Abstract
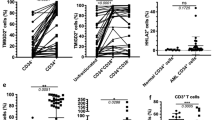
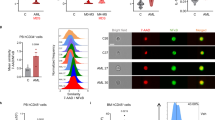
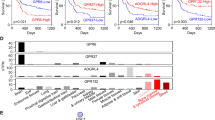
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is an aggressive disease with a poor 5-year survival of 21% that is characterized by the differentiation arrest of immature myeloid cells. For a rare subtype of AML (acute promyeloctyic leukemia, 5–10% of cases), all-trans retinoic acid therapy removes the differentiation block, yielding over a 90% cure rate. However, this treatment is not effective for the other 90–95% of AML patients, suggesting that new differentiation strategies are needed. Interestingly, differentiation is induced in normal hematopoietic cells through Toll-like receptor (TLR) stimulation and TLRs are expressed on AML cells. We present evidence that the TLR8 activation promotes AML differentiation and growth inhibition in a TLR8/MyD88/p38-dependent manner. We also show that that TLR7/TLR8 agonist, R848, considerably impairs the growth of human AML cells in immunodeficient mice. Our data suggests TLR8 activation has direct anti-leukemic effects independent of its immunomodulating properties that are currently under investigation for cancer therapy. Taken together, our results suggest that treatment with TLR8 agonists may be a promising new therapeutic strategy for AML.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Estey EH . General approach to, and perspectives on clinical research in, older patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia. Semin Hematol 2006; 43: 89–95.
Tallmann MS . Curative therapeutic approaches to APL. Ann Hematol 2004; 83: S81–S82.
Gupta K, Gulen F, Sun L, Aguilera R, Chakrabarti A, Kiselar J et al. GSK3 is a regulator of RAR-mediated differentiation. Leukemia 2012; 26: 1277–1285.
Wang Z, Smith KS, Murphy M, Piloto O, Somervaille TC, Cleary ML . Glycogen synthase kinase 3 in MLL leukaemia maintenance and targeted therapy. Nature 2008; 455: 1205–1209.
Nagai Y, Garrett KP, Ohta S, Bahrun U, Kouro T, Akira S et al. Toll-like receptors on hematopoietic progenitor cells stimulate innate immune system replenishment. Immunity 2006; 24: 801–812.
Akira STK . Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 2004; 2004 4: 499–511.
Akira S . Toll-like receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 38105–38108.
Milella M, Kornblau SM, Estrov Z, Carter BZ, Lapillonne H, Harris D et al. Therapeutic targeting of the MEK/MAPK signal transduction module in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clinical Invest 2001; 108: 851–859.
Park JCH, Jeong J, Han J, Kim I . Invovlement of p38 kinase in hydroxyurea-induced differentiation of K562 cells. Cell Growth Differ 2001; 12: 481–486.
Okamoto M, Hirai H, Taniguchi K, Shimura K, Inaba T, Shimazaki C et al. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are expressed by myeloid leukaemia cell lines, but fail to trigger differentiation in response to the respective TLR ligands. Br J Haematol 2009; 147: 585–587.
Sioud M, Fløisand Y . TLR agonists induce the differentiation of human bone marrow CD34+ progenitors into CD11c+ CD80/86+ DC capable of inducing a Th1-type response. Eur J Immunol 2007; 37: 2834–2846.
Spaner DE, Masellis A . Toll-like receptor agonists in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2006; 21: 53–60.
Bohnhorst J, Rasmussen T, Moen SH, Flottum M, Knudsen L, Borset M et al. Toll-like receptors mediate proliferation and survival of multiple myeloma cells. Leukemia 2006; 20: 1138–1144.
Hennessy EJ, Parker AE, O'Neill LAJ . Targeting Toll-like receptors: emerging therapeutics? Nat Rev Drug Discov 2010; 9: 293–307.
Larangé A, Antonios D, Pallardy M, Kerdine-Römer S . TLR7 and TLR8 agonists trigger different signaling pathways for human dendritic cell maturation. J Leukoc Biol 2009; 85: 673–683.
Oberg HHJM, Kabelitz D, Wesch D . Regulation of T cell activation by TLR ligands. Eur J Cell Biol 2011; 90: 582–592.
Peng G, Guo Z, Kiniwa Y, Ks Voo, Peng W, Fu T et al. Toll-like receptor 8-mediated reversal of CD4+ regulatory T cell function. Science 2005; 309: 1380–1384.
Wei MQ, Mengesha A, Good D, Anné J . Bacterial targeted tumour therapy-dawn of a new era. Cancer Lett 2008; 259: 16–27.
Wald DN, Vermaat HM, Zang S, Lavik A, Kang Z, Peleg G et al. Identification of 6-benzylthioinosine as a myeloid leukemia differentiation–inducing compound. Cancer Res 2008 2008; 68: 4369–4376.
Collins SJ, Ruscetti FW, Gallagher RE, Gallo RC . Normal functional characteristics of cultured human promyelocytic leukemia cells (HL-60) after induction of differentiation by dimethylsulfoxide. J Exp Med 1979; 149: 969–974.
Collins SJBA, Ting R, Gallo RC . Induction of morphological and functional differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells (HL-60) by compounds which induce differentiation of murine leukemia cells. Int J Cancer 1980; 25: 213–218.
Newburger P, Chovaniec M, Greenberger J, Cohen H . Functional changes in human leukemic cell line HL-60. A model for myeloid differentiation. J Cell Biol 1979; 82: 315–322.
Piedfer M, Bouchet S, Tang R, Billard C, Dauzonne D, Bauvois B . p70S6 kinase is a target of the novel proteasome inhibitor 3,3′-diamino-4′-methoxyflavone during apoptosis in human myeloid tumor cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013; 1833: 1316–1328.
Lu H, Dietsch GN, Matthews M-AH, Yang Y, Ghanekar S, Inokuma M et al. VTX-2337 is a novel TLR8 agonist that activates NK cells and augments ADCC. Clin Cancer Res 2012; 18: 499–509.
Dziarski R, Jin Y-p, Gupta D . Differential activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1, ERK2, p38, and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase mitogen-activated protein kinases by bacterial peptidoglycan. J Infect Dis 1996; 174: 777–785.
Chiacchiera F, Matrone A, Ferrari E, Ingravallo G, Lo Sasso G, Murzilli S et al. p38[alpha] blockade inhibits colorectal cancer growth in vivo by inducing a switch from HIF1[alpha]- to FoxO-dependent transcription. Cell Death Differ 2009; 16: 1203–1214.
Puri PL, Wu Z, Zhang P, Wood LD, Bhakta KS, Han J et al. Induction of terminal differentiation by constitutive activation of p38 MAP kinase in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Genes Dev 2000; 14: 574–584.
Sato A, Okada M, Shibuya K, Watanabe E, Seino S, Narita Y et al. Pivotal role for ROS activation of p38 MAPK in the control of differentiation and tumor-initiating capacity of glioma-initiating cells. Stem Cell Res 2014; 12: 119–131.
Delaunay J, Lecomte N, Bourcier S, Qi J, Gadhoum Z, Durand L et al. Contribution of GM-CSF and IL-8 to the CD44-induced differentiation of acute monoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2007; 22: 873–876.
Islam Z, Gray JS, Pestka JJ . p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates IL-8 induction by the ribotoxin deoxynivalenol in human monocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2006; 213: 235–244.
Jurk MHF, Vollmer J, Schetter C, Kreig AM, Wagner H, Lipford G, Bauer S . Human TLR7 or TLR8 indepednently confer responsiveness to the antiviral compound R-848. Nature Immunol 2002; 3: 499.
Baenziger S, Heikenwalder M, Johansen P, Schlaepfer E, Hofer U, Miller RC et al. Triggering TLR7 in mice induces immune activation and lymphoid system disruption, resembling HIV-mediated pathology. Blood 2009; 113: 377–388.
Ifrah N, James J-M, Viguie F, Marie J-P, Zittoun R . Spontaneous remission in adult acute leukemia. Cancer 1985; 56: 1187–1190.
Kazmierczak MSA, Czyz A, Rupa-Matysek J, Komarnicki M . Spontaneous hematological remission of acute myeloid leukemia. Contemp Oncol 2014; 18: 67–69.
Lachant NA, Goldberg J, Nelson DA, Gottlieb AJ . Spontaneous remission in acute myelogenous leukemia in the adult. Am J Med 1979; 67: 687–692.
Maywald O, Buchheidt D, Bergmann J, Schoch C, Ludwig WD, Reiter A et al. Spontaneous remission in adult acute myeloid leukemia in association with systemic bacterial infection—case report and review of the literature. Ann Hematol 2004; 83: 189–194.
Forsbach A, Nemorin J-G, Montino C, Müller C, Samulowitz U, Vicari AP et al. Identification of RNA Sequence Motifs Stimulating Sequence-Specific TLR8-Dependent Immune Responses. J Immunol 2008; 180: 3729–3738.
Heil F, Hemmi H, Hochrein H, Ampenberger F, Kirschning C, Akira S et al. Species-Specific Recognition of Single-Stranded RNA via Toll-like Receptor 7 and 8. Science 2004; 303: 1526–1529.
Xiong FWX, Zhang JH, Liu W, Sun S, Liu LQ, Wang P, Huang SA . Expression and role of toll-like receptors in U937 cells. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2007; 15: 449–453.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Athymic Animal and Xenograft Core Facility and the Cytometery and Imaging Microscopy Core Facility of the Case Comprehensive Cancer Center (P30CA043703) as well as the following grants: NIH T32 CA59366-17 /GM007250 (JJI-H) and National Natural Science Foundation of China 30400520 (HW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ignatz-Hoover, J., Wang, H., Moreton, S. et al. The role of TLR8 signaling in acute myeloid leukemia differentiation. Leukemia 29, 918–926 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.293
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.293
This article is cited by
-
Generation of a new therapeutic d-peptide that induces the differentiation of acute myeloid leukemia cells through A TLR-2 signaling pathway
Cell Death Discovery (2024)
-
Silencing TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway Alleviated Inflammation of Corneal Epithelial Cells Infected by ISE
Inflammation (2021)
-
Development of a novel TLR8 agonist for cancer immunotherapy
Molecular Biomedicine (2020)
-
Identification of prognostic genes in the acute myeloid leukemia immune microenvironment based on TCGA data analysis
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2019)
-
Imiquimod inhibits growth and induces differentiation of myeloid leukemia cell lines
Cancer Cell International (2018)