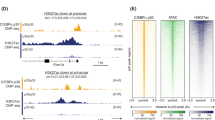
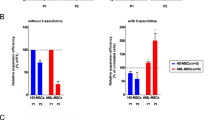
Abstract
The molecular bases of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are not fully understood. Trimethylated histone 3 lysine 4 (H3K4me3) is present in promoters of actively transcribed genes and has been shown to be involved in hematopoietic differentiation. We performed a genome-wide H3K4me3 CHIP-Seq (chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled with whole genome sequencing) analysis of primary MDS bone marrow (BM) CD34+ cells. This resulted in the identification of 36 genes marked by distinct higher levels of promoter H3K4me3 in MDS. A majority of these genes are involved in nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation and innate immunity signaling. We then analyzed expression of histone demethylases and observed significant overexpression of the JmjC-domain histone demethylase JMJD3 (KDM6b) in MDS CD34+ cells. Furthermore, we demonstrate that JMJD3 has a positive effect on transcription of multiple CHIP-Seq identified genes involved in NF-κB activation. Inhibition of JMJD3 using shRNA in primary BM MDS CD34+ cells resulted in an increased number of erythroid colonies in samples isolated from patients with lower-risk MDS. Taken together, these data indicate the deregulation of H3K4me3 and associated abnormal activation of innate immunity signals have a role in the pathogenesis of MDS and that targeting these signals may have potential therapeutic value in MDS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tefferi A, Vardiman JW . Myelodysplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361: 1872–1885.
Garcia-Manero G, Fenaux P . Hypomethylating agents and other novel strategies in myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 516–523.
Cutler CS, Lee SJ, Greenberg P, Deeg HJ, Perez WS, Anasetti C et al. A decision analysis of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for the myelodysplastic syndromes: delayed transplantation for low-risk myelodysplasia is associated with improved outcome. Blood 2004; 104: 579–585.
Slape C, Lin YW, Hartung H, Zhang Z, Wolff L, Aplan PD . NUP98-HOX translocations lead to myelodysplastic syndrome in mice and men. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 2008, 64–68.
Schanz J, Steidl C, Fonatsch C, Pfeilstocker M, Nosslinger T, Tuechler H et al. Coalesced multicentric analysis of 2,351 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes indicates an underestimation of poor-risk cytogenetics of myelodysplastic syndromes in the international prognostic scoring system. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 1963–1970.
Bejar R, Levine R, Ebert BL . Unraveling the molecular pathophysiology of myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 504–515.
Bejar R, Stevenson K, Abdel-Wahab O, Galili N, Nilsson B, Garcia-Manero G et al. Clinical effect of point mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med 2011; 364: 2496–2506.
Papaemmanuil E, Cazzola M, Boultwood J, Malcovati L, Vyas P, Bowen D et al. Somatic SF3B1 mutation in myelodysplasia with ring sideroblasts. N Engl J Med 2011; 365: 1384–1395.
Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh TY, Schones DE, Wang Z et al. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell 2007; 129: 823–837.
Orford K, Kharchenko P, Lai W, Dao MC, Worhunsky DJ, Ferro A et al. Differential H3K4 methylation identifies developmentally poised hematopoietic genes. Dev Cell 2008; 14: 798–809.
Jepsen K, Solum D, Zhou T, McEvilly RJ, Kim HJ, Glass CK et al. SMRT-mediated repression of an H3K27 demethylase in progression from neural stem cell to neuron. Nature 2007; 450: 415–419.
Li H, Durbin R . Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009; 25: 1754–1760.
Zhang Y, Liu T, Meyer CA, Eeckhoute J, Johnson DS, Bernstein BE et al. Model-based analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol 2008; 9: R137.
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 2010; 20: 1297–1303.
Bueso-Ramos CE, Rocha FC, Shishodia S, Medeiros LJ, Kantarjian HM, Vadhan-Raj S et al. Expression of constitutively active nuclear-kappa B RelA transcription factor in blasts of acute myeloid leukemia. Hum Pathol 2004; 35: 246–253.
Agger K, Cloos PA, Rudkjaer L, Williams K, Andersen G, Christensen J et al. The H3K27me3 demethylase JMJD3 contributes to the activation of the INK4A-ARF locus in response to oncogene- and stress-induced senescence. Genes Dev 2009; 23: 1171–1176.
Braun T, Carvalho G, Coquelle A, Vozenin MC, Lepelley P, Hirsch F et al. NF-kappaB constitutes a potential therapeutic target in high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2006; 107: 1156–1165.
Sakurai H, Chiba H, Miyoshi H, Sugita T, Toriumi W . IkappaB kinases phosphorylate NF-kappaB p65 subunit on serine 536 in the transactivation domain. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 30353–30356.
De Santa F, Totaro MG, Prosperini E, Notarbartolo S, Testa G, Natoli G . The histone H3 lysine-27 demethylase Jmjd3 links inflammation to inhibition of polycomb-mediated gene silencing. Cell 2007; 130: 1083–1094.
Sen GL, Webster DE, Barragan DI, Chang HY, Khavari PA . Control of differentiation in a self-renewing mammalian tissue by the histone demethylase JMJD3. Genes Dev 2008; 22: 1865–1870.
Cibull TL, Thomas AB, O'Malley DP, Billings SD . Myeloid leukemia cutis: a histologic and immunohistochemical review. J Cutan Pathol 2008; 35: 180–185.
De Santa F, Narang V, Yap ZH, Tusi BK, Burgold T, Austenaa L et al. Jmjd3 contributes to the control of gene expression in LPS-activated macrophages. EMBO J 2009; 28: 3341–3352.
Frisan E, Vandekerckhove J, de Thonel A, Pierre-Eugene C, Sternberg A, Arlet JB et al. Defective nuclear localization of Hsp70 is associated with dyserythropoiesis and GATA-1 cleavage in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2012; 119: 1532–1542.
Sawada K, Sato N, Notoya A, Tarumi T, Hirayama S, Takano H et al. Proliferation and differentiation of myelodysplastic CD34+ cells: phenotypic subpopulations of marrow CD34+ cells. Blood 1995; 85: 194–202.
Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1997; 89: 2079–2088.
Vastenhouw NL, Schier AF . Bivalent histone modifications in early embryogenesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2012; 24: 374–386.
Pellagatti A, Cazzola M, Giagounidis A, Perry J, Malcovati L, Della Porta MG et al. Deregulated gene expression pathways in myelodysplastic syndrome hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia 2010; 24: 756–764.
Takeuchi O, Akira S . Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010; 140: 805–820.
Starczynowski DT, Kuchenbauer F, Argiropoulos B, Sung S, Morin R, Muranyi A et al. Identification of miR-145 and miR-146a as mediators of the 5q- syndrome phenotype. Nat Med 2010; 16: 49–58.
Esplin BL, Shimazu T, Welner RS, Garrett KP, Nie L, Zhang Q et al. Chronic exposure to a TLR ligand injures hematopoietic stem cells. J Immunol 2011; 186: 5367–5375.
Nagai Y, Garrett KP, Ohta S, Bahrun U, Kouro T, Akira S et al. Toll-like receptors on hematopoietic progenitor cells stimulate innate immune system replenishment. Immunity 2006; 24: 801–812.
Chen S, Ma J, Wu F, Xiong LJ, Ma H, Xu W et al. The histone H3 Lys 27 demethylase JMJD3 regulates gene expression by impacting transcriptional elongation. Genes Dev 2012; 26: 1364–1375.
Miller SA, Mohn SE, Weinmann AS . Jmjd3 and UTX play a demethylase-independent role in chromatin remodeling to regulate T-box family member-dependent gene expression. Mol Cell 2010; 40: 594–605.
Kruidenier L, Chung CW, Cheng Z, Liddle J, Che K, Joberty G et al. A selective jumonji H3K27 demethylase inhibitor modulates the proinflammatory macrophage response. Nature 2012; 488: 404–408.
Rice JC, Allis CD . Code of silence. Nature 2001; 414: 258–261.
Bernstein BE, Mikkelsen TS, Xie X, Kamal M, Huebert DJ, Cuff J et al. A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell 2006; 125: 315–326.
Raaijmakers MH, Mukherjee S, Guo S, Zhang S, Kobayashi T, Schoonmaker JA et al. Bone progenitor dysfunction induces myelodysplasia and secondary leukaemia. Nature 2010; 464: 852–857.
Lopez-Villar O, Garcia JL, Sanchez-Guijo FM, Robledo C, Villaron EM, Hernandez-Campo P et al. Both expanded and uncultured mesenchymal stem cells from MDS patients are genomically abnormal, showing a specific genetic profile for the 5q- syndrome. Leukemia 2009; 23: 664–672.
Kinet JP . The high-affinity IgE receptor (Fc epsilon RI): from physiology to pathology. Annu Rev Immunol 1999; 17: 931–972.
Fillon S, Soulis K, Rajasekaran S, Benedict-Hamilton H, Radin JN, Orihuela CJ et al. Platelet-activating factor receptor and innate immunity: uptake of gram-positive bacterial cell wall into host cells and cell-specific pathophysiology. J Immunol 2006; 177: 6182–6191.
Vogl T, Tenbrock K, Ludwig S, Leukert N, Ehrhardt C, van Zoelen MA et al. Mrp8 and Mrp14 are endogenous activators of Toll-like receptor 4, promoting lethal, endotoxin-induced shock. Nat Med 2007; 13: 1042–1049.
Bave U, Magnusson M, Eloranta ML, Perers A, Alm GV, Ronnblom L . Fc gamma RIIa is expressed on natural IFN-alpha-producing cells (plasmacytoid dendritic cells) and is required for the IFN-alpha production induced by apoptotic cells combined with lupus IgG. J Immunol 2003; 171: 3296–3302.
Lowell CA, Soriano P, Varmus HE . Functional overlap in the src gene family: inactivation of hck and fgr impairs natural immunity. Genes Dev 1994; 8: 387–398.
Eklund EA, Kakar R . Recruitment of CREB-binding protein by PU.1, IFN-regulatory factor-1, and the IFN consensus sequence-binding protein is necessary for IFN-gamma-induced p67phox and gp91phox expression. J Immunol 1999; 163: 6095–6105.
Brown MH, Boles K, van der Merwe PA, Kumar V, Mathew PA, Barclay AN . 2B4, the natural killer and T cell immunoglobulin superfamily surface protein, is a ligand for CD48. J Exp Med 1998; 188: 2083–2090.
Godaly G, Hang L, Frendeus B, Svanborg C . Transepithelial neutrophil migration is CXCR1 dependent in vitro and is defective in IL-8 receptor knockout mice. J Immunol 2000; 165: 5287–5294.
Gomez MA, Li S, Tremblay ML, Olivier M . NRAMP-1 expression modulates protein-tyrosine phosphatase activity in macrophages: impact on host cell signaling and functions. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 36190–36198.
Coppolino MG, Krause M, Hagendorff P, Monner DA, Trimble W, Grinstein S et al. Evidence for a molecular complex consisting of Fyb/SLAP, SLP-76, Nck, VASP and WASP that links the actin cytoskeleton to Fcgamma receptor signalling during phagocytosis. J Cell Sci 2001; 114 (Pt 23): 4307–4318.
Matsushita M, Endo Y, Fujita T . Cutting edge: complement-activating complex of ficolin and mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease. J Immunol 2000; 164: 2281–2284.
Brass AL, Huang IC, Benita Y, John SP, Krishnan MN, Feeley EM et al. The IFITM proteins mediate cellular resistance to influenza A H1N1 virus, West Nile virus, and dengue virus. Cell 2009; 139: 1243–1254.
Gantner BN, Simmons RM, Canavera SJ, Akira S, Underhill DM . Collaborative induction of inflammatory responses by dectin-1 and Toll-like receptor 2. J Exp Med 2003; 197: 1107–1117.
Sukumaran B, Carlyon JA, Cai JL, Berliner N, Fikrig E . Early transcriptional response of human neutrophils to Anaplasma phagocytophilum infection. Infect Immun 2005; 73: 8089–8099.
Gumienny TL, Brugnera E, Tosello-Trampont AC, Kinchen JM, Haney LB, Nishiwaki K et al. CED-12/ELMO, a novel member of the CrkII/Dock180/Rac pathway, is required for phagocytosis and cell migration. Cell 2001; 107: 27–41.
Centola M, Wood G, Frucht DM, Galon J, Aringer M, Farrell C et al. The gene for familial Mediterranean fever, MEFV, is expressed in early leukocyte development and is regulated in response to inflammatory mediators. Blood 2000; 95: 3223–3231.
Gerard NP, Hodges MK, Drazen JM, Weller PF, Gerard C . Characterization of a receptor for C5a anaphylatoxin on human eosinophils. J Biol Chem 1989; 264: 1760–1766.
Le Y, Gong W, Li B, Dunlop NM, Shen W, Su SB et al. Utilization of two seven-transmembrane, G protein-coupled receptors, formyl peptide receptor-like 1 and formyl peptide receptor, by the synthetic hexapeptide WKYMVm for human phagocyte activation. J Immunol 1999; 163: 6777–6784.
Shen L, Collins JE, Schoenborn MA, Maliszewski CR . Lipopolysaccharide and cytokine augmentation of human monocyte IgA receptor expression and function. J Immunol 1994; 152: 4080–4086.
Tomasello E, Desmoulins PO, Chemin K, Guia S, Cremer H, Ortaldo J et al. Combined natural killer cell and dendritic cell functional deficiency in KARAP/DAP12 loss-of-function mutant mice. Immunity 2000; 13: 355–364.
Xu Y, Ma M, Ippolito GC, Schroeder HW Jr., Carroll MC, Volanakis JE . Complement activation in factor D-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 14577–14582.
Jeon JW, Jung JG, Shin EC, Choi HI, Kim HY, Cho ML et al. Soluble CD93 induces differentiation of monocytes and enhances TLR responses. J Immunol 2010; 185: 4921–4927.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grant RP100202 from the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT), the Ruth and Ken Arnold Fund (GGM), the MD Anderson Cancer Center Leukemia SPORE grant CA100632 and the MD Anderson Cancer Center CCSG CA016672. IG-G was funded by the Regional Ministry of Education of Castilla-la Mancha, Spain, supported by the European Social Fund (ESF). We are thankful for the efforts from Dr Hui Yao, Dr Lixia Diao and Dr Jing Wang (Department of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, MDACC) for initial analysis of CHIP-Seq data. We are also thankful to Dr Sean Post and Dr Zeev Estrov for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Y., Chen, R., Dimicoli, S. et al. Global H3K4me3 genome mapping reveals alterations of innate immunity signaling and overexpression of JMJD3 in human myelodysplastic syndrome CD34+ cells. Leukemia 27, 2177–2186 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.91
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.91
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The H3K27 demethylase controls the lateral line embryogenesis of zebrafish
Cell Biology and Toxicology (2023)
-
KDM6 demethylases integrate DNA repair gene regulation and loss of KDM6A sensitizes human acute myeloid leukemia to PARP and BCL2 inhibition
Leukemia (2023)
-
Targeting PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2022)
-
Cooperation between KDM6B overexpression and TET2 deficiency in the pathogenesis of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia
Leukemia (2022)
-
KDM6B promotes ESCC cell proliferation and metastasis by facilitating C/EBPβ transcription
BMC Cancer (2021)