Abstract
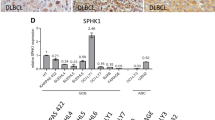
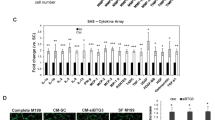
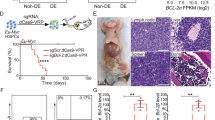
Angiogenesis associates with poor outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), but the contribution of the lymphoma cells to this process remains unclear. Addressing this knowledge gap may uncover unsuspecting proangiogenic signaling nodes and highlight alternative antiangiogenic therapies. Here, we identify the second messenger cyclic-AMP (cAMP) and the enzyme that terminates its activity, phosphodiesterase 4B (PDE4B), as regulators of B-cell lymphoma angiogenesis. We first show that cAMP, in a PDE4B-dependent manner, suppresses PI3K/AKT signals to downmodulate vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) secretion and vessel formation in vitro. Next, we create a novel mouse model that combines the lymphomagenic Myc transgene with germline deletion of Pde4b. We show that lymphomas developing in a Pde4b-null background display significantly lower microvessel density (MVD) in association with lower VEGF levels and PI3K/AKT activity. We recapitulate these observations by treating lymphoma-bearing mice with the FDA-approved PDE4 inhibitor, Roflumilast. Lastly, we show that primary human DLBCLs with high PDE4B expression display significantly higher MVD. Here, we defined an unsuspected signaling circuitry in which the cAMP generated in lymphoma cells downmodulates PI3K/AKT and VEGF secretion to negatively influence vessel development in the microenvironment. These data identify PDE4 as an actionable antiangiogenic target in DLBCL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Welti J, Loges S, Dimmeler S, Carmeliet P . Recent molecular discoveries in angiogenesis and antiangiogenic therapies in cancer. J Clin Invest 2013; 123: 3190–3200.
Jain RK . Antiangiogenesis strategies revisited: from starving tumors to alleviating hypoxia. Cancer Cell 2014; 26: 605–622.
Sehn LH, Gascoyne RD . Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: optimizing outcome in the context of clinical and biologic heterogeneity. Blood 2015; 125: 22–32.
Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 2000; 403: 503–511.
Lenz G, Wright G, Dave SS, Xiao W, Powell J, Zhao H et al. Stromal gene signatures in large-B-cell lymphomas. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 2313–2323.
Monti S, Savage KJ, Kutok JL, Feuerhake F, Kurtin P, Mihm M et al. Molecular profiling of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies robust subtypes including one characterized by host inflammatory response. Blood 2005; 105: 1851–1861.
Pasqualucci L . The genetic basis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Curr Opin Hematol 2013; 20: 336–344.
Weinstock DM, Dalla-Favera R, Gascoyne RD, Leonard JP, Levy R, Lossos IS et al. A roadmap for discovery and translation in lymphoma. Blood 2015; 125: 2175–2177.
Salven P, Orpana A, Teerenhovi L, Joensuu H . Simultaneous elevation in the serum concentrations of the angiogenic growth factors VEGF and bFGF is an independent predictor of poor prognosis in non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a single-institution study of 200 patients. Blood 2000; 96: 3712–3718.
Gratzinger D, Zhao S, Tibshirani RJ, Hsi ED, Hans CP, Pohlman B et al. Prognostic significance of VEGF, VEGF receptors, and microvessel density in diffuse large B cell lymphoma treated with anthracycline-based chemotherapy. Lab Invest 2008; 88: 38–47.
Cardesa-Salzmann TM, Colomo L, Gutierrez G, Chan WC, Weisenburger D, Climent F et al. High microvessel density determines a poor outcome in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab plus chemotherapy. Haematologica 2011; 96: 996–1001.
Liapis K, Clear A, Owen A, Coutinho R, Greaves P, Lee AM et al. The microenvironment of AIDS-related diffuse large B-cell lymphoma provides insight into the pathophysiology and indicates possible therapeutic strategies. Blood 2013; 122: 424–433.
Seymour JF, Pfreundschuh M, Trneny M, Sehn LH, Catalano J, Csinady E et al. R-CHOP with or without bevacizumab in patients with previously untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: final MAIN study outcomes. Haematologica 2014; 99: 1343–1349.
Stopeck AT, Unger JM, Rimsza LM, LeBlanc M, Farnsworth B, Iannone M et al. A phase 2 trial of standard-dose cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone (CHOP) and rituximab plus bevacizumab for patients with newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: SWOG 0515. Blood 2012; 120: 1210–1217.
Mosenden R, Tasken K . Cyclic AMP-mediated immune regulation—overview of mechanisms of action in T cells. Cell Signal 2011; 23: 1009–1016.
Levy FO, Rasmussen AM, Tasken K, Skalhegg BS, Huitfeldt HS, Funderud S et al. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase (cAK) in human B cells: co-localization of type I cAK (RI alpha 2 C2) with the antigen receptor during anti-immunoglobulin-induced B cell activation. Eur J Immunol 1996; 26: 1290–1296.
Kim SW, Rai D, McKeller MR, Aguiar RC . Rational combined targeting of phosphodiesterase 4B and SYK in DLBCL. Blood 2009; 113: 6153–6160.
Smith PG, Wang F, Wilkinson KN, Savage KJ, Klein U, Neuberg DS et al. The phosphodiesterase PDE4B limits cAMP-associated PI3K/AKT-dependent apoptosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2005; 105: 308–316.
Serezani CH, Ballinger MN, Aronoff DM, Peters-Golden M . Cyclic AMP: master regulator of innate immune cell function. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2008; 39: 127–132.
Conti M, Richter W, Mehats C, Livera G, Park JY, Jin C . Cyclic AMP-specific PDE4 phosphodiesterases as critical components of cyclic AMP signaling. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 5493–5496.
Shipp MA, Ross KN, Tamayo P, Weng AP, Kutok JL, Aguiar RC et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma outcome prediction by gene-expression profiling and supervised machine learning. Nat Med 2002; 8: 68–74.
Kim SW, Rai D, Aguiar RC . Gene set enrichment analysis unveils the mechanism for the phosphodiesterase 4B control of glucocorticoid response in B-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 6723–6732.
Mendes JB, Rocha MA, Araujo FA, Moura SA, Ferreira MA, Andrade SP . Differential effects of rolipram on chronic subcutaneous inflammatory angiogenesis and on peritoneal adhesion in mice. Microvasc Res 2009; 78: 265–271.
Favot L, Keravis T, Holl V, Le Bec A, Lugnier C . VEGF-induced HUVEC migration and proliferation are decreased by PDE2 and PDE4 inhibitors. Thromb Haemost 2003; 90: 334–343.
Jin H, Garmy-Susini B, Avraamides CJ, Stoletov K, Klemke RL, Varner JA . A PKA-Csk-pp60Src signaling pathway regulates the switch between endothelial cell invasion and cell-cell adhesion during vascular sprouting. Blood 2010; 116: 5773–5783.
Kim S, Bakre M, Yin H, Varner JA . Inhibition of endothelial cell survival and angiogenesis by protein kinase A. J Clin Invest 2002; 110: 933–941.
Lin AP, Abbas S, Kim SW, Ortega M, Bouamar H, Escobedo Y et al. D2HGDH regulates alpha-ketoglutarate levels and dioxygenase function by modulating IDH2. Nat Commun 2015; 6: 7768.
Jin SL, Conti M . Induction of the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase PDE4B is essential for LPS-activated TNF-alpha responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 7628–7633.
Jung I, Aguiar RC . MicroRNA-155 expression and outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 2009; 144: 138–140.
Bouamar H, Jiang D, Wang L, Lin AP, Ortega M, Aguiar RC . MicroRNA 155 Control of p53 Activity Is Context Dependent and Mediated by Aicda and Socs1. Mol Cell Biol 2015; 35: 1329–1340.
Mizukami Y, Kohgo Y, Chung DC . Hypoxia inducible factor-1 independent pathways in tumor angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13: 5670–5674.
Kotani A, Kakazu N, Tsuruyama T, Okazaki IM, Muramatsu M, Kinoshita K et al. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) promotes B cell lymphomagenesis in Emu-cmyc transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 1616–1620.
Schuster C, Berger A, Hoelzl MA, Putz EM, Frenzel A, Simma O et al. The cooperating mutation or "second hit" determines the immunologic visibility toward MYC-induced murine lymphomas. Blood 2011; 118: 4635–4645.
Hemann MT, Bric A, Teruya-Feldstein J, Herbst A, Nilsson JA, Cordon-Cardo C et al. Evasion of the p53 tumour surveillance network by tumour-derived MYC mutants. Nature 2005; 436: 807–811.
Schmitt CA, Rosenthal CT, Lowe SW . Genetic analysis of chemoresistance in primary murine lymphomas. Nat Med 2000; 6: 1029–1035.
Wendel HG, De Stanchina E, Fridman JS, Malina A, Ray S, Kogan S et al. Survival signalling by Akt and eIF4E in oncogenesis and cancer therapy. Nature 2004; 428: 332–337.
Nilsson JA, Keller UB, Baudino TA, Yang C, Norton S, Old JA et al. Targeting ornithine decarboxylase in Myc-induced lymphomagenesis prevents tumor formation. Cancer Cell 2005; 7: 433–444.
Wall M, Poortinga G, Stanley KL, Lindemann RK, Bots M, Chan CJ et al. The mTORC1 inhibitor everolimus prevents and treats Emu-Myc lymphoma by restoring oncogene-induced senescence. Cancer Discov 2013; 3: 82–95.
Bouamar H, Abbas S, Lin AP, Wang L, Jiang D, Holder KN et al. A capture-sequencing strategy identifies IRF8, EBF1, and APRIL as novel IGH fusion partners in B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2013; 122: 726–733.
Li C, Kim SW, Rai D, Bolla AR, Adhvaryu S, Kinney MC et al. Copy number abnormalities, MYC activity, and the genetic fingerprint of normal B cells mechanistically define the microRNA profile of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2009; 113: 6681–6690.
Gratzinger D, Zhao S, Marinelli RJ, Kapp AV, Tibshirani RJ, Hammer AS et al. Microvessel density and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma subtypes. Am J Pathol 2007; 170: 1362–1369.
Norrby K, Ridell B . Tumour-type-specific capillary endothelial cell stainability in malignant B-cell lymphomas using antibodies against CD31, CD34 and Factor VIII. APMIS 2003; 111: 483–489.
Gantner F, Gotz C, Gekeler V, Schudt C, Wendel A, Hatzelmann A . Phosphodiesterase profile of human B lymphocytes from normal and atopic donors and the effects of PDE inhibition on B cell proliferation. Br J Pharmacol 1998; 123: 1031–1038.
Tsunoda T, Ota T, Fujimoto T, Doi K, Tanaka Y, Yoshida Y et al. Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) activity triggers luminal apoptosis and AKT dephosphorylation in a 3-D colonic-crypt model. Mol Cancer 2012; 11: 46.
Sengupta R, Sun T, Warrington NM, Rubin JB . Treating brain tumors with PDE4 inhibitors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2011; 32: 337–344.
Wang P, Wu P, Ohleth KM, Egan RW, Billah MM . Phosphodiesterase 4B2 is the predominant phosphodiesterase species and undergoes differential regulation of gene expression in human monocytes and neutrophils. Mol Pharmacol 1999; 56: 170–174.
Pullamsetti SS, Banat GA, Schmall A, Szibor M, Pomagruk D, Hanze J et al. Phosphodiesterase-4 promotes proliferation and angiogenesis of lung cancer by crosstalk with HIF. Oncogene 2013; 32: 1121–1134.
Yang Q, Modi P, Newcomb T, Queva C, Gandhi V . Idelalisib: first-in-class PI3K delta inhibitor for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, small lymphocytic leukemia, and follicular lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 2015; 21: 1537–1542.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Cancer Therapy and Research Center at UTHSCSA Core Pathology Tissue Bank for procurement of the primary DLBCL samples. We acknowledge Patricia Dahia for insightful suggestions during the execution of this project. This work was supported by CPRIT awards RP110200 and RP150277 (to RCTA), a grant from the William and Ella Owens Medical Research Foundation (to RCTA), and a Cancer Center support grant P30 CA054174.
Author contributions
ANS designed and conducted experiments, and analyzed the data; LW conducted animal experiments; A-PL conducted experiments, HB performed animal husbandry; S-WK conducted experiments; AM and KH performed pathological analyses; RCTA designed and coordinated the study, analyzed data and wrote the manuscript, which was reviewed by all authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suhasini, A., Wang, L., Holder, K. et al. A phosphodiesterase 4B-dependent interplay between tumor cells and the microenvironment regulates angiogenesis in B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 30, 617–626 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.302
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.302
This article is cited by
-
The Endothelial Activation and Stress Index (EASIX) score is an independent prognostic factor in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
BMC Cancer (2022)
-
CircKDM4B suppresses breast cancer progression via the miR-675/NEDD4L axis
Oncogene (2022)
-
MYC, mitochondrial metabolism and O-GlcNAcylation converge to modulate the activity and subcellular localization of DNA and RNA demethylases
Leukemia (2022)
-
Regulation of PD-L1 expression is a novel facet of cyclic-AMP-mediated immunosuppression
Leukemia (2021)
-
PDE4 subtypes in cancer
Oncogene (2020)