Abstract
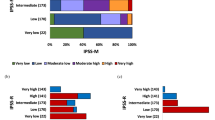
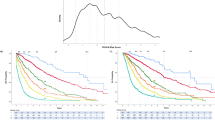
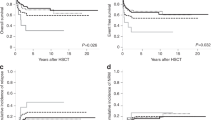
A risk-adapted treatment strategy is mandatory for myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). We refined the World Health Organization (WHO)-classification-based Prognostic Scoring System (WPSS) by determining the impact of the newer clinical and cytogenetic features, and we compared its prognostic power to that of the revised International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R). A population of 5326 untreated MDS was considered. We analyzed single WPSS parameters and confirmed that the WHO classification and severe anemia provide important prognostic information in MDS. A strong correlation was found between the WPSS including the new cytogenetic risk stratification and WPSS adopting original criteria. We then compared WPSS with the IPSS-R prognostic system. A highly significant correlation was found between the WPSS and IPSS-R risk classifications. Discrepancies did occur among lower-risk patients in whom the number of dysplastic hematopoietic lineages as assessed by morphology did not reflect the severity of peripheral blood cytopenias and/or increased marrow blast count. Moreover, severe anemia has higher prognostic weight in the WPSS versus IPSS-R model. Overall, both systems well represent the prognostic risk of MDS patients defined by WHO morphologic criteria. This study provides relevant in formation for the implementation of risk-adapted strategies in MDS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ades L, Itzykson R, Fenaux P . Myelodysplastic syndromes. Lancet 2014; 383: 2239–2252.
Malcovati L, Hellstrom-Lindberg E, Bowen D, Adès L, Cermak J, Del Cañizo C et al. Diagnosis and treatment of primary myelodysplastic syndromes in adults: recommendations from the European LeukemiaNet. Blood 2013; 122: 2943–2964.
Killick SB, Carter C, Culligan D, Dalley C, Das-Gupta E, Drummond M et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of adult myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 2014; 164: 503–525.
Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1997; 89: 2079–2088.
Cazzola M, Malcovati L . Myelodysplastic syndromes-coping with ineffective hematopoiesis. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 536–538.
Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood 2009; 114: 937–951.
Malcovati L, Della Porta MG, Pascutto C, Invernizzi R, Boni M, Travaglino E et al. Prognostic factors and life expectancy in myelodysplastic syndromes classified according to WHO criteria. A basis for clinical decision-making. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 7594–7603.
Della Porta MG, Travaglino E, Boveri E, Ponzoni M, Malcovati L, Papaemmanuil E et al. Minimal morphological criteria for defining bone marrow dysplasia: a basis for clinical implementation of WHO classification of myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 2014; 29: 66–75.
Germing U, Strupp C, Kuendgen A, Isa S, Knipp S, Hildebrandt B et al. Prospective validation of the WHO proposals for the classification of myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica 2006; 91: 1596–1604.
Della Porta MG, Malcovati L, Boveri E, Travaglino E, Pietra D, Pascutto C et al. Clinical relevance of bone marrow fibrosis and CD34-positive cell clusters in primary myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 754–762.
Malcovati L, Germing U, Kuendgen A, Della Porta MG, Pascutto C, Invernizzi R et al. Time-dependent prognostic scoring system for predicting survival and leukemic evolution in myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 3503–3510.
Malcovati L, Della Porta MG, Strupp C, Ambaglio I, Kuendgen A, Nachtkamp K et al. Impact of the degree of anemia on the outcome of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome and its integration into the WHO classification-based Prognostic Scoring System (WPSS). Haematologica 2011; 96: 1433–1440.
Greenberg PL, Attar E, Bennett JM, Bloomfield CD, Borate U, De Castro CM et al. NCCN practice guidelines for myelodysplastic syndromes, Version1. 2014. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2013; 11: 838–874.
Greenberg PL, Tuechler H, Schanz J, Sanz G, Garcia-Manero G, Solé F et al. Revised International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R) for myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2012; 120: 2454–2465.
Schanz J, Steidl C, Fonatsch C, Pfeilstöcker M, Nösslinger T, Tuechler H et al. Coalesced multicentric analysis of 2,351 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes indicates an underestimation of poor-risk cytogenetics of myelodysplastic syndromes in the international prognostic scoring system. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 1963–1970.
Schanz J, Tuchler H, Sole F, Mallo M, Luño E, Cervera J et al. New comprehensive cytogenetic scoring system for primary myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and oligoblastic acute myeloid leukemia after MDS derived from an international database merge. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 820–829.
Haase D, Germing U, Schanz J, Pfeilstöcker M, Nösslinger T, Hildebrandt B et al. New insights into the prognostic impact of the karyotype in MDS and correlation with subtypes: evidence from a core dataset of 2124 patients. Blood 2007; 110: 4385–4395.
Kao JM, McMillan A, Greenberg PL . International MDS risk analysis workshop (IMRAW)/IPSS reanalyzed: Impact of cytopenias on clinical outcomes in myelodysplastic syndromes. Am J Hematol 2008; 83: 765–770.
Voso MT, Fenu S, Latagliata R, Buccisano F, Piciocchi A, Aloe-Spiriti MA et al. Revised International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) predicts survival and leukemic evolution of myelodysplastic syndromes significantly better than IPSS and WHO Prognostic Scoring System: validation by the Gruppo Romano Mielodisplasie Italian Regional Database. J Clin Oncol 2013; 31: 2671–2677.
Neukirchen J, Lauseker M, Blum S, Giagounidis A, Lübbert M, Martino S et al. Validation of the revised international prognostic scoring system (IPSS-R) in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome: a multicenter study. Leuk Res 2014; 38: 57–64.
Della Porta MG, Alessandrino EP, Bacigalupo A, van Lint MT, Malcovati L, Pascutto C et al. Predictive factors for the outcome of allogeneic transplantation in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome stratified according to the revised International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R). Blood 2014; 123: 2333–2342.
Deeg HJ, Scott BL, Fang M, Shulman HM, Gyurkocza B, Myerson D et al. Five-group cytogenetic risk classification, monosomal karyotype and outcome after hematopoietic cell transplantation for MDS or acute leukemia evolving from MDS. Blood 2012; 120: 1398–1408.
Shaffer LG, Slovak ML, Campbell LJ (eds) . An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature: Recommendations of the International Standing Committee on Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature. Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2009.
R Development Core Team, R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna Austria. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. (Accessed 10 February 2015) http://www.r-project.org.
Therneau TM . A Package for Survival Analysis in S. R package version 2.37-7. (Accessed 10 February 2015) http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survival.
Cazzola M, Della Porta MG, Malcovati L . The genetic basis of myelodysplasia and its clinical relevance. Blood 2013; 122: 4021–4034.
Malcovati L, Papaemmanuil E, Ambaglio I, Elena C, Gallì A, Della Porta MG et al. Driver somatic mutations identify distinct disease entities within myeloid neoplasms with myelodysplasia. Blood 2014; 124: 1513–1521.
Yoshida K, Sanada M, Shiraishi Y, Nowak D, Nagata Y, Yamamoto R et al. Frequent pathway mutations of splicing machinery in myelodysplasia. Nature 2011; 478: 64–69.
Papaemmanuil E, Cazzola M, Boultwood J, Malcovati L, Vyas P, Bowen D et al. Somatic SF3B1 mutation in myelodysplasia with ring sideroblasts. N Engl J Med 2011; 365: 1384–1395.
Papaemmanuil E, Gerstung M, Malcovati L, Tauro S, Gundem G, Van Loo P et al. Clinical and biological implications of driver mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2013; 122: 3616–3627.
Cazzola M, Della Porta MG, Travaglino E, Malcovati L . Classification and prognostic evaluation of myelodysplastic syndromes. Semin Oncol 2011; 38: 627–634.
Cazzola M, Della Porta MG, Malcovati L . Clinical relevance of anemia and transfusion iron overload in myelodysplastic syndromes. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2008, 166–175.
Kuendgen A, Strupp C, Aivado M, Hildebrandt B, Haas R, Gattermann N et al. Myelodysplastic syndromes in patients younger than age 50. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 5358–5365.
Stauder R, Nösslinger T, Pfeilstöcker M, Sperr WR, Wimazal F, Krieger O et al. Impact of age and comorbidity in myelodysplastic syndromes. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2008; 6: 927–934.
Della Porta MG, Malcovati L, Strupp C, Ambaglio I, Kuendgen A, Zipperer E et al. Risk stratification based on both disease status and extra-hematologic comorbidities in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Haematologica 2011; 96: 441–449.
Naqvi K, Garcia-Manero G, Sardesai S, Oh J, Vigil CE, Pierce S et al. Association of comorbidities with overall survival in myelodysplastic syndrome: development of a prognostic model. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 2240–2246.
Sperr WR, Wimazal F, Kundi M, Baumgartner C, Nösslinger T, Makrai A et al. Comorbidity as prognostic variable in MDS: comparative evaluation of the HCT-CI and CCI in a core dataset of 419 patients of the Austrian MDS Study Group. Ann Oncol 2010; 21: 114–119.
van Spronsen MF, Ossenkoppele GJ, Holman R, van de Loosdrecht AA . Improved risk stratification by the integration of the revised international prognostic scoring system with the myelodysplastic syndromes comorbidity index. Eur J Cancer 2014; 18: 3198–3205.
Westers TM, Ireland R, Kern W, Alhan C, Balleisen JS, Bettelheim P et al. Standardization of flow cytometry in myelodysplastic syndromes: a report from an international consortium and the European LeukemiaNet Working Group. Leukemia 2012; 26: 1730–1741.
Senent L, Arenillas L, Luno E, Ruiz JC, Sanz G, Florensa L . Reproducibility of the World Health Organization 2008 criteria for myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica 2013; 98: 568–575.
Porwit A, van de Loosdrecht AA, Bettelheim P, Brodersen LE, Burbury K, Cremers E et al. Revisiting guidelines for integration of flow cytometry results in the WHO classification of myelodysplastic syndromes-proposal from the International/European LeukemiaNet Working Group for Flow Cytometry in MDS. Leukemia 2014; 28: 1793–1798.
Alhan C, Westers TM, Cremers EM, Cali C, Witte BI, Ossenkoppele GJ et al. High flow cytometric scores identify adverse prognostic subgroups within the revised international prognostic scoring system for myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 2014; 167: 100–109.
Gerstung M, Pellagatti A, Malcovati L, Giagounidis A, Della Porta MG, Jädersten M et al. Combining gene mutation with gene expression data improves outcome prediction in myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat Commun 2015; 6: 5901.
Bejar R, Stevenson K, Abdel-Wahab O, Galili N, Nilsson B, Garcia-Manero G et al. Clinical effect of point mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med 2011; 364: 2496–2506.
Haferlach T, Nagata Y, Grossmann V, Okuno Y, Bacher U, Nagae G et al. Landscape of genetic lesions in 944 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 2014; 28: 241–247.
Acknowledgements
We thank the MDS Foundation Inc., for statistical support (HT), Ms Tracey Iraca and MDS Foundation staff for helpful logistical assistance for the IWG-PM project. The study was supported by Fondazione Berlucchi, Brescia, Fondazione Veronesi, Milan, Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, Pavia, and Fondazione Cariplo/Regione Lombardia, Milan, Italy (MGDP and MC), and by Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro, Milan, Italy (LM and MC).
Author Contributions
MGDP, HT, LM, PLG and MC designed, performed and coordinated the research, collected, contributed, analyzed and interpreted the data, and wrote the manuscript; HT designed and performed the research, performed the statistical analyses, produced the figures and edited the manuscript; JS, GS, GG-M, FS, JMB, DB, PF, FD, HK, AK, AL, JC, CF, MMLB, MLS, OK, ML, JM, SMMM, YM, MP, MS, WRS, RS, ST, PV, TV, AAvdL, UG and DH collected and contributed data and critically reviewed the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Della Porta, M., Tuechler, H., Malcovati, L. et al. Validation of WHO classification-based Prognostic Scoring System (WPSS) for myelodysplastic syndromes and comparison with the revised International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R). A study of the International Working Group for Prognosis in Myelodysplasia (IWG-PM). Leukemia 29, 1502–1513 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.55
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.55
This article is cited by
-
The value of serum IL-4 to predict the survival of MDS patients
European Journal of Medical Research (2023)
-
Myelodysplastic syndromes
Nature Reviews Disease Primers (2022)
-
LINC01255 combined with BMI1 to regulate human mesenchymal stromal senescence and acute myeloid leukemia cell proliferation through repressing transcription of MCP-1
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2021)
-
Late treatment-related mortality versus competing causes of death after allogeneic transplantation for myelodysplastic syndromes and secondary acute myeloid leukemia
Leukemia (2019)