Abstract
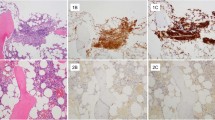
CD123 is the α-subunit of the interleukin-3 receptor; it represents a potential therapeutic target in systemic mastocytosis (SM) given its absent expression on normal/reactive mast cells (MCs) and aberrant expression on neoplastic MCs. We studied 58 SM patients to define CD123 expression patterns by immunohistochemistry and its clinical significance. Two hematopathologists independently scored bone marrow slides using predefined histologic parameters. In all, 23 patients had indolent SM (ISM), 10 aggressive SM (ASM), 23 SM with associated hematological neoplasm (SM-AHN) and 2 had mast cell leukemia (MCL). MC_CD123 expression was demonstrable in 37 (64%) cases; expression rates were 100%, 61%, 57% and 0% in ASM, ISM, SM-AHN and MCL, respectively (P=0.02). Focal proliferation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells (PDCs) around MC aggregates, suggesting a tumor-promoting role for PDCs, was noted in 44 (76%) cases, and was significantly higher in CD123-positive versus -negative cases (87% versus 50%, P=0.005). CD123 expression and its staining intensity had prognostic value in SM-chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and nonindolent SM patients, respectively. These observations suggest that targeting CD123 in SM may have direct (via MCs) and indirect (via PDCs) antitumor effects and clinical trials to that effect require laboratory correlative studies to address the observed target expression heterogeneity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Woodcock JM, Bagley CJ, Zacharakis B, Lopez AF . A single tyrosine residue in the membrane-proximal domain of the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, interleukin (IL)-3, and IL-5 receptor common beta-chain is necessary and sufficient for high affinity binding and signaling by all three ligands. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 25999–26006.
Testa U, Fossati C, Samoggia P, Masciulli R, Mariani G, Hassan HJ et al. Expression of growth factor receptors in unilineage differentiation culture of purified hematopoietic progenitors. Blood 1996; 88: 3391–3406.
Militi S, Riccioni R, Parolini I, Sposi NM, Samoggia P, Pelosi E et al. Expression of interleukin 3 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor common chain betac, betaIT in normal haematopoiesis: lineage specificity and proliferation-independent induction. Br J Haematol 2000; 111: 441–451.
Reichard KK, Burks EJ, Foucar MK, Wilson CS, Viswanatha DS, Hozier JC et al. CD4(+) CD56(+) lineage-negative malignancies are rare tumors of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Am J Surg Pathol 2005; 29: 1274–1283.
Testa U, Pelosi E, Frankel A . CD 123 is a membrane biomarker and a therapeutic target in hematologic malignancies. Biomark Res 2014; 2: 4.
Valent P, Besemer J, Sillaber C, Butterfield JH, Eher R, Majdic O et al. Failure to detect IL-3-binding sites on human mast cells. J Immunol 1990; 145: 3432–3437.
Pardanani A, Lasho T, Chen D, Kimlinger TK, Finke C, Zblewski D et al. Aberrant expression of CD123 (interleukin-3 receptor-alpha) on neoplastic mast cells. Leukemia 2015; 29: 1605–1608.
Horny HP, Metcalfe DD, Bennett JM, Bain BJ, Akin C, Escribano L et al Mastocytosis. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H et al (eds) WHO Classification of Tumors of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 4th edn. International Agency for Research and Cancer (IARC): Lyon, 2008; pp 54–63.
Testa U, Riccioni R, Diverio D, Rossini A, Lo Coco F, Peschle C . Interleukin-3 receptor in acute leukemia. Leukemia 2004; 18: 219–226.
Testa U, Riccioni R, Militi S, Coccia E, Stellacci E, Samoggia P et al. Elevated expression of IL-3Ralpha in acute myelogenous leukemia is associated with enhanced blast proliferation, increased cellularity, and poor prognosis. Blood 2002; 100: 2980–2988.
De Waele M, Renmans W, Vander Gucht K, Jochmans K, Schots R, Otten J et al. Growth factor receptor profile of CD34+ cells in AML and B-lineage ALL and in their normal bone marrow counterparts. Eur J Haematol 2001; 66: 178–187.
Chauhan D, Singh AV, Brahmandam M, Carrasco R, Bandi M, Hideshima T et al. Functional interaction of plasmacytoid dendritic cells with multiple myeloma cells: a therapeutic target. Cancer Cell 2009; 16: 309–323.
Chen YC, Chou JM, Ketterling RP, Letendre L, Li CY . Histologic and immunohistochemical study of bone marrow monocytic nodules in 21 cases with myelodysplasia. Am J Clin Pathol 2003; 120: 874–881.
Vermi W, Facchetti F, Rosati S, Vergoni F, Rossi E, Festa S et al. Nodal and extranodal tumor-forming accumulation of plasmacytoid monocytes/interferon-producing cells associated with myeloid disorders. Am J Surg Pathol 2004; 28: 585–595.
Ray A, Das DS, Song Y, Richardson P, Munshi NC, Chauhan D et al. Targeting PD1-PDL1 immune checkpoint in plasmacytoid dendritic cell interactions with T cells, natural killer cells and multiple myeloma cells. Leukemia 2015; 29: 1441–1444.
Acknowledgements
The study was funded by a grant from the Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA.
Author contributions
AP, KKR and DC designed the project and analyzed the data. KKR and DC performed the primary blinded review of bone marrow slides with scoring of predefined histological parameters. CAH, KLG and WGM provided additional hematopathology review. DZ, RAA and EAW abstracted clinical data from patient medical charts. AT and CB assisted in scientific review and data analysis. AP wrote the first draft of the paper. All the authors reviewed the manuscript draft, provided critical input and approved the final version of the manuscript. AP and DC had full access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
AP received a research grant from Stemline therapeutics for preclinical study of the CD123-targeting drug, SL-701. CB is an employee of Stemline Therapeutics.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pardanani, A., Reichard, K., Zblewski, D. et al. CD123 immunostaining patterns in systemic mastocytosis: differential expression in disease subgroups and potential prognostic value. Leukemia 30, 914–918 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.348
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.348
This article is cited by
-
Systemic mastocytosis mimicking blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: a case report
Diagnostic Pathology (2023)
-
Immunohistochemistry Innovations for Diagnosis and Tissue-Based Biomarker Detection
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2019)
-
Biology and prognostic impact of clonal plasmacytoid dendritic cells in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia
Leukemia (2019)
-
Blastic Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Neoplasm
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2018)
-
Predictors of survival in WHO-defined hypereosinophilic syndrome and idiopathic hypereosinophilia and the role of next-generation sequencing
Leukemia (2016)