Abstract
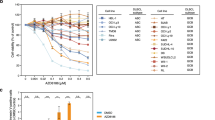
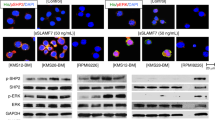
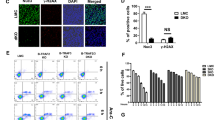
Multiple myeloma (MM) is an incurable malignancy of terminally differentiated B-lymphoid cells. Here, we investigate the role of Fas apoptosis inhibitory molecule (FAIM) in MM. We demonstrate that insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) treatment upregulated FAIM expression in MM cells in a dose-dependent manner. Silencing of FAIM expression attenuates Akt signaling downstream of IGF-1 and compromises the viability of MM cells. We further showed that IGF-1 stimulation of MM cells leads to enhanced expression of IRF4, a known ‘addictive’ factor for MM. This upregulation of IRF4 expression by IGF-1 treatment of MM cells is abrogated when FAIM expression is silenced or Akt activation is inhibited. Thus, FAIM modulates IGF-1-induced Akt activation and IRF4 expression and has a role in MM cell survival. Consistent with these findings, FAIM expression is shown to be higher in plasma cells of symptomatic MM patients compared with normal individuals or patients with premalignant conditions. Moreover, a higher level of FAIM expression is shown to correlate with poorer survival outcomes of newly diagnosed MM patients treated with stem cell transplantation or relapsed MM patients treated in clinical trials with Bortezomib. Thus taken together, our study reveals a novel, as well as clinically relevant role for FAIM in MM.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Kyle RA, Rajkumar SV . Multiple myeloma. Blood 2008; 111: 2962–2972.
Kyle RA, Rajkumar SV . Multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 1860–1873.
Hideshima T, Mitsiades C, Tonon G, Richardson PG, Anderson KC . Understanding multiple myeloma pathogenesis in the bone marrow to identify new therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7: 585–598.
Laubach J, Richardson P, Anderson K . Multiple myeloma. Annu Rev Med 2011; 62: 249–264.
Thomas ED, Lochte HL, Lu WC, Ferrebee JW . Intravenous infusion of bone marrow in patients receiving radiation and chemotherapy. N Engl J Med 1957; 257: 491–496.
Osserman EF, DiRe LB, DiRe J, Sherman WH, Hersman JA, Storb R . Identical twin marrow transplantation in multiple myeloma. Acta Haematol 1982; 68: 215–223.
Fefer A, Cheever MA, Greenberg PD . Identical-twin (syngeneic) marrow transplantation for hematologic cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1986; 76: 1269–1273.
Richardson PG, Barlogie B, Berenson J, Singhal S, Jagannath S, Irwin D et al. A phase 2 study of bortezomib in relapsed, refractory myeloma. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 2609–2617.
Richardson PG, Sonneveld P, Schuster MW, Irwin D, Stadtmauer EA, Facon T et al. Bortezomib or high-dose dexamethasone for relapsed multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 2487–2498.
Rajkumar SV, Hayman SR, Lacy MQ, Dispenzieri A, Geyer SM, Kabat B et al. Combination therapy with lenalidomide plus dexamethasone (Rev/Dex) for newly diagnosed myeloma. Blood 2005; 106: 4050–4053.
Richardson PG, Blood E, Mitsiades CS, Jagannath S, Zeldenrust SR, Alsina M et al. A randomized phase 2 study of lenalidomide therapy for patients with relapsed or relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2006; 108: 3458–3464.
Chapman MA, Lawrence MS, Keats JJ, Cibulskis K, Sougnez C, Schinzel AC et al. Initial genome sequencing and analysis of multiple myeloma. Nature 2011; 471: 467–472.
Hallek M, Bergsagel PL, Anderson KC . Multiple myeloma: increasing evidence for a multistep transformation process. Blood 1998; 91: 3–21.
Palumbo A, Anderson K . Multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 2011; 364: 1046–1060.
Shaffer AL, Emre NC, Lamy L, Ngo VN, Wright G, Xiao W et al. IRF4 addiction in multiple myeloma. Nature 2008; 454: 226–231.
Uranishi M, Iida S, Sanda T, Ishida T, Tajima E, Ito M et al. Multiple myeloma oncogene 1 (MUM1)/interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) upregulates monokine induced by interferon-gamma (MIG) gene expression in B-cell malignancy. Leukemia 2005; 19: 1471–1478.
Schneider TJ, Fischer GM, Donohoe TJ, Colarusso TP, Rothstein TL . A novel gene coding for a Fas apoptosis inhibitory molecule (FAIM) isolated from inducibly Fas-resistant B lymphocytes. J Exp Med 1999; 189: 949–956.
Sole C, Dolcet X, Segura MF, Gutierrez H, Diaz-Meco MT, Gozzelino R et al. The death receptor antagonist FAIM promotes neurite outgrowth by a mechanism that depends on ERK and NF-kapp B signaling. J Cell Biol 2004; 167: 479–492.
Huo J, Xu S, Guo K, Zeng Q, Lam KP . Genetic deletion of faim reveals its role in modulating c-FLIP expression during CD95-mediated apoptosis of lymphocytes and hepatocytes. Cell Death Differ 2009; 16: 1062–1070.
Huo J, Xu S, Lam KP . Fas apoptosis inhibitory molecule regulates T cell receptor-mediated apoptosis of thymocytes by modulating Akt activation and Nur77 expression. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 11827–11835.
Moore PS, Barbi S, Donadelli M, Costanzo C, Bassi C, Palmieri M et al. Gene expression profiling after treatment with the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A reveals altered expression of both pro- and anti-apoptotic genes in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 2004; 1693: 167–176.
Kaku H, Rothstein TL . Fas apoptosis inhibitory molecule enhances CD40 signaling in B cells and augments the plasma cell compartment. J Immunol 2009; 183: 1667–1674.
Kaku H, Rothstein TL . Fas apoptosis inhibitory molecule expression in B cells is regulated through IRF4 in a feed-forward mechanism. J Immunol 2009; 183: 5575–5581.
Iida S, Rao PH, Butler M, Corradini P, Boccadoro M, Klein B et al. Deregulation of MUM1/IRF4 by chromosomal translocation in multiple myeloma. Nat Genet 1997; 17: 226–230.
Urashima M, Chauhan D, Uchiyama H, Freeman GJ, Anderson KC . CD40 ligand triggered interleukin-6 secretion in multiple myeloma. Blood 1995; 85: 1903–1912.
Westendorf JJ, Ahmann GJ, Armitage RJ, Spriggs MK, Lust JA, Greipp PR et al. CD40 expression in malignant plasma cells. Role in stimulation of autocrine IL-6 secretion by a human myeloma cell line. J Immunol 1994; 152: 117–128.
Chauhan D, Uchiyama H, Akbarali Y, Urashima M, Yamamoto K, Libermann TA et al. Multiple myeloma cell adhesion-induced interleukin-6 expression in bone marrow stromal cells involves activation of NF-kappa B. Blood 1996; 87: 1104–1112.
Chng WJ, Kumar S, Vanwier S, Ahmann G, Price-Troska T, Henderson K et al. Molecular dissection of hyperdiploid multiple myeloma by gene expression profiling. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 2982–2989.
Turner CA, Mack DH, Davis MM . Blimp-1, a novel zinc finger-containing protein that can drive the maturation of B lymphocytes into immunoglobulin-secreting cells. Cell 1994; 77: 297–306.
Zhang B, Gojo I, Fenton RG . Myeloid cell factor-1 is a critical survival factor for multiple myeloma. Blood 2002; 99: 1885–1893.
Freund GG, Kulas DT, Mooney RA . Insulin and IGF-1 increase mitogenesis and glucose metabolism in the multiple myeloma cell line, RPMI 8226. J Immunol 1993; 151: 1811–1820.
Menu E, van Valckenborgh E, Van Camp B, Vanderkerken K . The role of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor axis in multiple myeloma. Arch Physiol Biochem 2009; 115: 49–57.
Kawano M, Hirano T, Matsuda T, Taga T, Horii Y, Iwato K et al. Autocrine generation and requirement of BSF-2/IL-6 for human multiple myelomas. Nature 1988; 332: 83–85.
Ge NL, Rudikoff S . Insulin-like growth factor I is a dual effector of multiple myeloma cell growth. Blood 2000; 96: 2856–2861.
Vanderkerken K, Asosingh K, Braet F, Van RI, Van Camp B . Insulin-like growth factor-1 acts as a chemoattractant factor for 5T2 multiple myeloma cells. Blood 1999; 93: 235–241.
Chng WJ, Gualberto A, Fonseca R . IGF-1R is overexpressed in poor-prognostic subtypes of multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2006; 20: 174–176.
Zhan F, Huang Y, Colla S, Stewart JP, Hanamura I, Gupta S et al. The molecular classification of multiple myeloma. Blood 2006; 108: 2020–2028.
Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades NS, McMullan CJ, Poulaki V, Shringarpure R, Akiyama M et al. Inhibition of the insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 tyrosine kinase activity as a therapeutic strategy for multiple myeloma, other hematologic malignancies, and solid tumors. Cancer Cell 2004; 5: 221–230.
Hsu J, Shi Y, Krajewski S, Renner S, Fisher M, Reed JC et al. The AKT kinase is activated in multiple myeloma tumor cells. Blood 2001; 98: 2853–2855.
Hideshima T, Nakamura N, Chauhan D, Anderson KC . Biologic sequelae of interleukin-6 induced PI3-K/Akt signaling in multiple myeloma. Oncogene 2001; 20: 5991–6000.
Pal R, Janz M, Galson DL, Gries M, Li S, Johrens K et al. C/EBPbeta regulates transcription factors critical for proliferation and survival of multiple myeloma cells. Blood 2009; 114: 3890–3898.
Tognon R, Gasparotto EP, Leroy JM, Oliveira GL, Neves RP, Carrara RC et al. Differential expression of apoptosis-related genes from death receptor pathway in chronic myeloproliferative diseases. J Clin Pathol 2011; 64: 75–82.
Acknowledgements
We thank Ong MH for technical assistance and members of the laboratory for insightful discussions and the Biomedical Research Council of the Agency for Science, Technology and Research for funding this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huo, J., Xu, S., Lin, B. et al. Fas apoptosis inhibitory molecule is upregulated by IGF-1 signaling and modulates Akt activation and IRF4 expression in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 27, 1165–1171 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.326
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.326
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The RNA-binding protein hnRNP F is required for the germinal center B cell response
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Molecular analysis of the Sydney rock oyster (Saccostrea glomerata) CO2 stress response
Climate Change Responses (2016)
-
Loss of Fas apoptosis inhibitory molecule leads to spontaneous obesity and hepatosteatosis
Cell Death & Disease (2016)
-
Obesity, diabetes and cancer: insight into the relationship from a cohort with growth hormone receptor deficiency
Diabetologia (2015)
-
Fe3O4 nanoparticle loaded paclitaxel induce multiple myeloma apoptosis by cell cycle arrest and increase cleavage of caspases in vitro
Journal of Nanoparticle Research (2013)