-regulates miR-21 and the miRNAs hosted in the CLCN5 gene in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. PLoS One 2015; 10: e0124936.
Asslaber D, Pinon JD, Seyfried I, Desch P, Stocher M, Tinhofer I et al. microRNA-34a expression correlates with MDM2 SNP309 polymorphism and treatment-free survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2010; 115: 4191–4197.
Sotillo E, Laver T, Mellert H, Schelter JM, Cleary MA, McMahon S et al. Myc overexpression brings out unexpected antiapoptotic effects of miR-34a. Oncogene 2011; 30: 2587–2594.
Santoro F, Botrugno OA, Dal Zuffo R, Pallavicini I, Matthews GM, Cluse L et al. A dual role for Hdac1: oncosuppressor in tumorigenesis, oncogene in tumor maintenance. Blood 2013; 121: 3459–3468.
Huang Y, Qi Y, Du JQ, Zhang DF . MicroRNA-34a regulates cardiac fibrosis after myocardial infarction by targeting Smad4. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2014; 18: 1355–1365.
Jones S, Stransky N, McCord CL, Cerami E, Lagowski J, Kelly D et al. Genomic analyses of gynaecologic carcinosarcomas reveal frequent mutations in chromatin remodelling genes. Nat Commun 2014; 5: 5006.
Shao F, Guo T, Chua PJ, Tang L, Thike AA, Tan PH et al. Clinicopathological significance of ARID1B in breast invasive ductal carcinoma. Histopathology 2015; 67: 709–718.
Shain AH, Pollack JR . The spectrum of SWI/SNF mutations, ubiquitous in human cancers. PLoS One 2013; 8: e55119.
Wu W, Zhu H, Fu Y, Shen W, Xu J, Miao K et al. Clinical significance of down-regulated cylindromatosis gene in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 2014; 55: 588–594.
Liu P, Xu B, Shen W, Zhu H, Wu W, Fu Y et al. Dysregulation of TNFα-induced necroptotic signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: suppression of CYLD gene by LEF1. Leukemia 2012; 26: 1293–1300.
Strobel P, Zettl A, Ren Z, Starostik P, Riedmiller H, Storkel S et al. Spiradenocylindroma of the kidney: clinical and genetic findings suggesting a role of somatic mutation of the CYLD1 gene in the oncogenesis of an unusual renal neoplasm. Am J Surg Pathol 2002; 26: 119–124.
Spatuzza C, Schiavone M, Di Salle E, Janda E, Sardiello M, Fiume G et al. Physical and functional characterization of the genetic locus of IBtk, an inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase: evidence for three protein isoforms of IBtk. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36: 4402–4416.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health Division of Intramural Research, NIH Clinical Center, and National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. The content of this publication does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the Department of Health and Human Services. We thank Dr Masanori Daibata (Kochi University Medical School, Kochi, Japan) for use of the SP53 cell line.
Author contributions
LMS, WW, SEMH, NKA, ZZ, OE, HAA, AW and KRC designed the study. LMS, WW, SEMH, NSS, EB, MC-C and VA performed the experiments. LMS, WW, VA and KRC analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. SMS and LMS performed the statistical analyses. MF and CS provided clinical care and patient samples. AW, SEMH, ZZ and HAA assisted in editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
AW has received research funding from Pharmacyclics. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saleh, L., Wang, W., Herman, S. et al. Ibrutinib downregulates a subset of miRNA leading to upregulation of tumor suppressors and inhibition of cell proliferation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 31, 340–349 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.181
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.181
This article is cited by
-
The emerging role of microRNA-22 in the Leukemia: experimental and clinical implications
Molecular Biology Reports (2024)
-
SWI/SNF complexes in hematological malignancies: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities
Molecular Cancer (2023)
-
Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via let-7b-5p
Cell and Tissue Research (2023)
-
Non-coding RNAs in leukemia drug resistance: new perspectives on molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways
Annals of Hematology (2023)
-
Down-regulation of cylindromatosis protein phosphorylation by BTK inhibitor promotes apoptosis of non-GCB-diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Cancer Cell International (2021)