Abstract
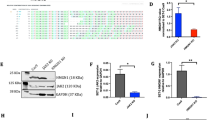
Still 20% of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) patients relapse on or after current treatment strategies. Treatment failure is associated with resistance to prednisolone. We aimed to find new druggable targets that modulate prednisolone resistance. We generated microarray gene expression profiles of 256 pediatric ALL patient samples and identified a 3.4-fold increase in epithelial membrane protein 1 (EMP1) expression in in vitro prednisolone-resistant compared with -sensitive patients (P=0.003). EMP1 silencing in six precursor-B ALL (BCP-ALL) and T-ALL cell lines induced apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest leading to 84.1±4.5% reduction in survival compared with non-silencing control transduced cells (non-silencing control short hairpin, shNSC) (P=0.014). Moreover, EMP1 silencing sensitized to prednisolone up to 18.8-fold (P<0.001). EMP1 silencing also abrogated migration and adhesion to mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) by 78.3±9.0 and 29.3±4.1% compared with shNSC (P<0.05). We discovered that EMP1 contributes to MSC-mediated prednisolone resistance. Pathway analysis indicated that EMP1 signals through the Src kinase family. EMP1-high BCP-ALL patients showed a poorer 5-year event-free survival compared with EMP1-low patients (77±2 vs 89±2%, P=0.003). Multivariate analysis taking along white blood cell count, age, prednisolone resistance and subtype identified EMP1 as an independent predictor for poor outcome in BCP-ALL (P=0.004, hazard ratio: 2.36 (1.31–4.25). This study provides preclinical evidence that EMP1 is an interesting candidate for drug development to optimize treatment of BCP-ALL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pui CH, Carroll WL, Meshinchi S, Arceci RJ . Biology, risk stratification, and therapy of pediatric acute leukemias: an update. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 551–565.
Kaspers GJ, Pieters R, Van Zantwijk CH, Van Wering ER, Van Der Does-Van Den Berg A, Veerman AJ . Prednisolone resistance in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: vitro-vivo correlations and cross-resistance to other drugs. Blood 1998; 92: 259–266.
Klumper E, Pieters R, Veerman AJ, Huismans DR, Loonen AH, Hählen K et al. In vitro cellular drug resistance in children with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 1995; 86: 3861–3868.
Kfir-Erenfeld S, Sionov RV, Spokoini R, Cohen O, Yefenof E . Protein kinase networks regulating glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis of hematopoietic cancer cells: fundamental aspects and practical considerations. Leuk Lymphoma 2010; 51: 1968–2005.
Taylor V, Welcher AA, Program AE, Suter U . Epithelial membrane protein-1, peripheral myelin protein 22, and lens membrane protein 20 define a novel gene family. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 28824–28833.
Bangsow T, Baumann E, Bangsow C, Jaeger MH, Pelzer B, Gruhn P et al. The epithelial membrane protein 1 is a novel tight junction protein of the blood-brain barrier. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2008; 28: 1249–1260.
Lee H-S, Sherley JL, Chen JJW, Chiu C-C, Chiou L-L, Liang J-D et al. EMP-1 is a junctional protein in a liver stem cell line and in the liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 334: 996–1003.
Ben-Porath I, Yanuka O, Benvenisty N . The tmp gene, encoding a membrane protein, is a c-Myc target with a tumorigenic activity. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 3529–3539.
Bredel M, Bredel C, Juric D, Harsh GR, Vogel H, Recht LD et al. Functional network analysis reveals extended gliomagenesis pathway maps and three novel MYC-interacting genes in human gliomas. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 8679–8689.
Turashvili G, Bouchal J, Ehrmann J, Fridman E, Skarda J, Kolar Z . Novel immunohistochemical markers for the differentiation of lobular and ductal invasive breast carcinomas. Biomed Papers 2007; 151: 59–64.
Jain A, Tindell CA, Laux I, Hunter JB, Curran J, Galkin A et al. Epithelial membrane protein-1 is a biomarker of gefitinib resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 11858–11863.
Holleman A, Cheok MH, den Boer ML, Yang W, Veerman AJP, Kazemier KM et al. Gene-expression patterns in drug-resistant acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells and response to treatment. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 533–542.
Den Boer ML, Harms DO, Pieters R, Kazemier KM, Gobel U, Körholz D et al. Patient stratification based on prednisolone-vincristine-asparaginase resistance profiles in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 3262–3268.
Den Boer ML, van Slegtenhorst M, De Menezes RX, Cheok MH, JGCAM Buijs-Gladdines, STCJM Peters et al. A subtype of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia with poor treatment outcome: a genome-wide classification study. Lancet Oncol 2009; 10: 125–134.
Mihara K, Imai C, Coustan-Smith E, Dome JS, Dominici M, Vanin E et al. Development and functional characterization of human bone marrow mesenchymal cells immortalized by enforced expression of telomerase. Br J Haematol 2003; 120: 846–849.
Huber W, von Heydebreck A, Sültmann H, Poustka A, Vingron M . Variance stabilization applied to microarray data calibration and to the quantification of differential expression. Bioinformatics 2002; 18 (Suppl 1): S96–S104.
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y . Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc 1995; 57: 289–300.
Fine JP, Gray RJ . A proportional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk. J Am Stat Assoc 1999; 94: 496–509.
de Wreede LC, Fiocco M, Putter H . mstate: an R package for the analysis of competing risks and multi-state models. J Stat Softw 2011; 38.
Gray R . Cmprsk: Subdistribution Analysis of Competing Risks. R package version 2.2-2 2011.
Pillozzi S, Masselli M, De Lorenzo E, Accordi B, Cilia E, Crociani O et al. Chemotherapy resistance in acute lymphoblastic leukemia requires hERG1 channels and is overcome by hERG1 blockers. Blood 2011; 117: 902–914.
Iwamoto S, Mihara K, Downing JR, Pui C-H, Campana D . Mesenchymal cells regulate the response of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells to asparaginase. J Clin Investig 2007; 117: 1049–1057.
Sionov RV, Spokoini R, Kfir-Erenfeld S, Cohen O, Yefenof E . Mechanisms regulating the susceptibility of hematopoietic malignancies to glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. Adv Cancer Res 2008; 101: 127–248.
Pieters R, Kaspers GJ, van Wering ER, Huismans DR, Loonen AH, Hählen K et al. Cellular drug resistance profiles that might explain the prognostic value of immunophenotype and age in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 1993; 7: 392–397.
Désarnaud F, Bidichandani S, Patel PI, Baulieu E-E, Schumacher M . Glucocorticosteroids stimulate the activity of the promoters of peripheral myelin protein-22 and protein zero genes in Schwann cells. Brain Res 2000; 865: 12–16.
Wadehra M, Mainigi M, Morales SA, Rao RG, Gordon LK, Williams CJ et al. Steroid hormone regulation of EMP2 expression and localization in the endometrium. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2008; 6: 15.
Li Z-Y, Xiong S-H, Hu M, Zhang C-S . Epithelial membrane protein 1 inhibits human spinal chondrocyte differentiation. Anat Record 2011; 294: 1015–1024.
Ben-Porath I, Benvenisty N . Characterization of a tumor-associated gene, a member of a novel family of genes encoding membrane glycoproteins. Gene 1996; 183: 69–75.
Sison EAR, Brown P . The bone marrow microenvironment and leukemia: biology and therapeutic targeting. Expert Rev Hematol 2011; 4: 271–283.
Masson K, Rönnstrand L . Oncogenic signaling from the hematopoietic growth factor receptors c-Kit and Flt3. Cell Signal 2009; 21: 1717–1726.
Lai S, Wang G, Cao X, Li Z, Hu J, Wang J . EMP-1 promotes tumorigenesis of NSCLC through PI3K/AKT pathway. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci 2012; 32: 834–838.
Morales SA, Mareninov S, Coulam P, Wadehra M, Goodglick L, Braun J et al. Functional consequences of interactions between FAK and epithelial membrane protein 2 (EMP2). Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2009; 50: 4949–4956.
Gauld SB, Cambier JC . Src-family kinases in B-cell development and signaling. Oncogene 2004; 23: 8001–8006.
Palacios EH, Weiss A . Function of the Src-family kinases, Lck and Fyn, in T-cell development and activation. Oncogene 2004; 23: 7990–8000.
Silva CM . Role of STATs as downstream signal transducers in Src family kinase-mediated tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2004; 23: 8017–8023.
Quintas-Cardama A, Verstovsek S . Molecular pathways: JAK/STAT pathway: mutations, inhibitors, and resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 2013; 19: 1933–1940.
Malin S, McManus S, Busslinger M . STAT5 in B cell development and leukemia. Curr Opin Immunol 2010; 22: 168–176.
Mangolini M, de Boer J, Walf-Vorderwülbecke V, Pieters R, den Boer ML, Williams O . STAT3 mediates oncogenic addiction to TEL-AML1 in t(12;21) acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2013; 122: 542–549.
Pignatello R, Musumeci T, Basile L, Carbone C, Puglisi G . Biomembrane models and drug-biomembrane interaction studies: Involvement in drug design and development. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 2011; 3: 4–14.
Acknowledgements
Dr D Campana, St. Jude Childrens’ Research Hospital, Memphis, USA, is highly acknowledged for supplying of MSC-hTERT cell line. This work was supported by the Dutch Cancer Society (MLDB, RP, EMCR 2005-3313 and AMC 2008-4265). The funding source had no role in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the paper for publication.
Author contributions
IMA designed and performed experiments, analyzed and interpreted data, and wrote the paper; ISJ and ERD assisted in part of the experiments; LCJVDB performed and analyzed flowsort experiment; JMB assisted with the statistical analysis of microarray data; MH and GE provided COALL survival data; RP and MLDB designed research, interpreted data and revised the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ariës, I., Jerchel, I., van den Dungen, R. et al. EMP1, a novel poor prognostic factor in pediatric leukemia regulates prednisolone resistance, cell proliferation, migration and adhesion. Leukemia 28, 1828–1837 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.80
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.80
This article is cited by
-
CUL4B-DDB1-COP1-mediated UTX downregulation promotes colorectal cancer progression
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2023)
-
Fibroma of tendon sheath is defined by a USP6 gene fusion—morphologic and molecular reappraisal of the entity
Modern Pathology (2021)
-
Deciphering molecular heterogeneity in pediatric AML using a cancer vs. normal transcriptomic approach
Pediatric Research (2021)
-
Integrative genomic analyses reveal mechanisms of glucocorticoid resistance in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Nature Cancer (2020)
-
Epithelial membrane protein 1 promotes tumor metastasis by enhancing cell migration via copine-III and Rac1
Oncogene (2018)