Abstract
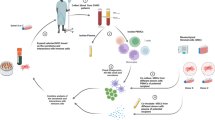
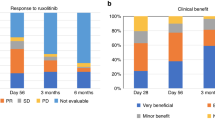
We performed a prospective phase II study to evaluate clinical safety and outcome in 48 patients with steroid-refractory grade II–IV acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD) treated with mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs). Clinical outcomes were correlated to comprehensive analyses of soluble and cellular biomarkers. Complete resolution (CR) of aGVHD at day 28 (CR-28) occurred in 12 (25%) patients, CR lasting >1 month (CR-B) occurred in 24 (50%) patients. One-year overall survival was significantly improved in CR-28 (75 versus 33%, P=0.020) and CR-B (79 versus 8%, P<0.001) versus non-CR patients. A six soluble biomarker-panel was predictive for mortality (HR 2.924; CI 1.485–5.758) when measured before MSC-administration. Suppression of tumorigenicity 2 (ST2) was only predictive for mortality 2 weeks after but not before MSC-administration (HR 2.389; CI 1.144–4.989). In addition, an increase in immature myeloid dendritic cells associated with decreased mortality (HR 0.554, CI 0.389–0.790). Patients had persisting T-cell responses against defined virus- and leukemia-associated antigens. In conclusion, our data emphasize the need to carefully assess biomarkers in cohorts with homogeneous GVHD treatments. Biomarkers might become an additional valuable component of composite end points for the rapid and efficient testing of novel compounds to decrease lifecycle of clinical testing and improve the success rate of phase II/III trials.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
MacMillan ML, Couriel D, Weisdorf DJ, Schwab G, Havrilla N, Fleming TR et al. A phase 2/3 multicenter randomized clinical trial of ABX-CBL versus ATG as secondary therapy for steroid-resistant acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2007; 109: 2657–2662.
Lee SJ, Zahrieh D, Agura E, MacMillan ML, Maziarz RT, McCarthy PL Jr et al. Effect of up-front daclizumab when combined with steroids for the treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease: results of a randomized trial. Blood 2004; 104: 1559–1564.
Alousi AM, Weisdorf DJ, Logan BR, Bolanos-Meade J, Carter S, Difronzo N et al. Etanercept, mycophenolate, denileukin, or pentostatin plus corticosteroids for acute graft-versus-host disease: a randomized phase 2 trial from the Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network. Blood 2009; 114: 511–517.
Levine JE, Paczesny S, Mineishi S, Braun T, Choi SW, Hutchinson RJ et al. Etanercept plus methylprednisolone as initial therapy for acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2008; 111: 2470–2475.
Bolanos-Meade J, Logan BR, Alousi AM, Antin JH, Barowski K, Carter SL et al. Phase 3 clinical trial of steroids/mycophenolate mofetil vs steroids/placebo as therapy for acute GVHD: BMT CTN 0802. Blood 2014; 124: 3221–3227.
Le Blanc K, Rasmusson I, Sundberg B, Gotherstrom C, Hassan M, Uzunel M et al. Treatment of severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet 2004; 363: 1439–1441.
Ringden O, Uzunel M, Rasmusson I, Remberger M, Sundberg B, Lonnies H et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of therapy-resistant graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation 2006; 81: 1390–1397.
Le Blanc K, Frassoni F, Ball L, Locatelli F, Roelofs H, Lewis I et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase II study. Lancet 2008; 371: 1579–1586.
Uccelli A, Moretta L, Pistoia V . Mesenchymal stem cells in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2008; 8: 726–736.
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 1999; 284: 143–147.
Porada CD, Zanjani ED, Meida-Porad G . Adult mesenchymal stem cells: a pluripotent population with multiple applications. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 2006; 1: 365–369.
von BM, Stolzel F, Goedecke A, Richter K, Wuschek N, Holig K et al. Treatment of refractory acute GVHD with third-party MSC expanded in platelet lysate-containing medium. Bone Marrow Transplant 2009; 43: 245–251.
Kebriaei P, Isola L, Bahceci E, Holland K, Rowley S, McGuirk J et al. Adult human mesenchymal stem cells added to corticosteroid therapy for the treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 804–811.
Lucchini G, Introna M, Dander E, Rovelli A, Balduzzi A, Bonanomi S et al. Platelet-lysate-expanded mesenchymal stromal cells as a salvage therapy for severe resistant graft-versus-host disease in a pediatric population. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2010; 16: 1293–1301.
Prasad VK, Lucas KG, Kleiner GI, Talano JA, Jacobsohn D, Broadwater G et al. Efficacy and safety of ex vivo cultured adult human mesenchymal stem cells (Prochymal) in pediatric patients with severe refractory acute graft-versus-host disease in a compassionate use study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2011; 17: 534–541.
Perez-Simon JA, Lopez-Villar O, Andreu EJ, Rifon J, Muntion S, Campelo MD et al. Mesenchymal stem cells expanded in vitro with human serum for the treatment of acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease: results of a phase I/II clinical trial. Haematologica 2011; 96: 1072–1076.
Herrmann R, Sturm M, Shaw K, Purtill D, Cooney J, Wright M et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for steroid-refractory acute and chronic graft versus host disease: a phase 1 study. Int J Hematol 2012; 95: 182–188.
Dander E, Lucchini G, Vinci P, Introna M, Masciocchi F, Perseghin P et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells for the treatment of graft-versus-host disease: understanding the in vivo biological effect through patient immune monitoring. Leukemia 2012; 26: 1681–1684.
Muroi K, Miyamura K, Ohashi K, Murata M, Eto T, Kobayashi N et al. Unrelated allogeneic bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase I/II study. Int J Hematol 2013; 98: 206–213.
Ball LM, Bernardo ME, Roelofs H, van Tol MJ, Contoli B, Zwaginga JJ et al. Multiple infusions of mesenchymal stromal cells induce sustained remission in children with steroid-refractory, grade III-IV acute graft-versus-host disease. Br J Haematol 2013; 163: 501–509.
Resnick IB, Barkats C, Shapira MY, Stepensky P, Bloom AI, Shimoni A et al. Treatment of severe steroid resistant acute GVHD with mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC). Am J Blood Res 2013; 3: 225–238.
Kurtzberg J, Prockop S, Teira P, Bittencourt H, Lewis V, Chan KW et al. Allogeneic human mesenchymal stem cell therapy (remestemcel-L, Prochymal) as a rescue agent for severe refractory acute graft-versus-host disease in pediatric patients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2014; 20: 229–235.
Introna M, Lucchini G, Dander E, Galimberti S, Rovelli A, Balduzzi A et al. Treatment of graft versus host disease with mesenchymal stromal cells: a phase I study on 40 adult and pediatric patients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 20: 375–381.
Levine JE, Logan BR, Wu J, Alousi AM, Bolanos-Meade J, Ferrara JL et al. Acute graft-versus-host disease biomarkers measured during therapy can predict treatment outcomes: a Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network study. Blood 2012; 119: 3854–3860.
Vander Lugt MT, Braun TM, Hanash S, Ritz J, Ho VT, Antin JH et al. ST2 as a marker for risk of therapy-resistant graft-versus-host disease and death. N Engl J Med 2013; 369: 529–539.
Ponce DM, Hilden P, Mumaw C, Devlin SM, Lubin M, Giralt S et al. High day 28 ST2 levels predict for acute graft-versus-host disease and transplant-related mortality after cord blood transplantation. Blood 2014; 125: 199–205.
Quah BJ, Warren HS, Parish CR . Monitoring lymphocyte proliferation in vitro and in vivo with the intracellular fluorescent dye carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester. Nat Protoc 2007; 2: 2049–2056.
Kuball J, de BK Wagner E, Wattad M, Antunes E, Weeratna RD et al. Pitfalls of vaccinations with WT1-, proteinase3- and MUC1-derived peptides in combination with MontanideISA51 and CpG7909. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2011; 60: 161–171.
MacMillan ML, DeFor TE, Weisdorf DJ . The best endpoint for acute GVHD treatment trials. Blood 2010; 115: 5412–5417.
Martin PJ, Rizzo JD, Wingard JR, Ballen K, Curtin PT, Cutler C et al. First- and second-line systemic treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease: recommendations of the American Society of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2012; 18: 1150–1163.
Schmoor C, Schumacher M, Finke J, Beyersmann J . Competing risks and multistate models. Clin Cancer Res 2013; 19: 12–21.
Paczesny S, Krijanovski OI, Braun TM, Choi SW, Clouthier SG, Kuick R et al. A biomarker panel for acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2009; 113: 273–278.
Ferrara JL, Harris AC, Greenson JK, Braun TM, Holler E, Teshima T et al. Regenerating islet-derived 3-alpha is a biomarker of gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2011; 118: 6702–6708.
Paczesny S, Braun TM, Levine JE, Hogan J, Crawford J, Coffing B et al. Elafin is a biomarker of graft-versus-host disease of the skin. Sci Transl Med 2010; 2: 13ra2.
Maccario R, Podesta M, Moretta A, Cometa A, Comoli P, Montagna D et al. Interaction of human mesenchymal stem cells with cells involved in alloantigen-specific immune response favors the differentiation of CD4+ T-cell subsets expressing a regulatory/suppressive phenotype. Haematologica 2005; 90: 516–525.
Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF . Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood 2005; 105: 1815–1822.
Jiang XX, Zhang Y, Liu B, Zhang SX, Wu Y, Yu XD et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells inhibit differentiation and function of monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Blood 2005; 105: 4120–4126.
Beyth S, Borovsky Z, Mevorach D, Liebergall M, Gazit Z, Aslan H et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells alter antigen-presenting cell maturation and induce T-cell unresponsiveness. Blood 2005; 105: 2214–2219.
Spaggiari GM, Abdelrazik H, Becchetti F, Moretta L . MSCs inhibit monocyte-derived DC maturation and function by selectively interfering with the generation of immature DCs: central role of MSC-derived prostaglandin E2. Blood 2009; 113: 6576–6583.
Vakkila J, Thomson AW, Hovi L, Vettenranta K, Saarinen-Pihkala UM . Circulating dendritic cell subset levels after allogeneic stem cell transplantation in children correlate with time post transplant and severity of acute graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 35: 501–507.
Jitschin R, Mougiakakos D, Von BL, Volkl S, Moll G, Ringden O et al. Alterations in the cellular immune compartment of patients treated with third-party mesenchymal stromal cells following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Stem Cells 2013; 31: 1715–1725.
Hawiger D, Inaba K, Dorsett Y, Guo M, Mahnke K, Rivera M et al. Dendritic cells induce peripheral T cell unresponsiveness under steady state conditions in vivo. J Exp Med 2001; 194: 769–779.
Lutz MB, Schuler G . Immature, semi-mature and fully mature dendritic cells: which signals induce tolerance or immunity? Trends Immunol 2002; 23: 445–449.
Johnson TR, Johnson CN, Corbett KS, Edwards GC, Graham BS . Primary human mDC1, mDC2, and pDC dendritic cells are differentially infected and activated by respiratory syncytial virus. PLoS One 2011; 6: e16458.
Maggini J, Mirkin G, Bognanni I, Holmberg J, Piazzon IM, Nepomnaschy I et al. Mouse bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells turn activated macrophages into a regulatory-like profile. PLoS One 2010; 5: e9252.
Rasmusson I, Ringden O, Sundberg B, Le BK . Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit lymphocyte proliferation by mitogens and alloantigens by different mechanisms. Exp Cell Res 2005; 305: 33–41.
Krampera M, Glennie S, Dyson J, Scott D, Laylor R, Simpson E et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the response of naive and memory antigen-specific T cells to their cognate peptide. Blood 2003; 101: 3722–3729.
Harris AC, Ferrara JL, Braun TM, Holler E, Teshima T, Levine JE et al. Plasma biomarkers of lower gastrointestinal and liver acute GVHD. Blood 2012; 119: 2960–2963.
Liu X, Qu X, Chen Y, Liao L, Cheng K, Shao C et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells induce the generation of novel IL-10-dependent regulatory dendritic cells by SOCS3 activation. J Immunol 2012; 189: 1182–1192.
Chiesa S, Morbelli S, Morando S, Massollo M, Marini C, Bertoni A et al. Mesenchymal stem cells impair in vivo T-cell priming by dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 17384–17389.
Lucchini G, Dander E, Pavan F, Di CI, Balduzzi A, Perseghin P et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells do not increase the risk of viral reactivation nor the severity of viral events in recipients of allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Stem Cells Int 2012; 2012: 690236.
Acknowledgements
We thank the research technicians S Heijhuurs, S Hol and Z Stachova for processing patient materials and also thank the multiplex immunoassay core facility at the UMC Utrecht for their cooperation. This work was partly supported by a grant from the Dutch Cancer Society to LEvdW (UU 2011-5250).
Author Contributions
LCJtB, CM, LEvdW, JK, JJB and CAL designed, interpreted and analyzed the data. CM, LEvdW and MP performed experiments. CM, LEvdW, LCJtB and JK wrote the manuscript. NMW, ICMS-C, JK, LCJtB and JJB designed the study. EJP, ES, KAT, KW, MB, AECB, MLHC, GI, JJJ, CH, SZ, GH, MP and NMW provided suggestions on the experiments and commented on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
te Boome, L., Mansilla, C., van der Wagen, L. et al. Biomarker profiling of steroid-resistant acute GVHD in patients after infusion of mesenchymal stromal cells. Leukemia 29, 1839–1846 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.89
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.89
This article is cited by
-
A review of the application of mesenchymal stem cells in the field of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
European Journal of Medical Research (2023)
-
Current perspectives on mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for graft versus host disease
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2023)
-
Current status of clinical trials assessing mesenchymal stem cell therapy for graft versus host disease: a systematic review
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2022)
-
Efficacy of MSC for steroid-refractory acute GVHD associates with MSC donor age and a defined molecular profile
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2020)
-
The role of mesenchymal stem cells in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: prevention and treatment of graft-versus-host disease
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2019)