Abstract
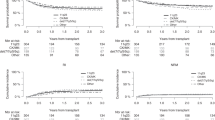
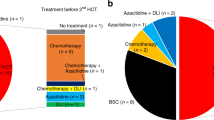
Treatment algorithms for poor cytogenetic-risk myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), defined by chromosome 7 abnormalities or complex karyotype (CK), include allogeneic stem cell transplantation (alloSCT). We studied outcome of alloSCT in chromosome 7 abnormal MDS patients as this data are scarce in literature. We specifically focused on the impact of the extra presence of CK and monosomal karyotype (MK). The European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation database contained data on 277 adult MDS patients with a chromosome 7 abnormality treated with alloSCT. Median age at alloSCT was 45 years. Median follow-up of patients alive was 5 years. Five-year progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were 22% and 28%, respectively. In multivariate analysis, statistically significant predictors for worse PFS were higher MDS stages treated, but not in complete remission (CR) (hazards ratio (HR) 1.7), and the presence of CK (HR 1.5) or MK (HR 1.8). Negative predictive factors for OS were higher MDS stages treated, but not in CR (HR 1.8), and the presence of CK (HR 1.6) or MK (HR 1.7). By means of the cross-validated log partial likelihood, MK showed to have a better predictive value than CK. The results are relevant when considering alloSCT for higher-stage MDS patients having MK including a chromosome 7 abnormality.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1997; 89: 2079–2088.
Grimwade D, Walker H, Oliver F, Wheatley K, Harrison C, Harrison G et al. The importance of diagnostic cytogenetics on outcome in AML: analysis of 1,612 patients entered into the MRC AML 10 trial. The Medical Research Council Adult and Children's Leukaemia Working Parties. Blood 1998; 92: 2322–2333.
Slovak ML, Kopecky KJ, Cassileth PA, Harrington DH, Theil KS, Mohamed A et al. Karyotypic analysis predicts outcome of preremission and postremission therapy in adult acute myeloid leukemia: a Southwest Oncology Group/Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study. Blood 2000; 96: 4075–4083.
Breems DA, Van Putten WL, De Greef GE, Van Zelderen-Bhola SL, Gerssen-Schoorl KB, Mellink CH et al. Monosomal karyotype in acute myeloid leukemia: a better indicator of poor prognosis than a complex karyotype. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 4791–4797.
Estey EH, Pierce S, Keating MJ . Identification of a group of AML/MDS patients with a relatively favorable prognosis who have chromosome 5 and/or 7 abnormalities. Haematologica 2000; 85: 246–249.
Oosterveld M, Suciu S, Verhoef G, Labar B, Belhabri A, Aul C et al. The presence of an HLA-identical sibling donor has no impact on outcome of patients with high-risk MDS or secondary AML (sAML) treated with intensive chemotherapy followed by transplantation: results of a prospective study of the EORTC, EBMT, SAKK and GIMEMA Leukemia Groups (EORTC study 06921). Leukemia 2003; 17: 859–868.
Hofmann WK, Heil G, Zander C, Wiebe S, Ottmann OG, Bergmann L et al. Intensive chemotherapy with idarubicin, cytarabine, etoposide, and G-CSF priming in patients with advanced myelodysplastic syndrome and high-risk acute myeloid leukemia. Ann Hematol 2004; 83: 498–503.
Knipp S, Hildebrand B, Kundgen A, Giagounidis A, Kobbe G, Haas R et al. Intensive chemotherapy is not recommended for patients aged >60 years who have myelodysplastic syndromes or acute myeloid leukemia with high-risk karyotypes. Cancer 2007; 110: 345–352.
Bernasconi C, Alessandrino EP, Bernasconi P, Bonfichi M, Lazzarino M, Canevari A et al. Randomized clinical study comparing aggressive chemotherapy with or without G-CSF support for high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes or secondary acute myeloid leukaemia evolving from MDS. Br J Haematol 1998; 102: 678–683.
Estey EH, Kantarjian HM, O'Brien S, Kornblau S, Andreeff M, Beran M et al. High remission rate, short remission duration in patients with refractory anemia with excess blasts (RAEB) in transformation (RAEB-t) given acute myelogenous leukemia (AML)-type chemotherapy in combination with granulocyte-CSF (G-CSF). Cytokines Mol Ther 1995; 1: 21–28.
Gardin C, Chaibi P, de Revel T, Rousselot P, Turlure P, Miclea JM et al. Intensive chemotherapy with idarubicin, cytosine arabinoside, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) in patients with secondary and therapy-related acute myelogenous leukemia. Club de Reflexion en Hematologie. Leukemia 1997; 11: 16–21.
Nevill TJ, Fung HC, Shepherd JD, Horsman DE, Nantel SH, Klingemann HG et al. Cytogenetic abnormalities in primary myelodysplastic syndrome are highly predictive of outcome after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1998; 92: 1910–1917.
Nakai K, Kanda Y, Fukuhara S, Sakamaki H, Okamoto S, Kodera Y et al. Value of chemotherapy before allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from an HLA-identical sibling donor for myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia 2005; 19: 396–401.
Chang C, Storer BE, Scott BL, Bryant EM, Shulman HM, Flowers ME et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myeloid leukemia arising from myelodysplastic syndrome: similar outcomes in patients with de novo disease and disease following prior therapy or antecedent hematologic disorders. Blood 2007; 110: 1379–1387.
Alessandrino EP, Della Porta MG, Bacigalupo A, Van Lint MT, Falda M, Onida F et al. WHO classification and WPSS predict posttransplantation outcome in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome: a study from the Gruppo Italiano Trapianto di Midollo Osseo (GITMO). Blood 2008; 112: 895–902.
Kroger N, Brand R, van Biezen A, Zander A, Dierlamm J, Niederwieser D et al. Risk factors for therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia treated with allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica 2009; 94: 542–549.
Appelbaum FR, Anderson J . Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for myelodysplastic syndrome: outcomes analysis according to IPSS score. Leukemia 1998; 12 (Suppl 1): S25–S29.
Cutler CS, Lee SJ, Greenberg P, Deeg HJ, Perez WS, Anasetti C et al. A decision analysis of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for the myelodysplastic syndromes: delayed transplantation for low-risk myelodysplasia is associated with improved outcome. Blood 2004; 104: 579–585.
Armand P, Deeg HJ, Kim HT, Lee H, Armistead P, de Lima M et al. Multicenter validation study of a transplantation-specific cytogenetics grouping scheme for patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Bone Marrow Transplant 2010; 45: 877–885.
Onida F, Brand R, van Biezen A, Frassoni F, Beelen D, Finke J et al. Effect of cytogenetics classification according to IPSS on the outcome of allogeneic HSCT from HLA-identical siblings in patients with MDS or secondary AML: a retrospective analysis from the EBMT-CLWP. Bone Marrow Transplant 2007; 39 (Suppl 1): 454.
de Witte T, Suciu S, Verhoef G, Labar B, Archimbaud E, Aul C et al. Intensive chemotherapy followed by allogeneic or autologous stem cell transplantation for patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDSs) and acute myeloid leukemia following MDS. Blood 2001; 98: 2326–2331.
Castro-Malaspina H, Jabubowski AA, Papadopoulos EB, Boulad F, Young JW, Kernan NA et al. Transplantation in remission improves the disease-free survival of patients with advanced myelodysplastic syndromes treated with myeloablative T cell-depleted stem cell transplants from HLA-identical siblings. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14: 458–468.
de Witte T, Hagemeijer A, Suciu S, Belhabri A, Delforge M, Kobbe G et al. Value of allogeneic versus autologous stem cell transplantation and chemotherapy in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes and secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Final results of a prospective randomized European Intergroup Trial. Haematologica 2010; 95: 1754–1761.
Demuynck H, Verhoef GE, Zachee P, Emonds MP, van der Schueren E, van den Berghe H et al. Treatment of patients with myelodysplastic syndromes with allogeneic bone marrow transplantation from genotypically HLA-identical sibling and alternative donors. Bone Marrow Transplant 1996; 17: 745–751.
Al-Ali HK, Brand R, van Biezen A, Finke J, Boogaerts M, Fauser AA et al. A retrospective comparison of autologous and unrelated donor hematopoietic cell transplantation in myelodysplastic syndrome and secondary acute myeloid leukemia: a report on behalf of the Chronic Leukemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Leukemia 2007; 21: 1945–1951.
Runde V, de Witte T, Arnold R, Gratwohl A, Hermans J, van Biezen A et al. Bone marrow transplantation from HLA-identical siblings as first-line treatment in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: early transplantation is associated with improved outcome. Chronic Leukemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 21: 255–261.
Warlick ED, Cioc A, Defor T, Dolan M, Weisdorf D . Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for adults with myelodysplastic syndromes: importance of pretransplant disease burden. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 30–38.
Yakoub-Agha I, de La Salmoniere P, Ribaud P, Sutton L, Wattel E, Kuentz M et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia: a long-term study of 70 patients-report of the French society of bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 963–971.
Anderson JE, Gooley TA, Schoch G, Anasetti C, Bensinger WI, Clift RA et al. Stem cell transplantation for secondary acute myeloid leukemia: evaluation of transplantation as initial therapy or following induction chemotherapy. Blood 1997; 89: 2578–2585.
Gratwohl A, Stern M, Brand R, Apperley J, Baldomero H, de Witte T et al. Risk score for outcome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a retrospective analysis. Cancer 2009; 115: 4715–4726.
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR et al. Proposals for the classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 1982; 51: 189–199.
Ljungman P . CMV infections after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2008; 42 (Suppl 1): S70–S72.
Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Kantarjian H, Pinto A, Schiffer CA, Nimer SD et al. Report of an international working group to standardize response criteria for myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2000; 96: 3671–3674.
de Witte T, Brand R, van Biezen A, Mufti G, Ruutu T, Finke J et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for patients with refractory anaemia with matched related and unrelated donors: delay of the transplant is associated with inferior survival. Br J Haematol 2009; 146: 627–636.
Lim Z, Brand R, Martino R, van Biezen A, Finke J, Bacigalupo A et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for patients 50 years or older with myelodysplastic syndromes or secondary acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 405–411.
Goeman JJ . L1 penalized estimation in the Cox proportional hazards model. Biom J 2010; 52: 70–84.
de Lima M, Anagnostopoulos A, Munsell M, Shahjahan M, Ueno N, Ippoliti C et al. Nonablative versus reduced-intensity conditioning regimens in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome: dose is relevant for long-term disease control after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2004; 104: 865–872.
Schanz J, Tuchler H, Sole F, Mallo M, Luno E, Cervera J et al. New comprehensive cytogenetic scoring system for primary myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and oligoblastic acute myeloid leukemia after mds derived from an international database merge. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 820–829.
Brands-Nijenhuis A, van Gelder M, de Witte T, Schetelig J, van Biezen A, Kroger N . Complex karyotype predicts outcome better than monosomal karyotype in patients with mds/secondary acute leukemia treated with allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT): a retrospective survey on behalf of the Chronic Leukemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Blood 2010; 116: 578.
Anderson JE, Appelbaum FR, Schoch G, Gooley T, Anasetti C, Bensinger WI et al. Allogeneic marrow transplantation for refractory anemia: a comparison of two preparative regimens and analysis of prognostic factors. Blood 1996; 87: 51–58.
Sutton L, Chastang C, Ribaud P, Jouet JP, Kuentz M, Attal M et al. Factors influencing outcome in de novo myelodysplastic syndromes treated by allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: a long-term study of 71 patients Societe Francaise de Greffe de Moelle. Blood 1996; 88: 358–365.
Lee JH, Lee JH, Lim SN, Kim DY, Kim SH, Lee YS et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for myelodysplastic syndrome: prognostic significance of pre-transplant IPSS score and comorbidity. Bone Marrow Transplant 2010; 45: 450–457.
Martino R, Iacobelli S, Brand R, Jansen T, van Biezen A, Finke J et al. Retrospective comparison of reduced-intensity conditioning and conventional high-dose conditioning for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation using HLA-identical sibling donors in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2006; 108: 836–846.
Laport GG, Sandmaier BM, Storer BE, Scott BL, Stuart MJ, Lange T et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning followed by allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for adult patients with myelodysplastic syndrome and myeloproliferative disorders. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14: 246–255.
Cornelissen JJ, Breems D, van Putten WL, Gratwohl AA, Passweg JR, Pabst T et al. Comparative analysis of the value of allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia with monosomal karyotype versus other cytogenetic risk categories. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 2140–2146.
Platzbecker U, Wermke M, Radke J, Oelschlaegel U, Seltmann F, Kiani A et al. Azacitidine for treatment of imminent relapse in MDS or AML patients after allogeneic HSCT: results of the RELAZA trial. Leukemia 2012; 26: 381–389.
Depil S, Deconinck E, Milpied N, Sutton L, Witz F, Jouet JP et al. Donor lymphocyte infusion to treat relapse after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for myelodysplastic syndrome. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33: 531–534.
Campregher PV, Gooley T, Scott BL, Moravec C, Sandmaier B, Martin PJ et al. Results of donor lymphocyte infusions for relapsed myelodysplastic syndrome after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2007; 40: 965–971.
Ravandi F, Kantarjian H, Cohen A, Davis M, O'Brien S, Anderlini P et al. Decitabine with allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in the therapy of leukemia relapse following a prior transplant: results of a phase I study. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 27: 1221–1225.
Warlick ED, DeFor T, Blazar BR, Burns L, Verneris MR, Ustun C et al. Successful remission rates and survival after lymphodepleting chemotherapy and donor lymphocyte infusion for relapsed hematologic malignancies postallogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2012; 18: 480–486.
Acknowledgements
We thank to all centers completing ‘MedB forms’ for the EBMT registry. We also thank Dr Cécile de Pont and Dr Peter de Leeuw for thoroughly checking grammar and stylistic errors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Gelder, M., de Wreede, L., Schetelig, J. et al. Monosomal karyotype predicts poor survival after allogeneic stem cell transplantation in chromosome 7 abnormal myelodysplastic syndrome and secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 27, 879–888 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.297
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.297
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Outcome after allogeneic stem cell transplantation with haploidentical versus HLA-matched donors in patients with higher-risk MDS
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2023)
-
Indications for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in Myelodysplastic Syndrome
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2020)
-
Relapse of AML after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: methods of monitoring and preventive strategies. A review from the ALWP of the EBMT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2016)
-
Comparing i.v. BU dose intensity between two regimens (FB2 vs FB4) for allogeneic HCT for AML in CR1: a report from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of EBMT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2014)
-
Specific abnormalities versus number of abnormalities and cytogenetic scoring systems for outcome prediction after allogeneic hematopoietic SCT for myelodysplastic syndromes
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2014)